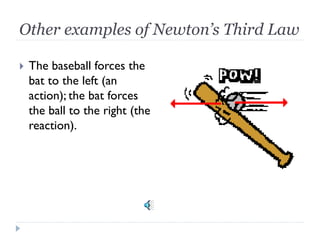
1) Newton's three laws of motion are described, including the first law of inertia, the second law relating force, mass and acceleration, and the third law of equal and opposite reactions.
2) The first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Friction is given as an example of a force that can slow objects down.
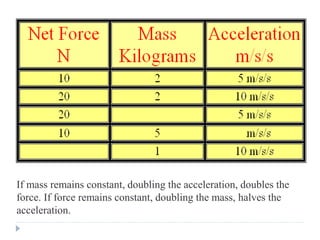
3) The second law establishes the formula F=ma, where force equals mass times acceleration. Several examples are given to illustrate applications of this law.