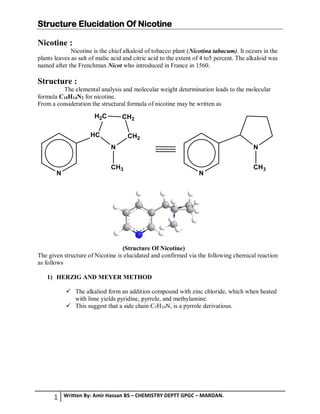
1. Nicotine is the chief alkaloid found in tobacco plants, occurring up to 5% in the leaves. Its molecular formula is C10H14N2.
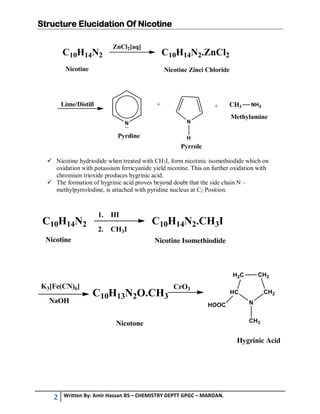
2. Herzig and Meyer's method and Pinner's method were used to elucidate nicotine's structure. Herzig and Meyer's method showed the side chain is a pyrrole derivative attached at the C2 position of the pyridine nucleus.
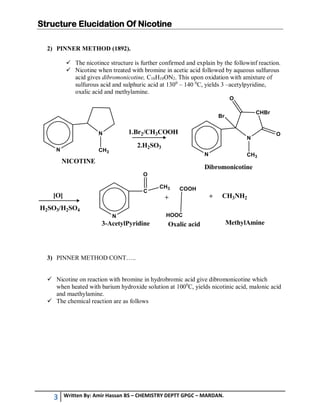
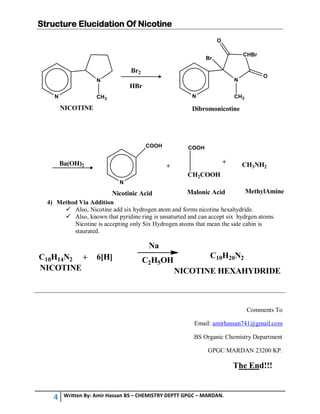
3. Pinner's method involved reactions that produced 3-acetylpyridine, oxalic acid, and methylamine, confirming nicotine's structure. Nicotine reacts with bromine and barium hydroxide in ways that further supported the identified structure.