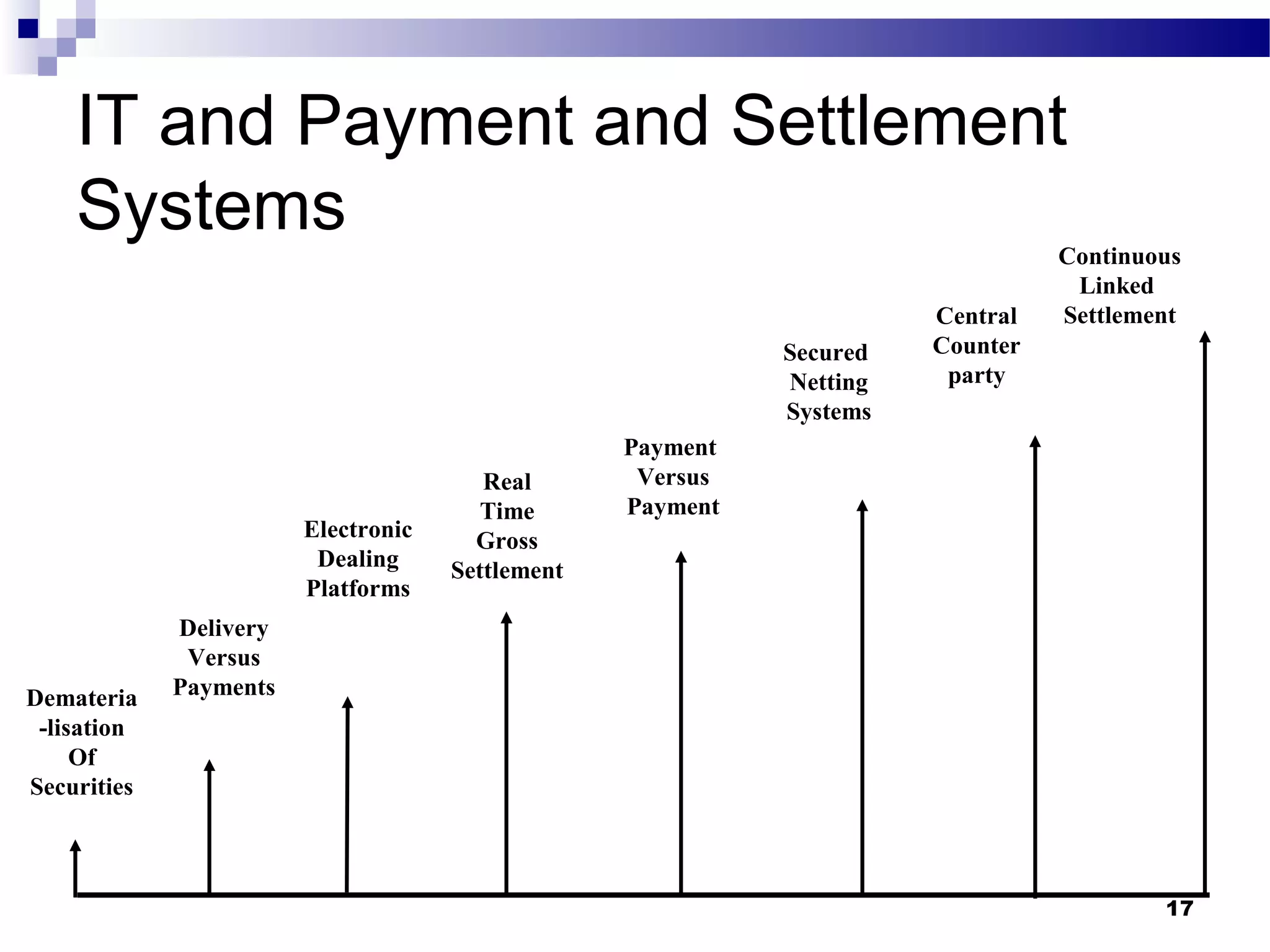
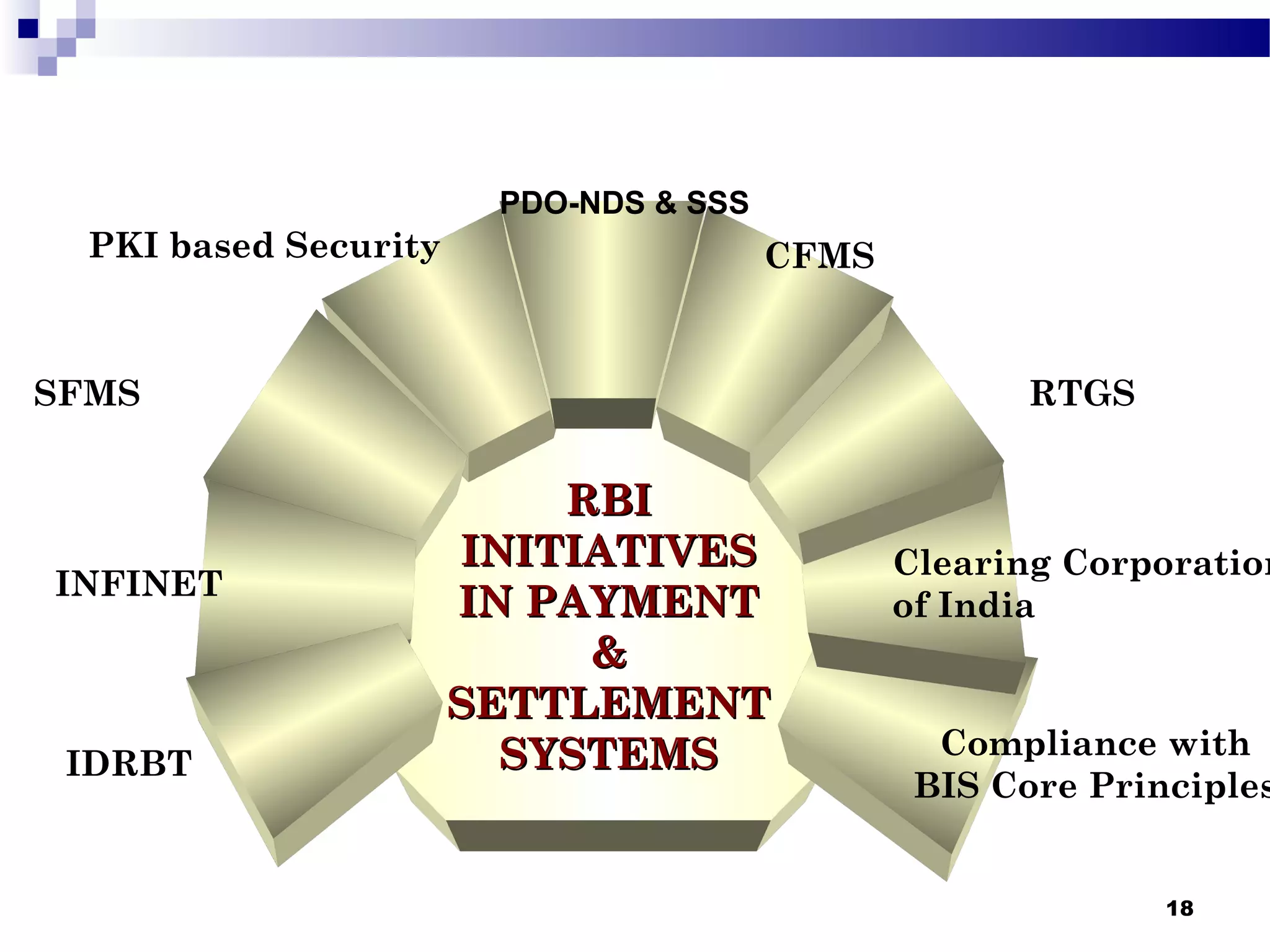
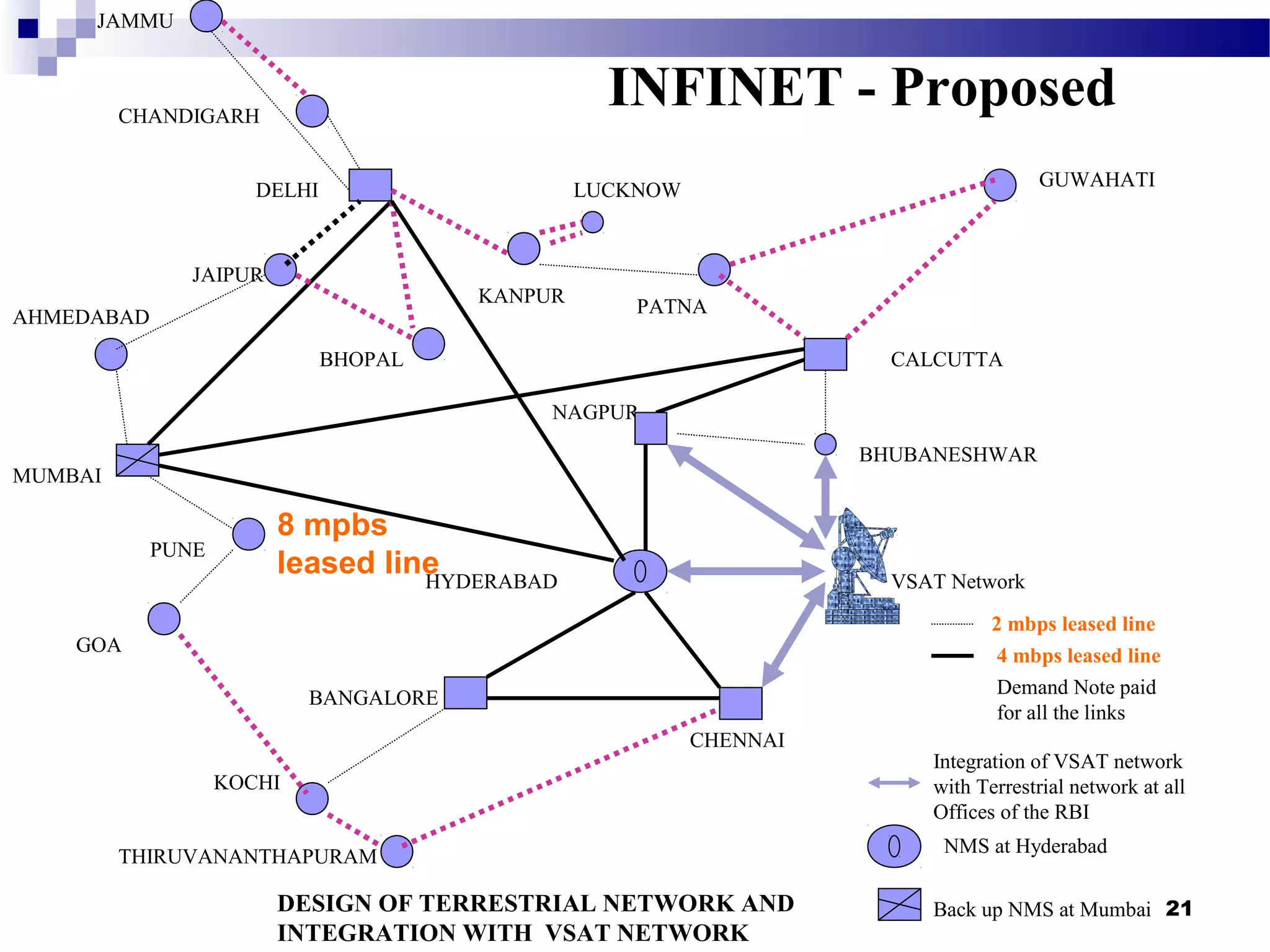
