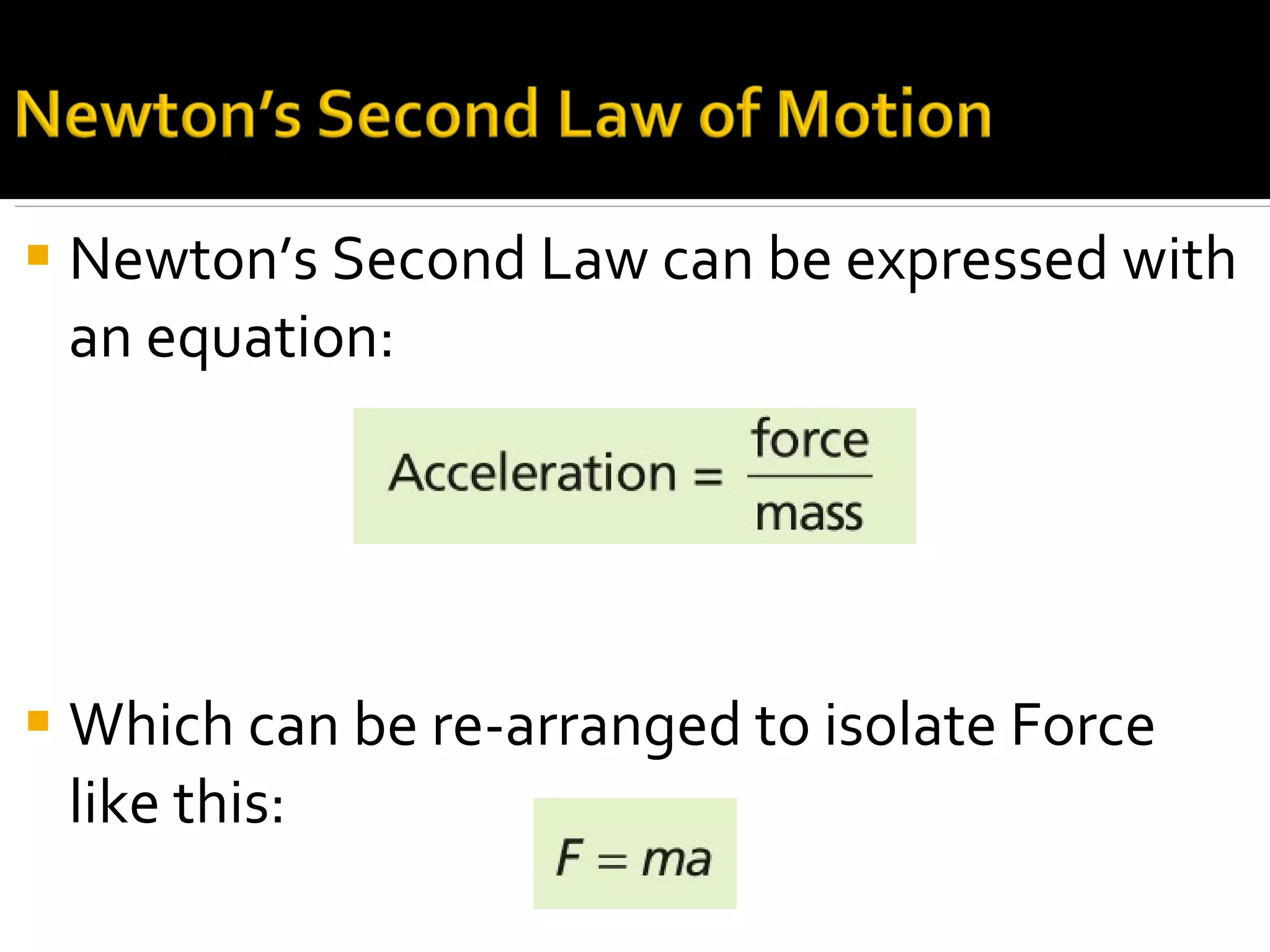
Newton's Second Law relates force, mass, and acceleration using the equation F=ma. The equation can be rearranged to solve for force. Force is measured in Newtons, where 1 Newton is the force needed to accelerate a 1 kilogram mass at 1 meter per second squared. If acceleration is held constant and an object's mass doubles, the force needs to double to maintain the same acceleration according to the Second Law.