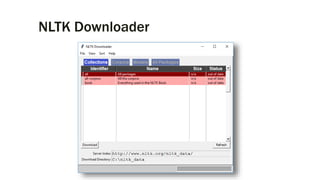
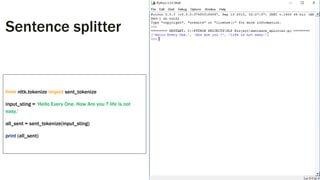
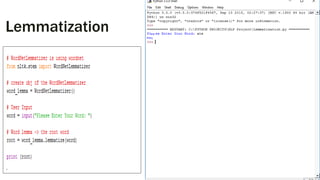
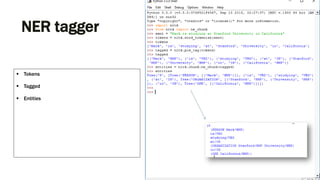
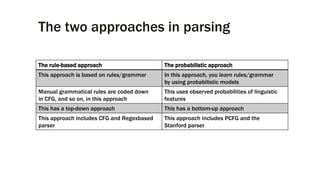
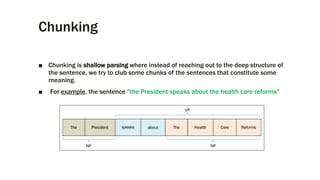
The document provides an overview of the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK), detailing its features, installation guidelines, and basic functionalities in natural language processing. It covers various tasks such as tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, parsing, and chunking, along with code snippets for implementation. Additionally, it includes resources for further learning and contact information for the author.
























![Display a parse tree
# import treebank corpus
from nltk.corpus import treebank
t = treebank.parsed_sents('wsj_0001.mrg')[0]
t.draw()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nltk-160315163803/85/NLTK-33-320.jpg)
![Resources
■ NLTK 3.0 documentation
– http://www.nltk.org/
■ NLTK Essentials
– https://www.packtpub.com/big-data-and-business-intelligence/nltk-essentials
■ nltk_tutorial_repo [Code]
– https://git.io/vaRIR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nltk-160315163803/85/NLTK-35-320.jpg)
