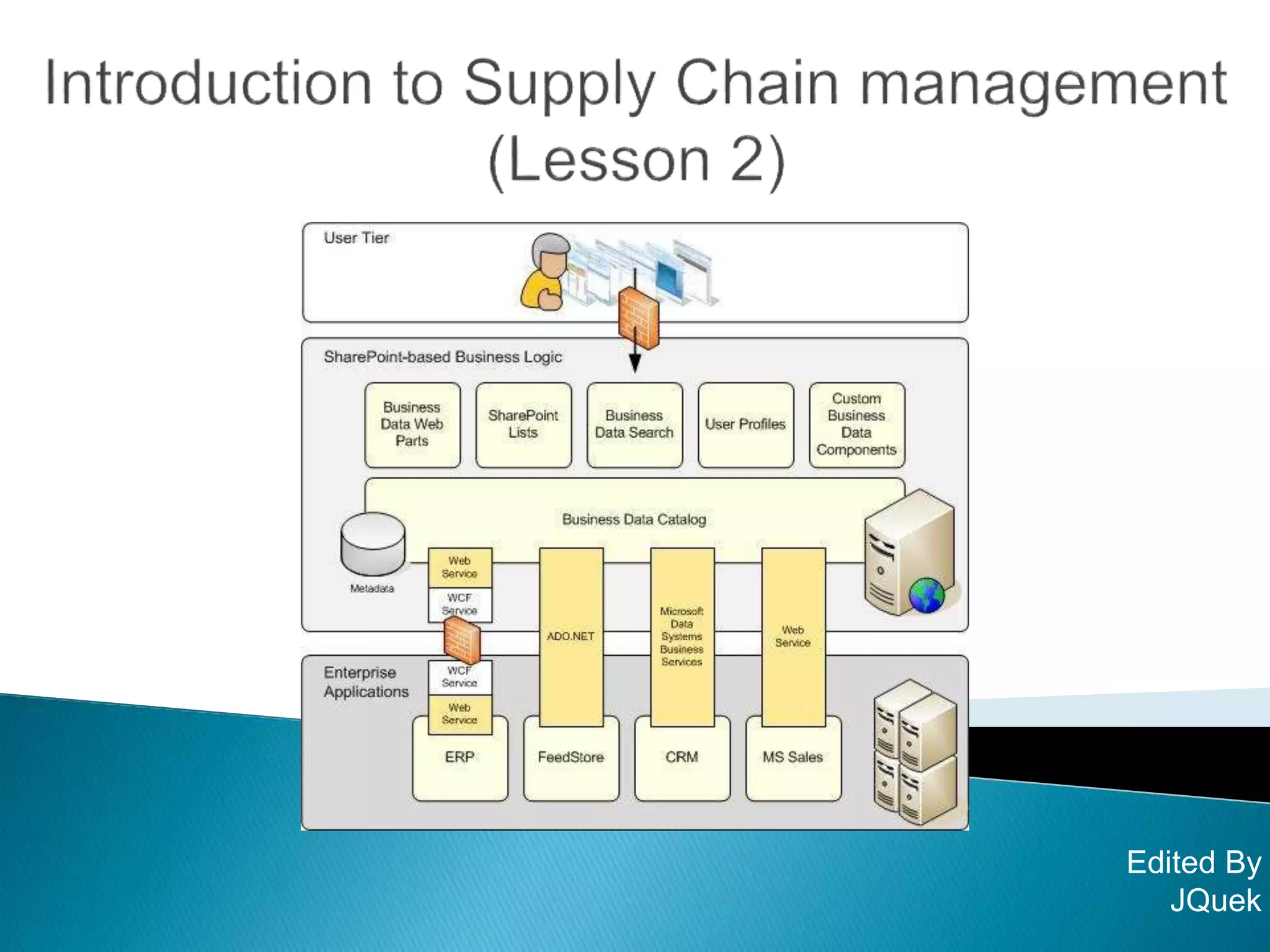
This document discusses supply chain information systems and decision support. It describes technologies like transportation management systems, warehouse management systems, and global visibility tools that provide supply chain visibility and efficiency. It also covers labor management systems. The benefits of information sharing and collaboration between companies are discussed. Potential resistance to new technologies from employees and vendors is addressed. Key supply chain metrics and performance indicators are defined.