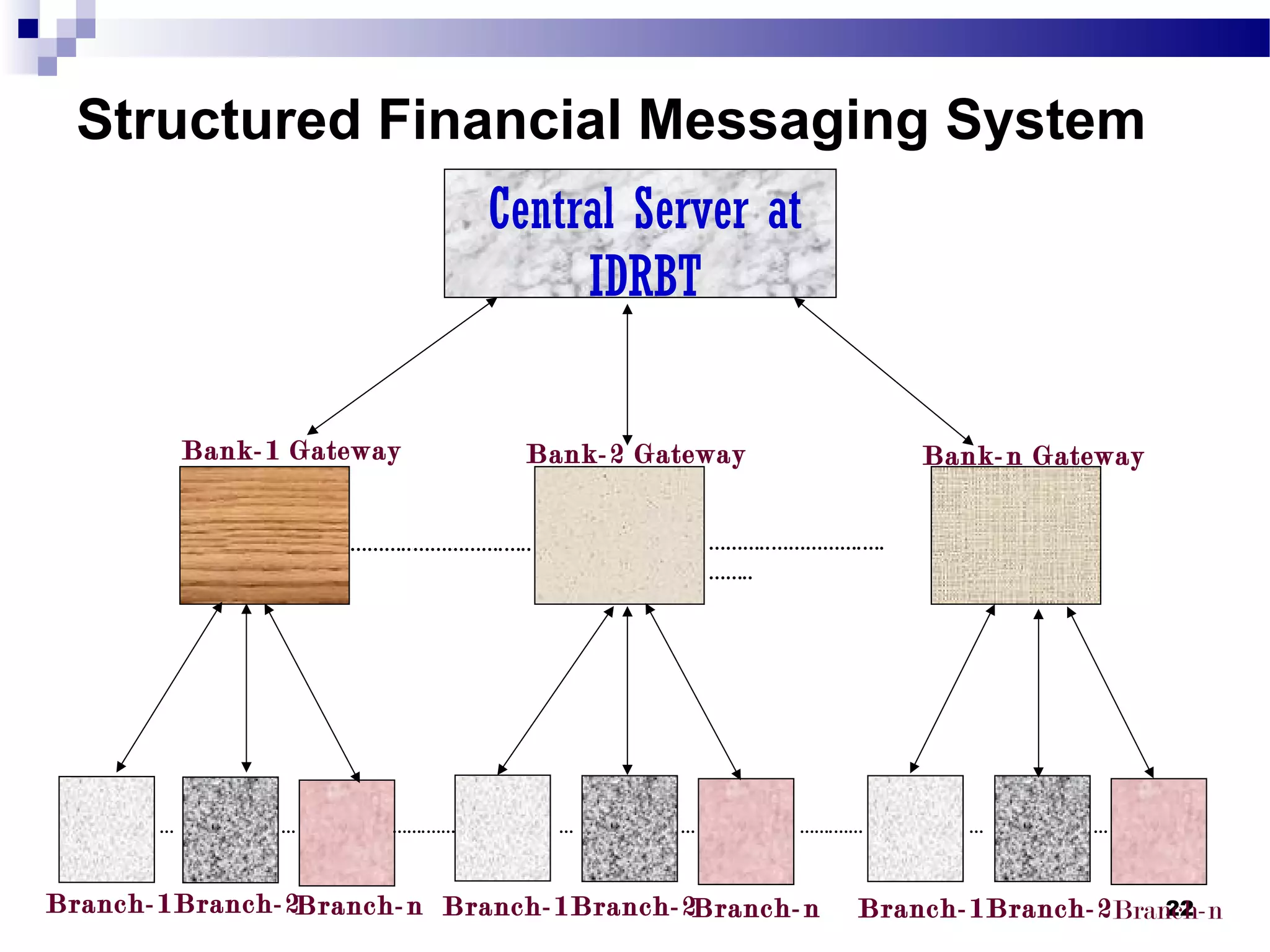
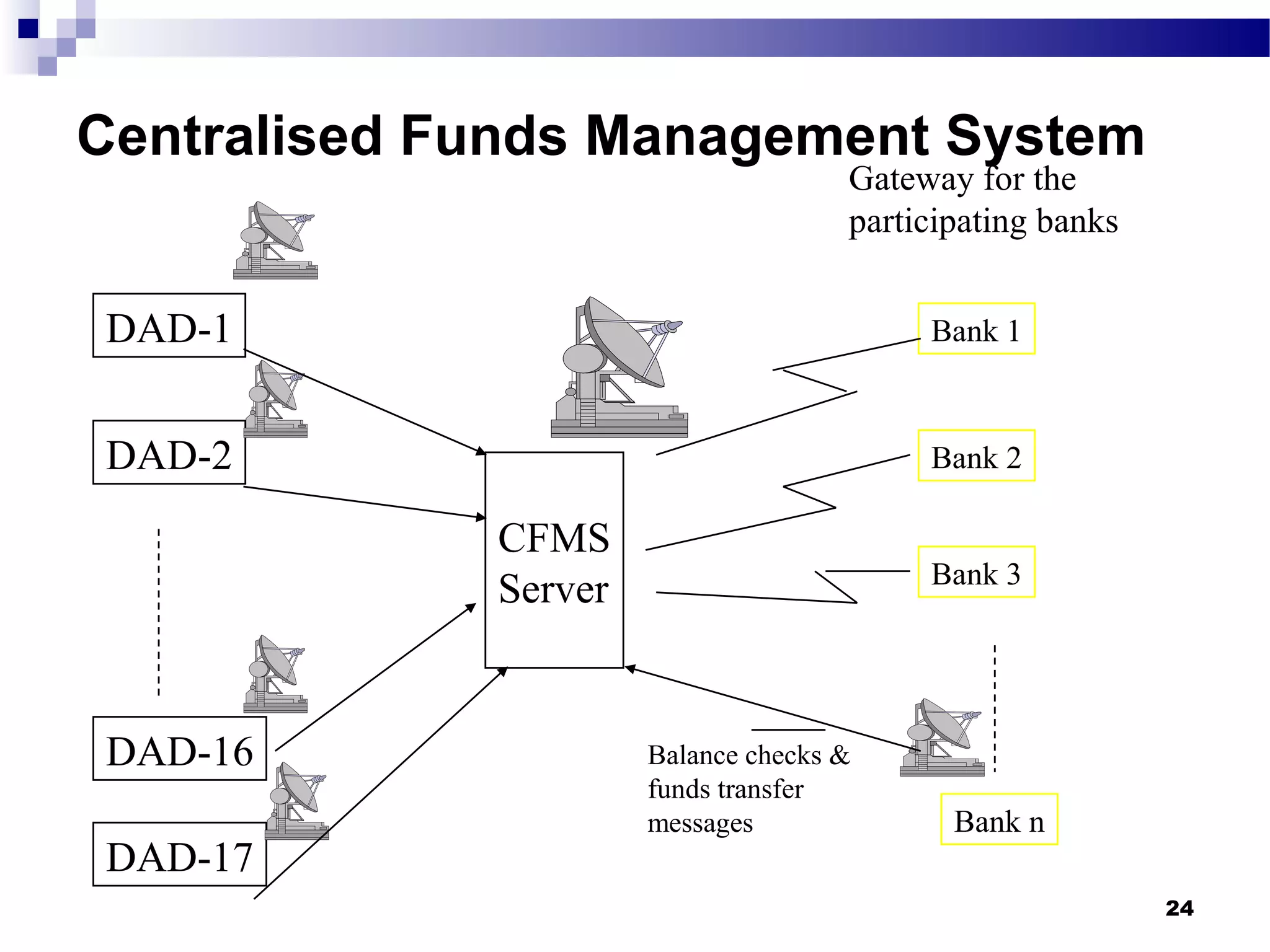
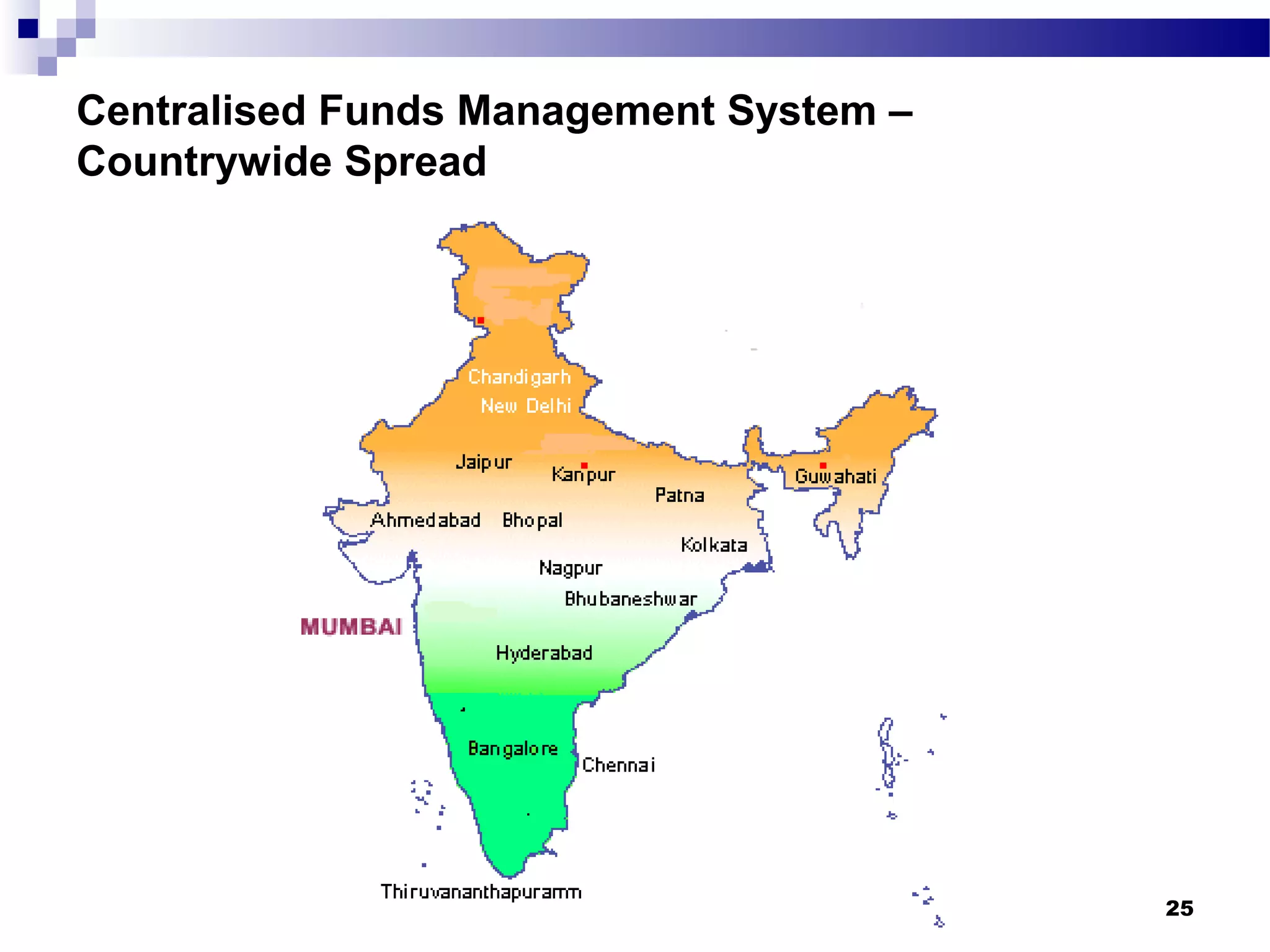
