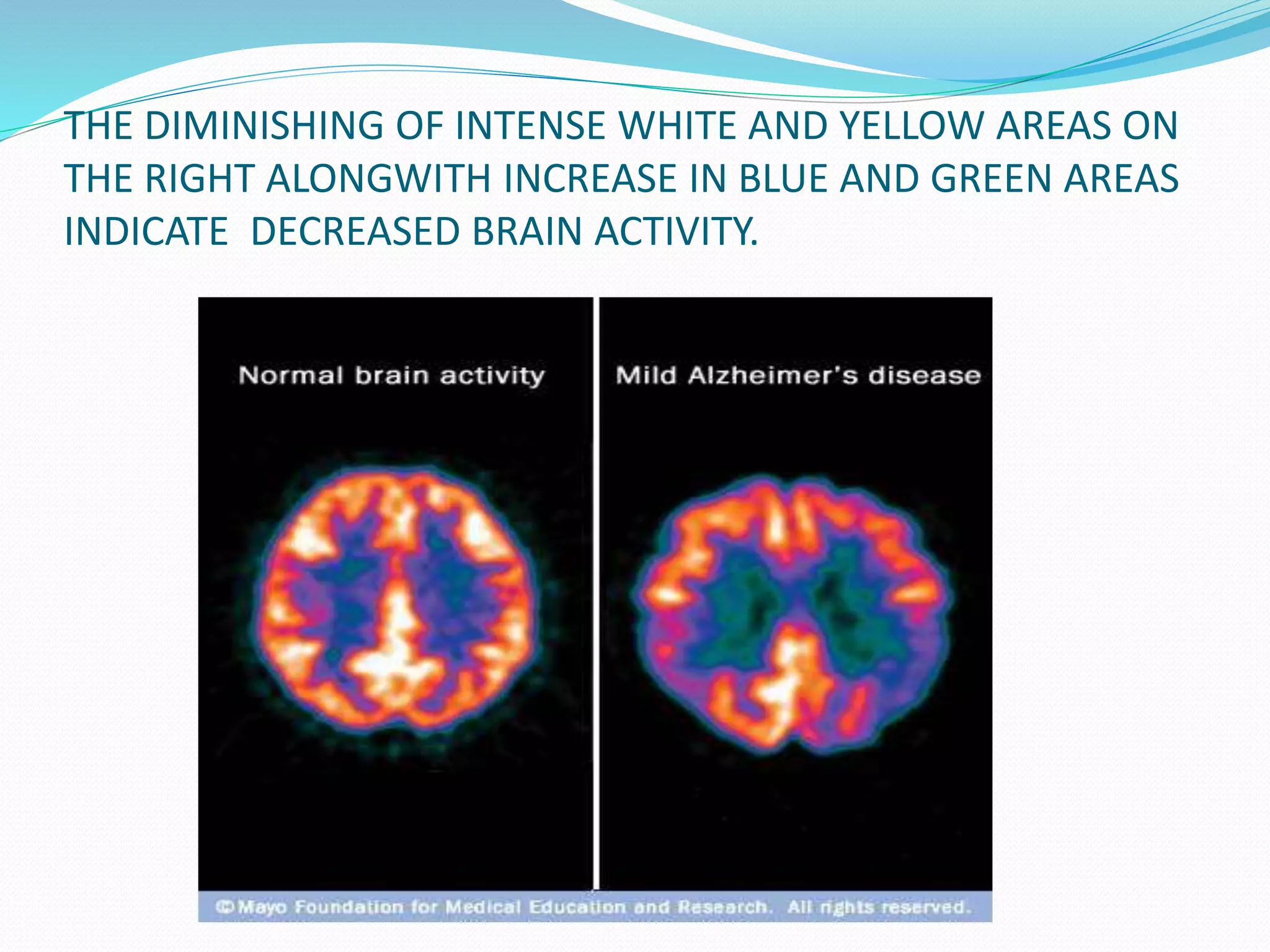
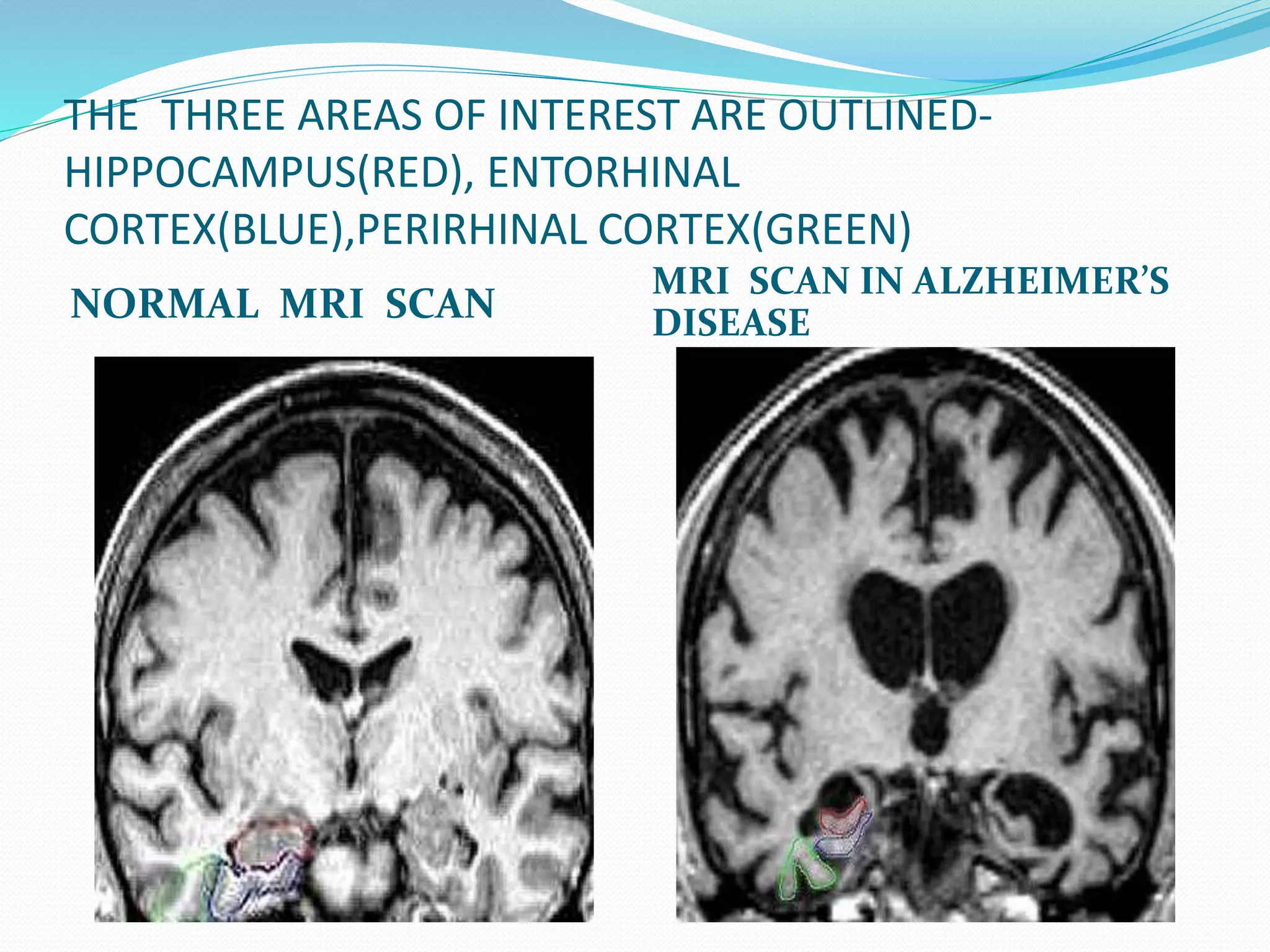
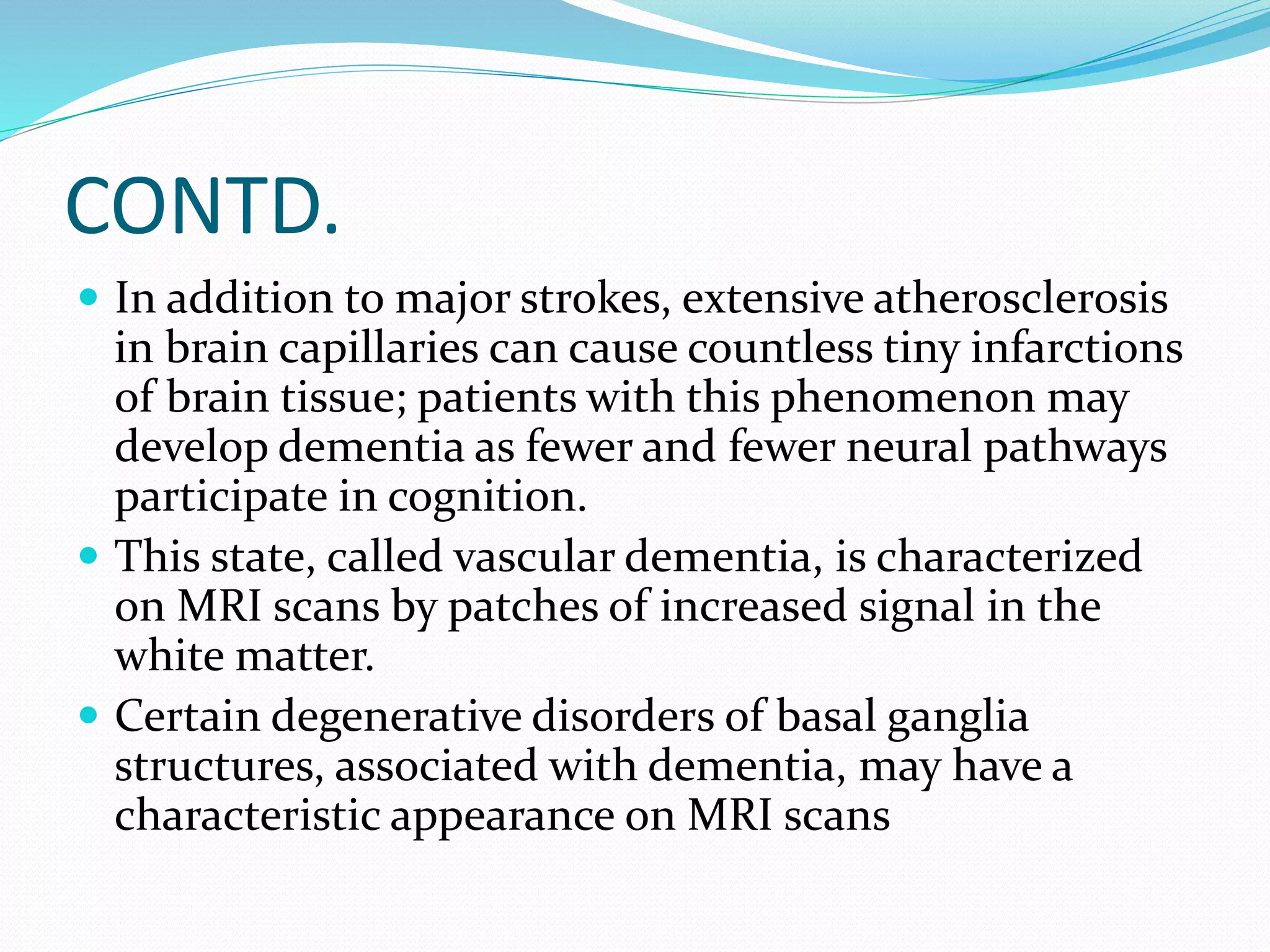
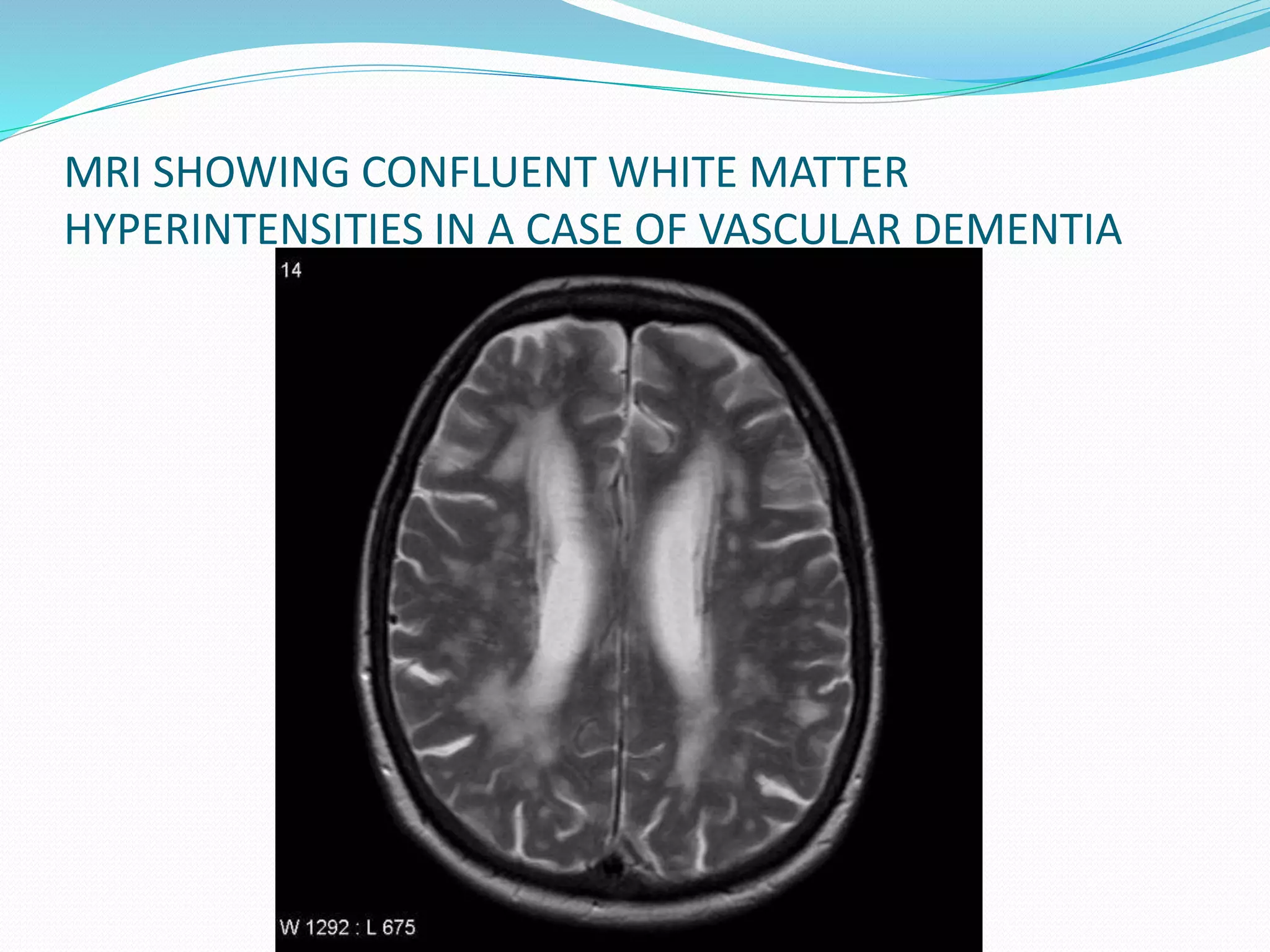
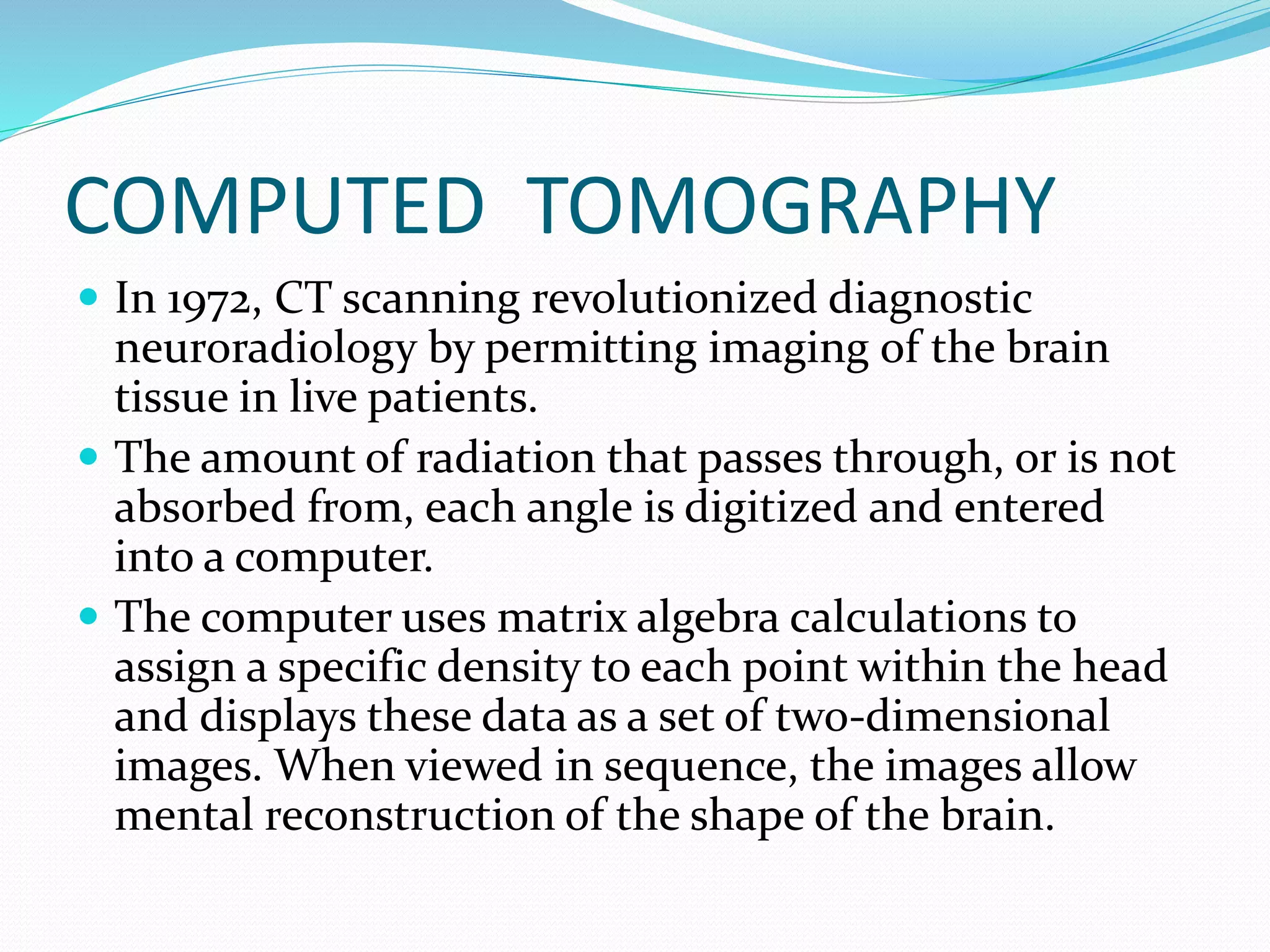
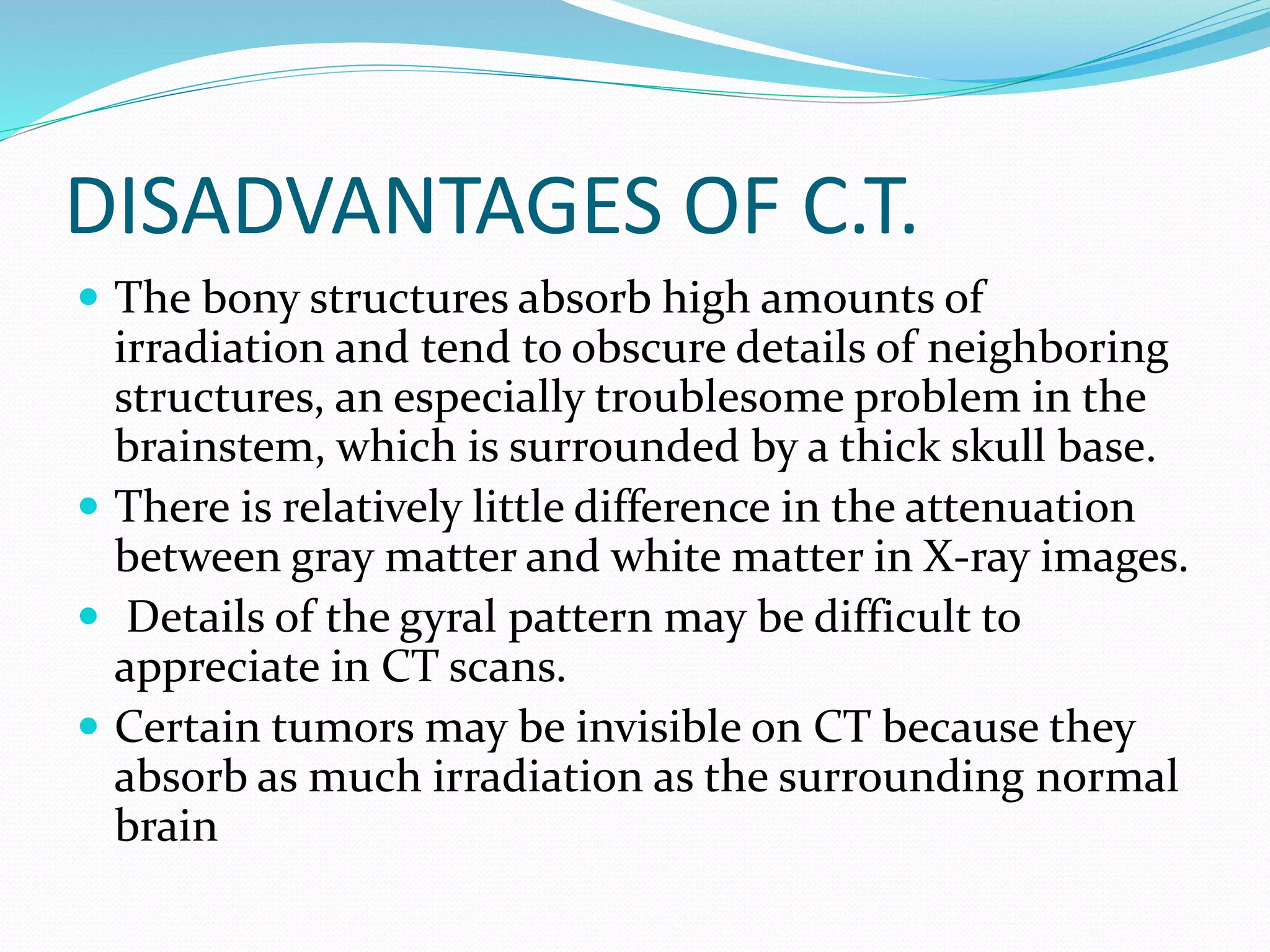
