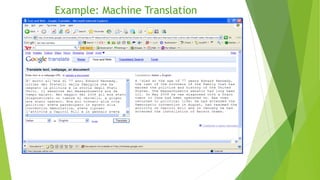
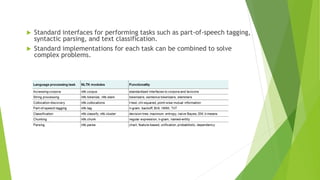
This document provides an introduction to natural language processing (NLP) and the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) module for Python. It discusses how NLP aims to develop systems that can understand human language at a deep level, lists common NLP applications, and explains why NLP is difficult due to language ambiguity and complexity. It then describes how corpus-based statistical approaches are used in NLTK to tackle NLP problems by extracting features from text corpora and using statistical models. The document gives an overview of the main NLTK modules and interfaces for common NLP tasks like tagging, parsing, and classification. It provides an example of word tokenization and discusses tokens and types in NLTK.