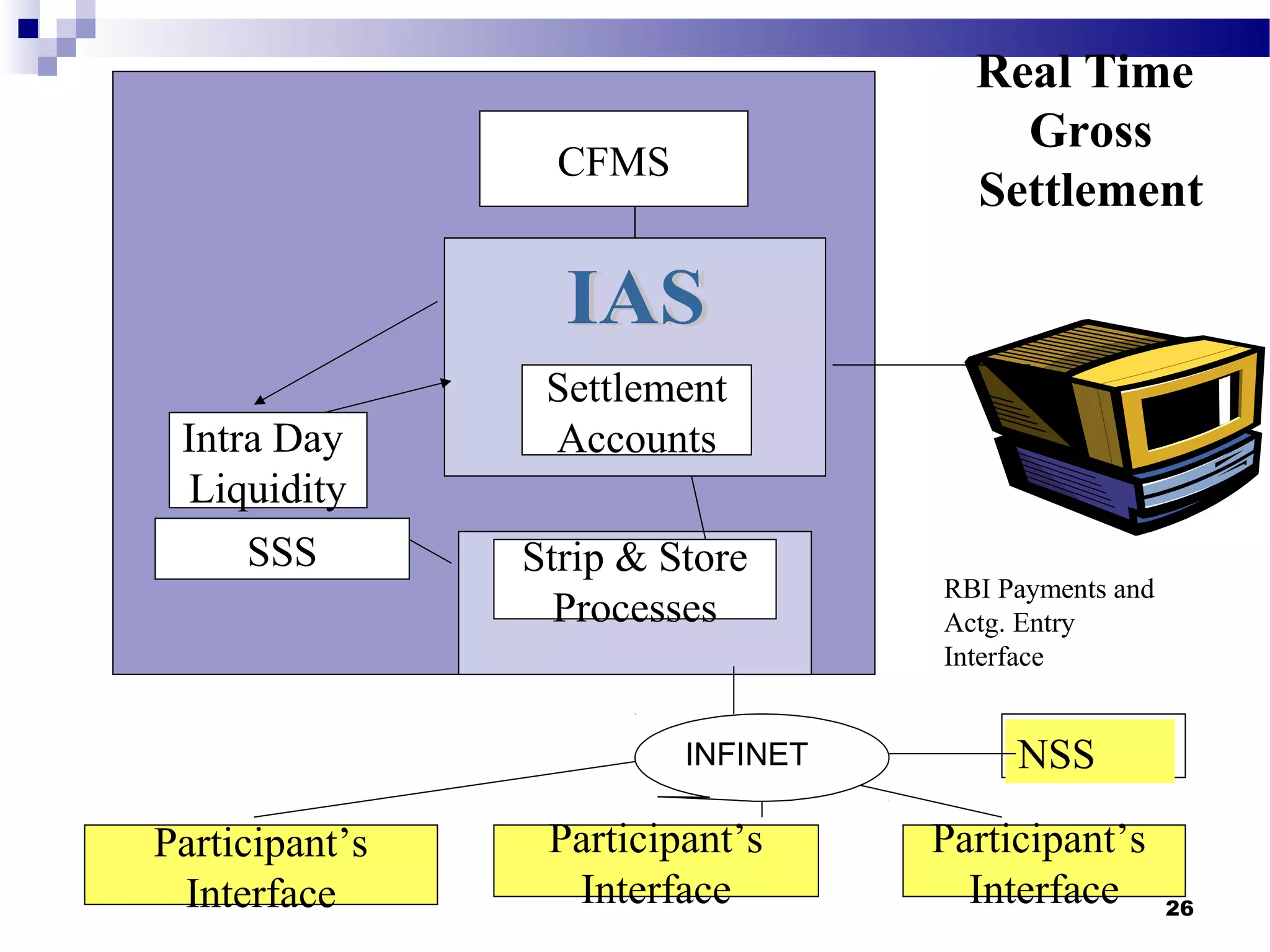
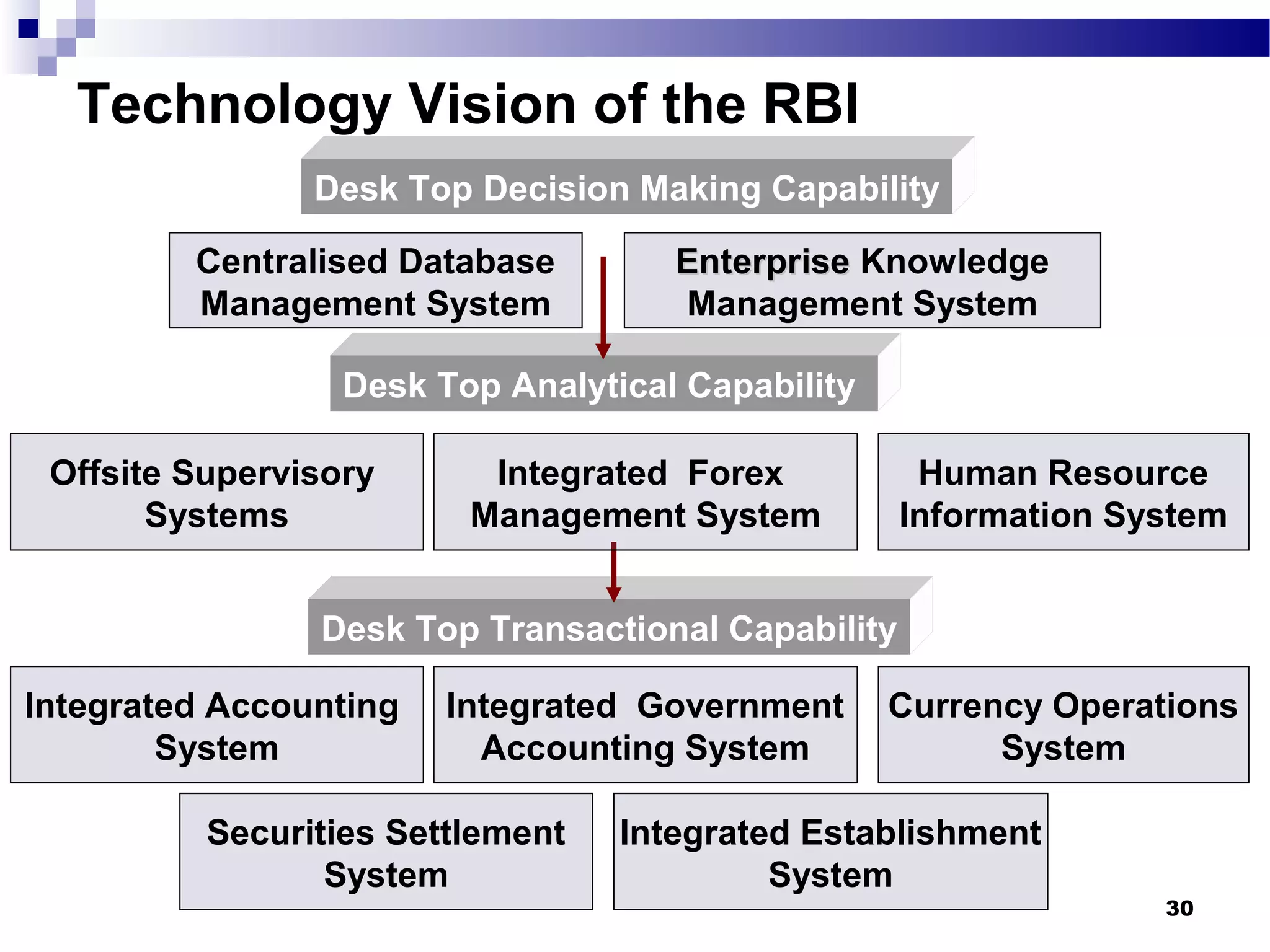
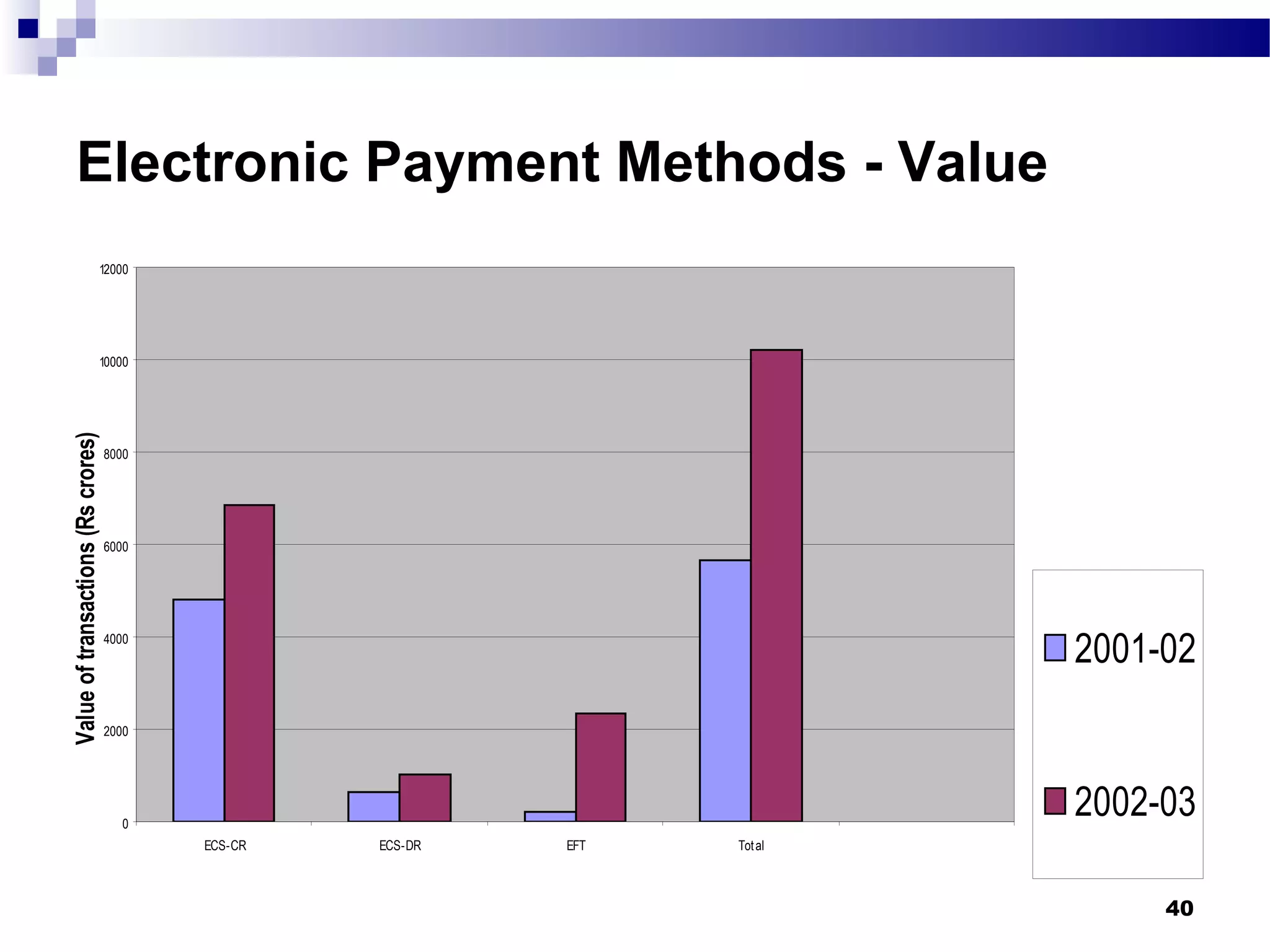
Recent Technological Developments In Indian Banking discusses the Reserve Bank of India's use of technology across its core functions and initiatives. Technology has impacted every aspect of central banking including supervision, currency management, and monetary policy. The RBI has harnessed technology through initiatives like INFINET, SFMS, real-time gross settlement, and the securities settlement system to modernize payment systems, improve supervision, and enable more efficient internal processes. Technology has also improved how the RBI provides services and disseminates information to customers.