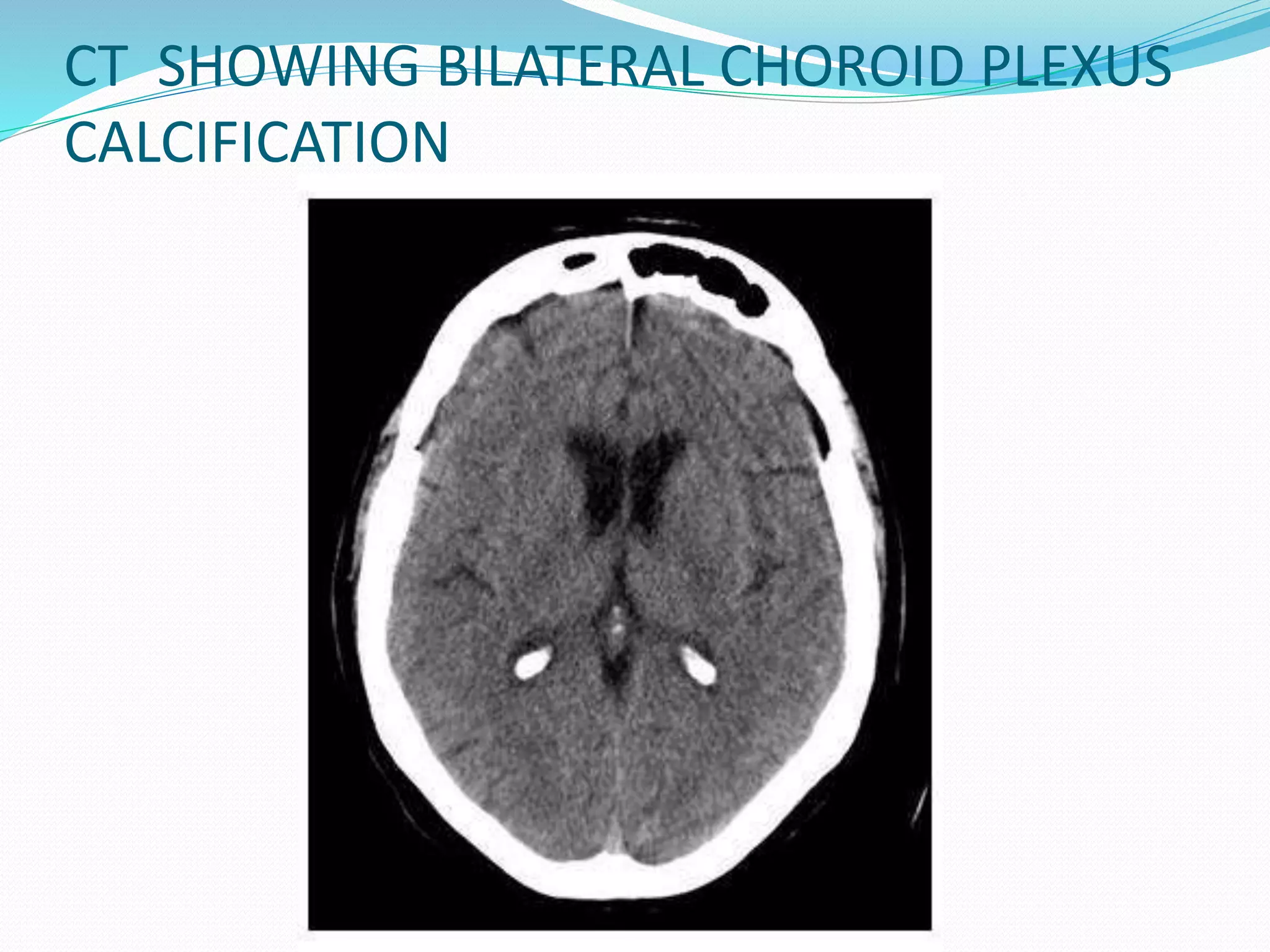
This document discusses various neuroimaging techniques used to study the structure and function of the living human brain, including their applications and limitations. It describes computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), functional MRI (fMRI), and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). CT and MRI are used to examine brain structure, while fMRI, MRS and SPECT provide insights into brain function by detecting changes in blood flow, metabolism or radiotracer distribution associated with neuronal activity. These techniques have advanced understanding of neurological and psychiatric disorders but each has specific strengths and weaknesses for clinical or research applications.














