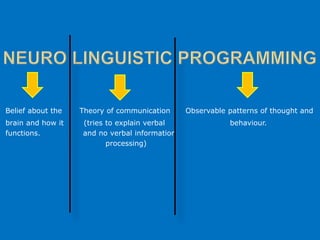
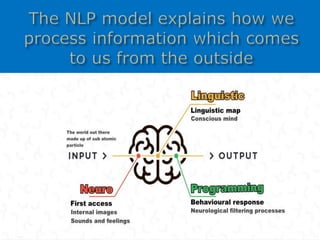
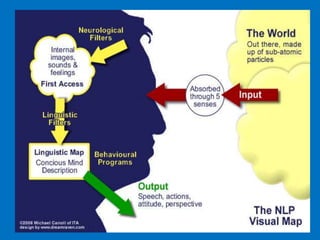
NLP is a training philosophy developed by John Grindler and Richard Bandler in the mid-1970s focused on communication, how the mind works, and modeling behavior. Some key aspects of NLP include establishing rapport, increasing sensory acuity, and flexibility. NLP can be applied to language learning through its 13 presuppositions and the central practice of modeling, such as a teacher drawing a mind map to connect new vocabulary words for visual learners. Effective NLP in the classroom uses diverse techniques to address different types of intelligence in students.