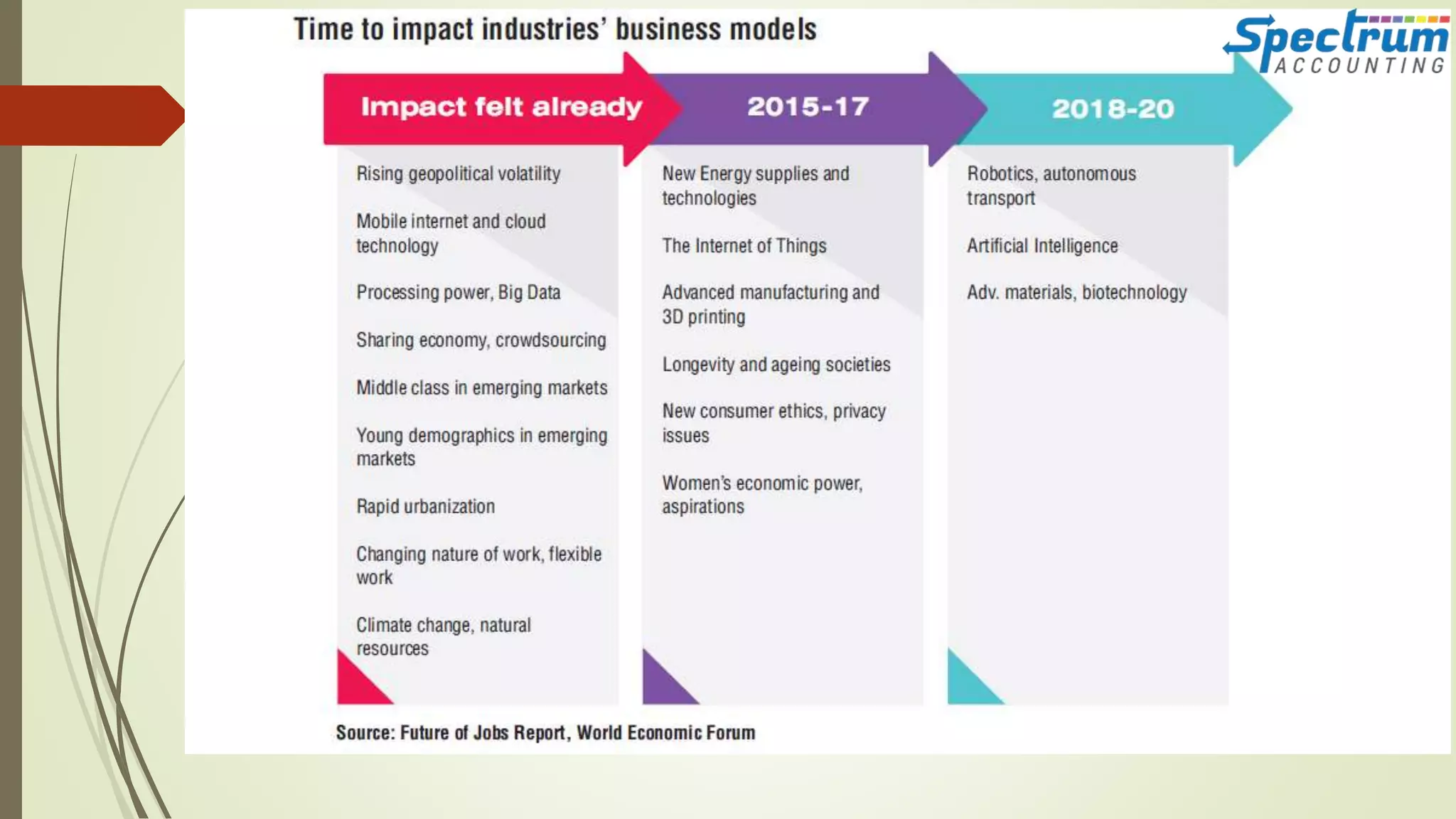
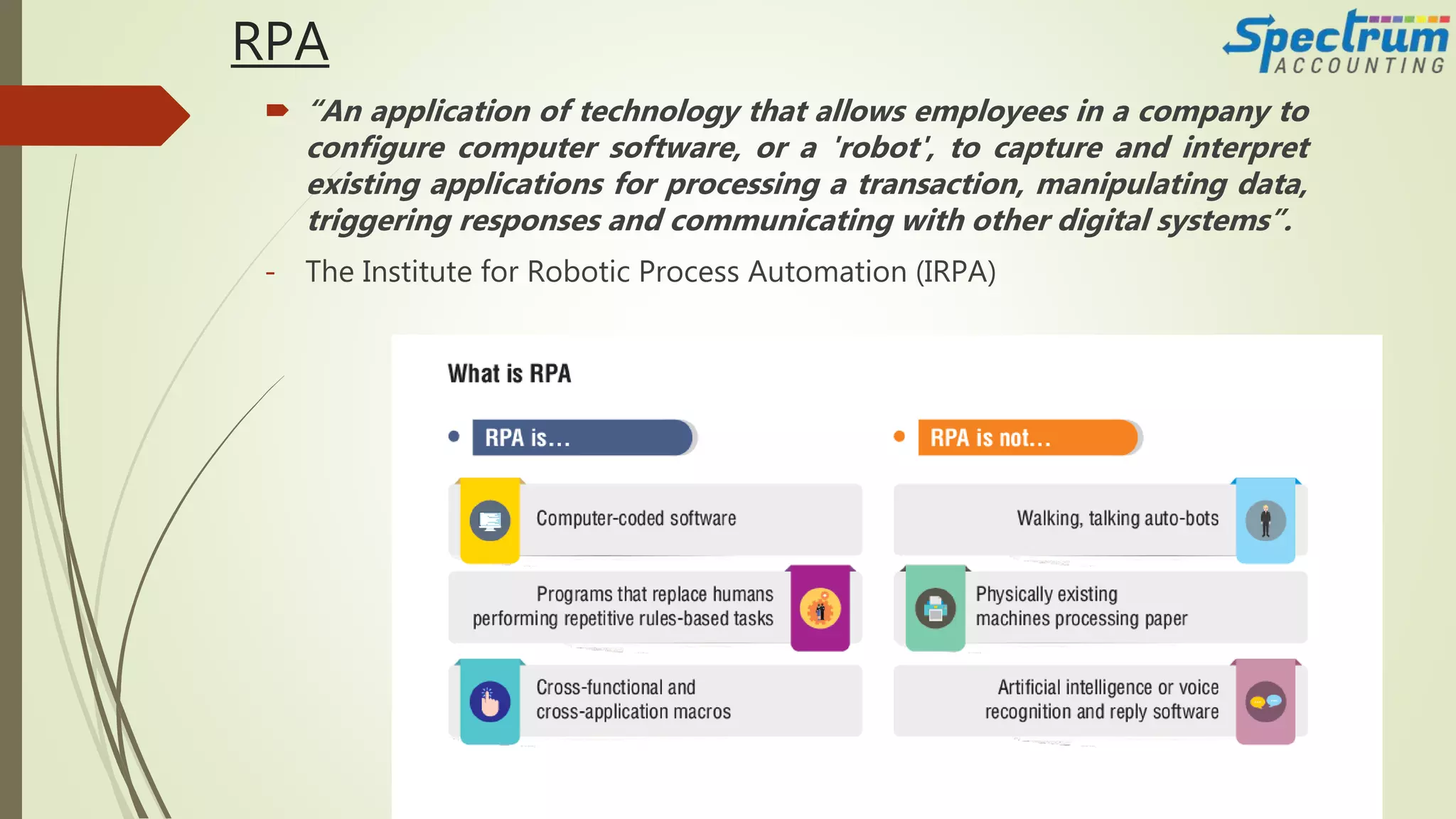
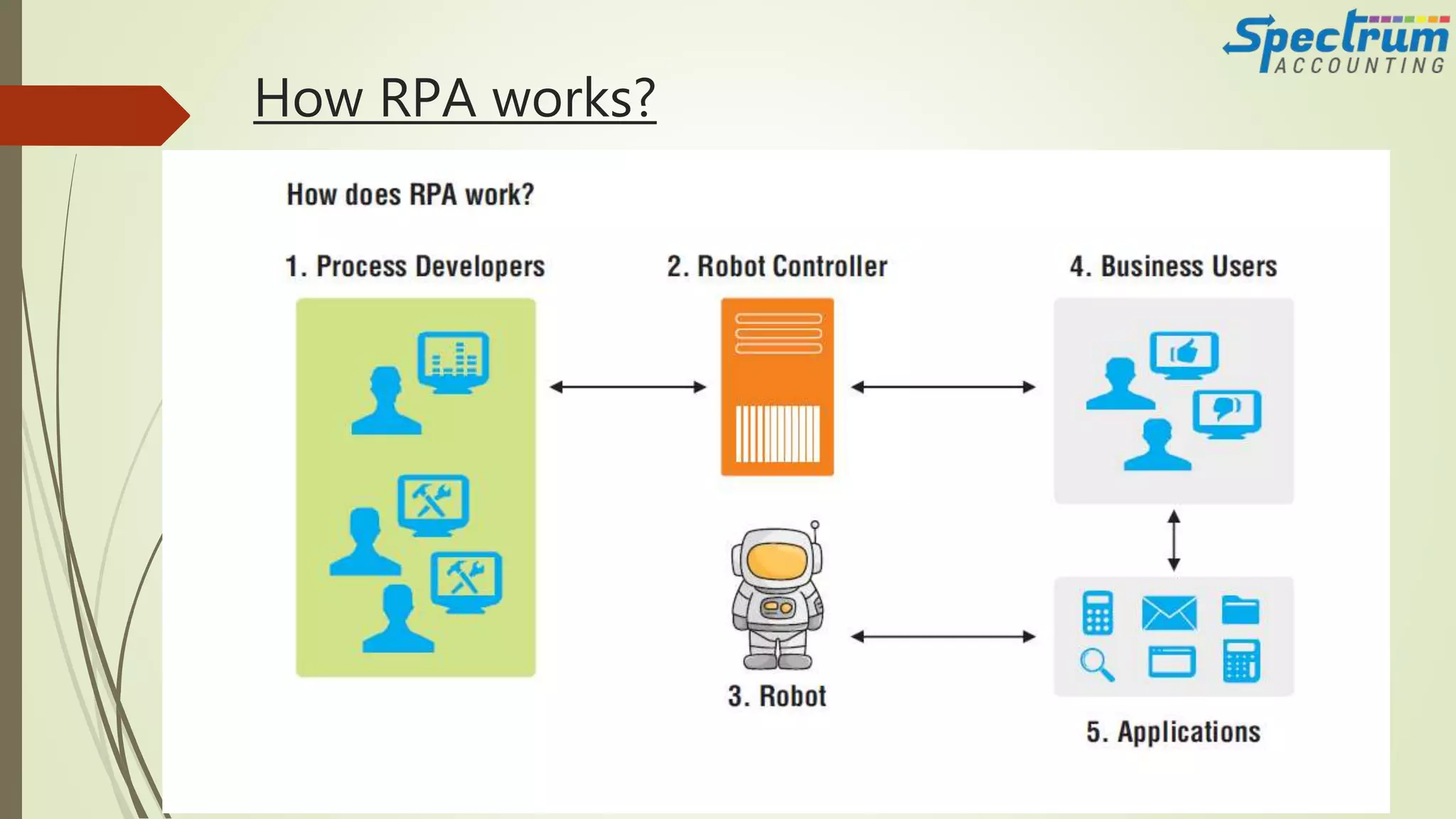
The document discusses how artificial intelligence is being adopted in the accounting field. It provides an overview of AI and accounting, explaining how tasks like bank reconciliations can now be automated. While machines will be valuable colleagues, humans still provide important emotional intelligence. The document outlines various areas where RPA and AI are being used in accounting for tasks like invoice processing and compliance. It also discusses how accountants can prepare for AI and the future widespread availability of these technologies for smaller firms. Case studies show how AI has automated accounting tasks with varying levels of success.