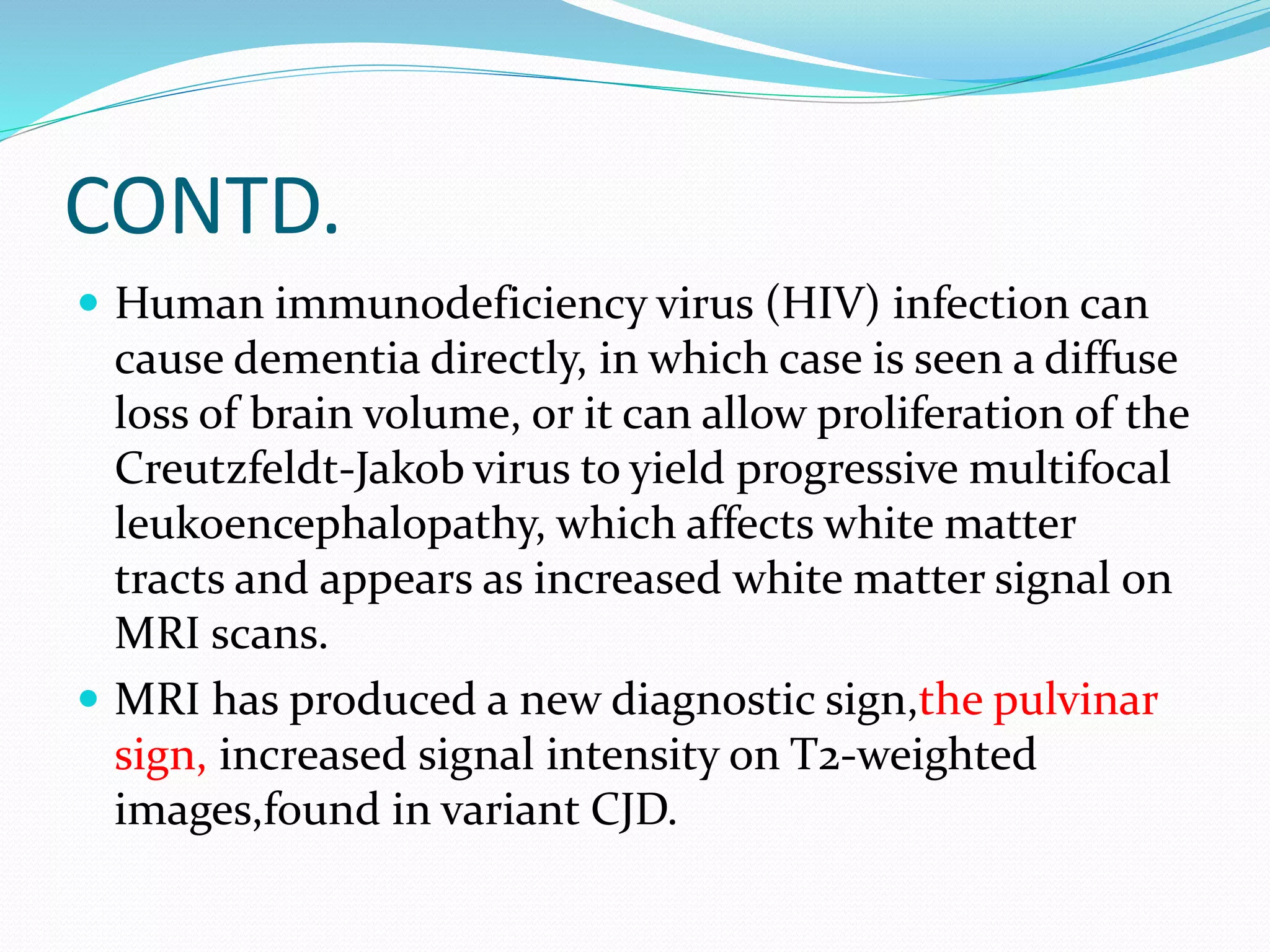
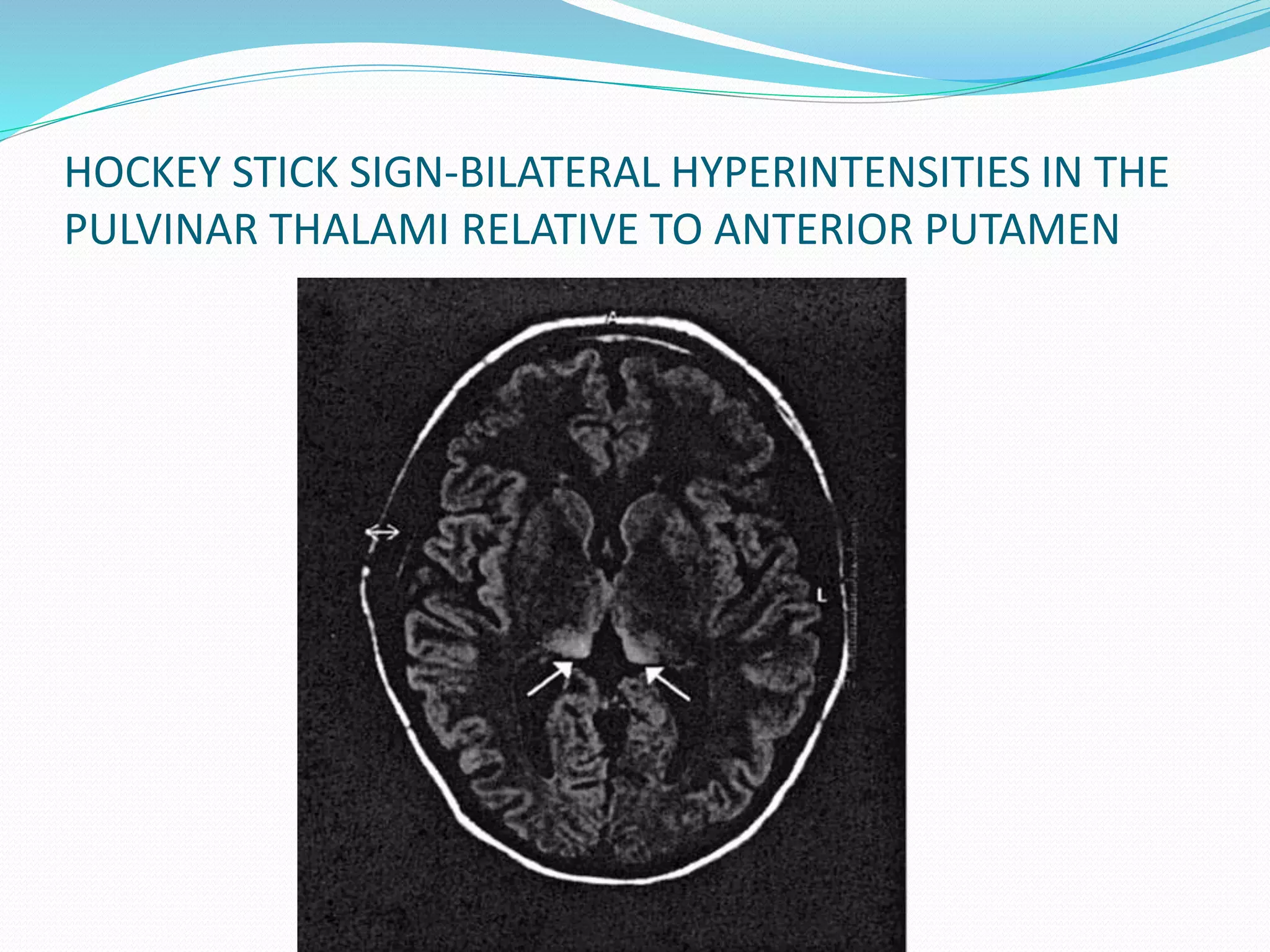
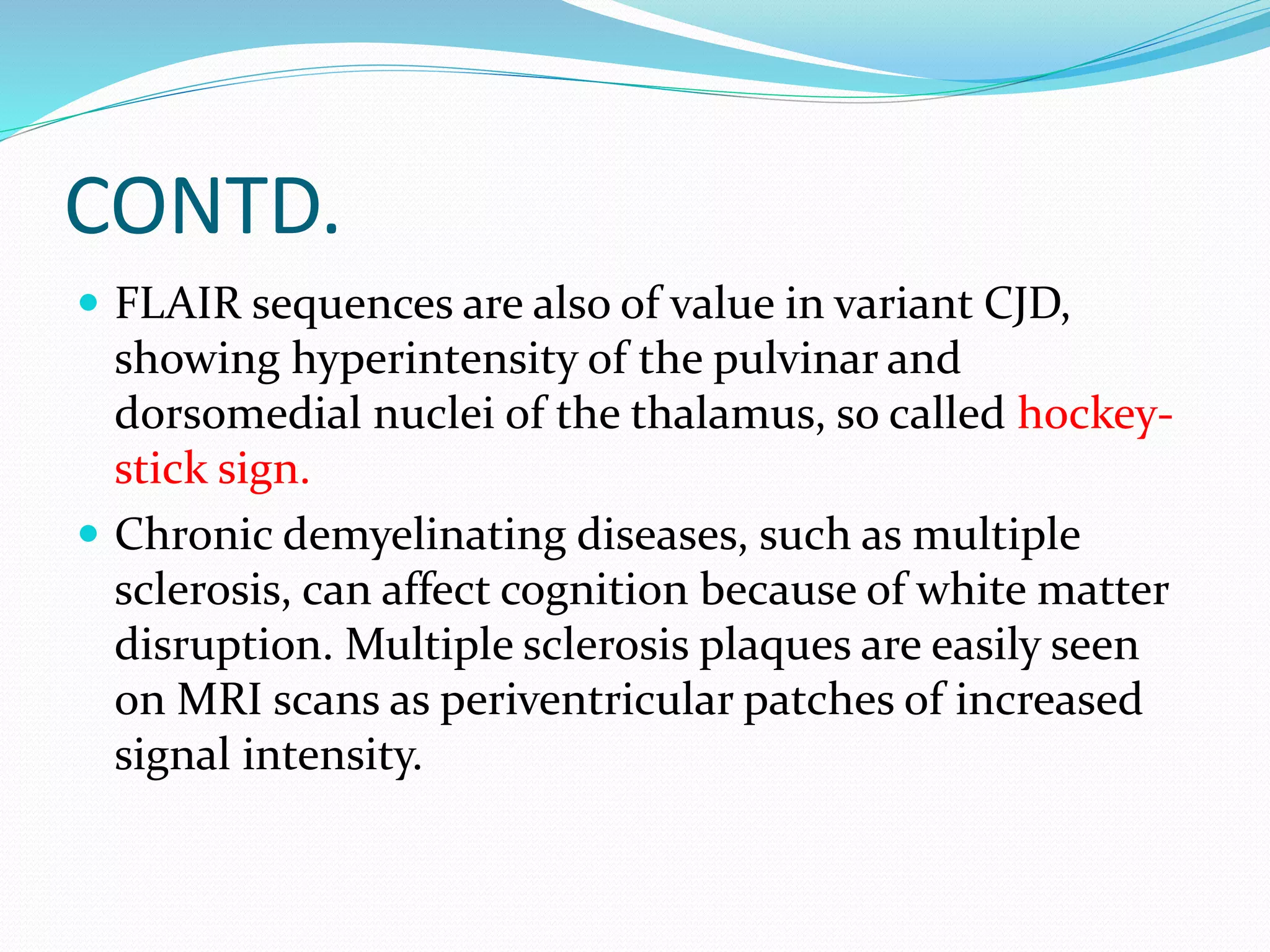
![CONTD.
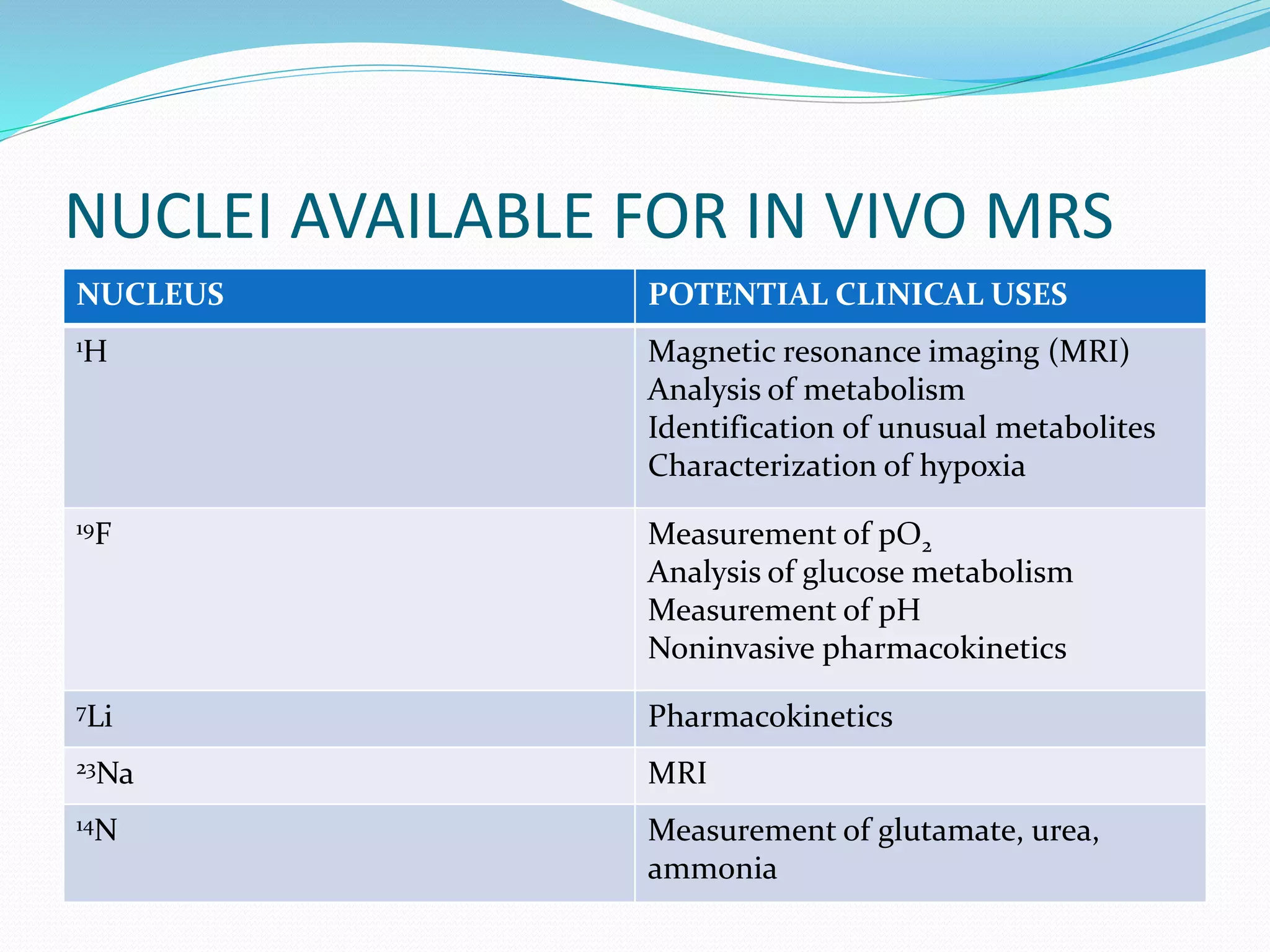
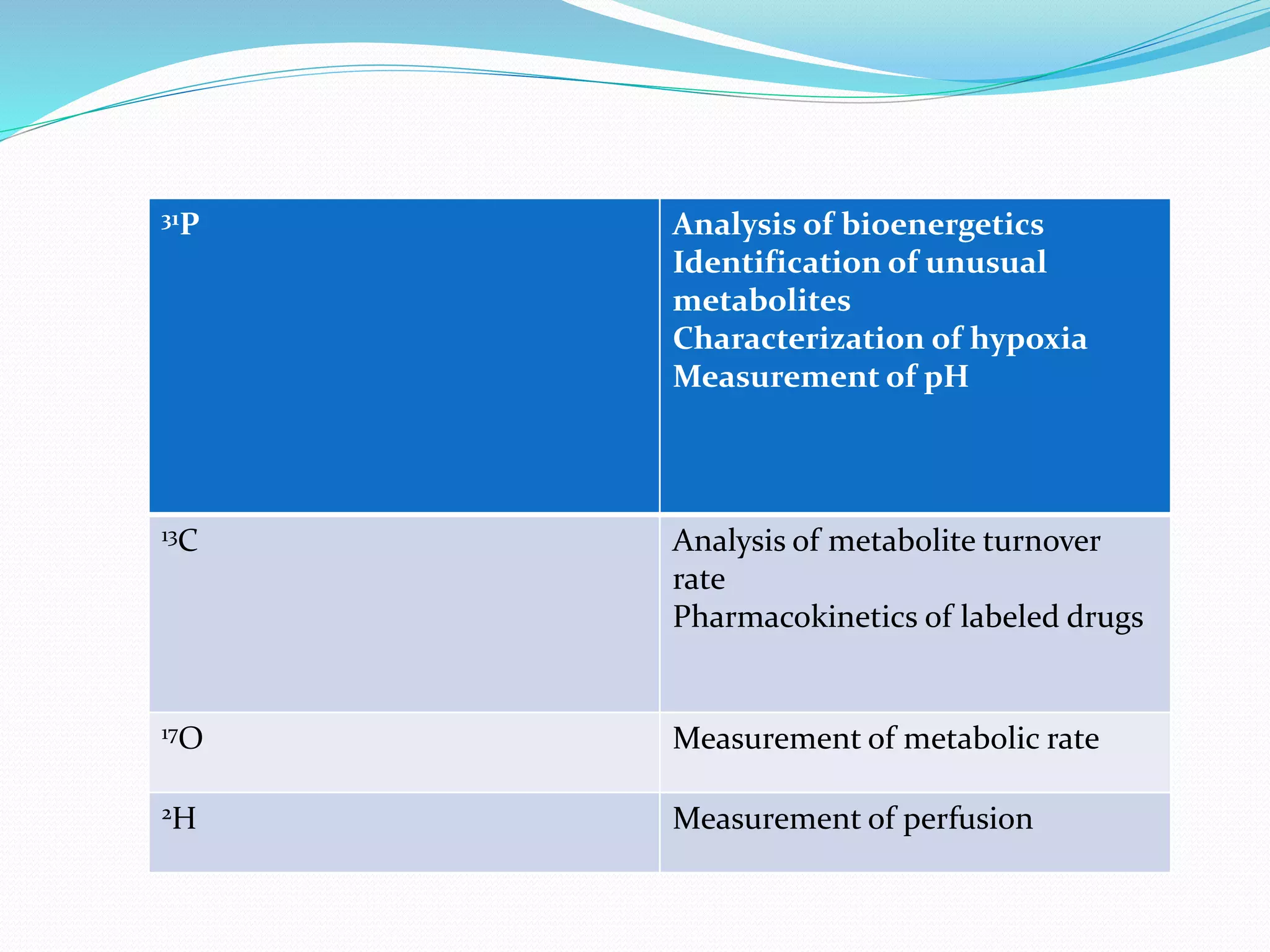
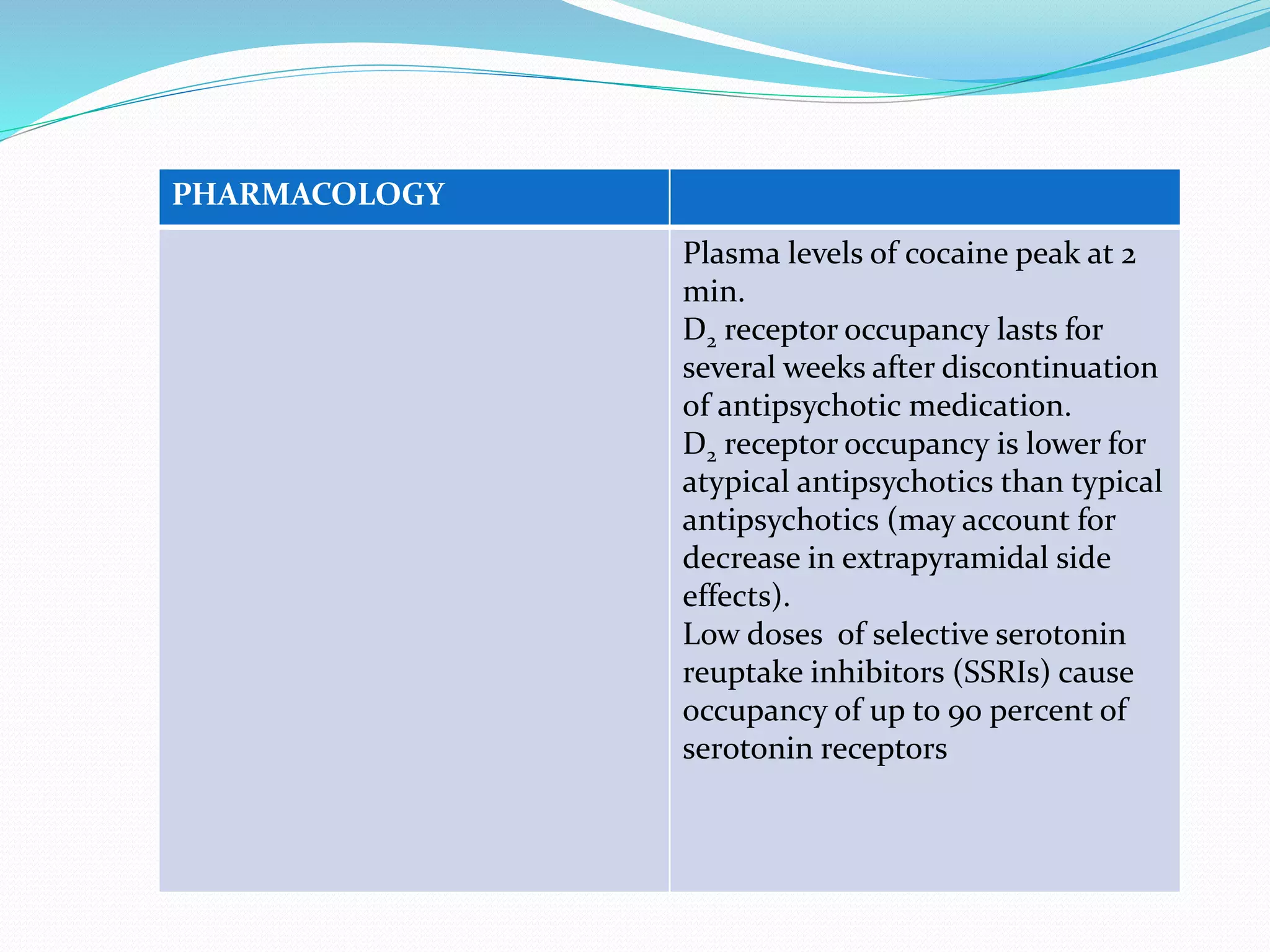
MRS of phosphorus-31 can be used to determine the
pH of brain regions and the concentrations of
phosphorus-containing compounds (e.g., adenosine
triphosphate [ATP] and guanosine triphosphate
[GTP]), which are important in the energy metabolism
of the brain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuroimaginganditsimplicationsinpsychiatry-141201080814-conversion-gate01/75/Neuroimaging-and-its-implications-in-psychiatry-19-2048.jpg)



![CONTD.
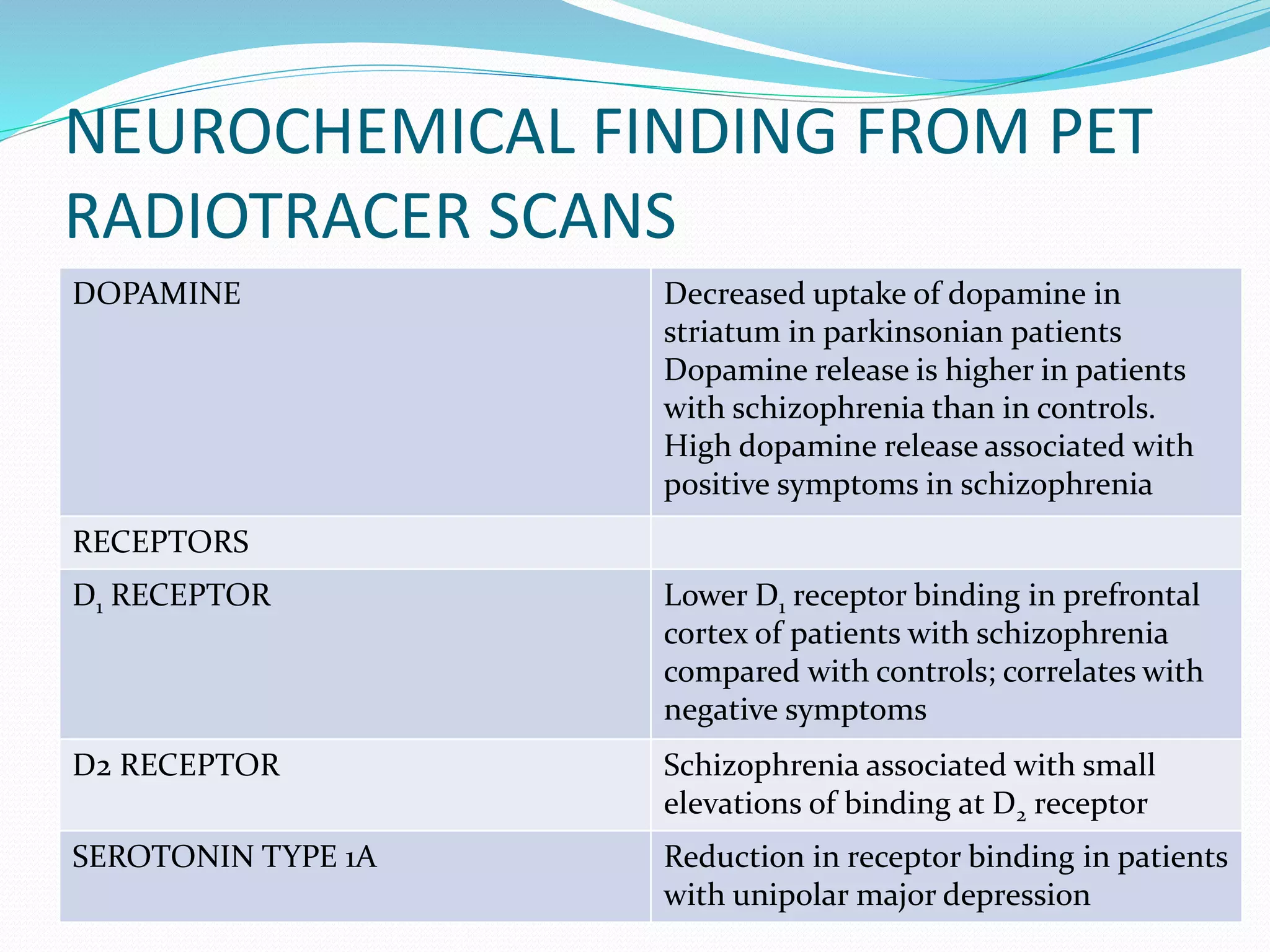
The most commonly reported ligand has been
[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), an analogue of glucose
that the brain cannot metabolize.
Thus, the brain regions with the highest metabolic rate
and the highest blood flow take up the most FDG but
cannot metabolize and excrete the usual metabolic
products. The concentration of 18F builds up in these
neurons and is detected by the PET camera.
Water-15 (H2
15O) and nitrogen-13 (13N) are used to
measure blood flow, and oxygen-15 (15O) can be used
to determine metabolic rate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuroimaginganditsimplicationsinpsychiatry-141201080814-conversion-gate01/75/Neuroimaging-and-its-implications-in-psychiatry-26-2048.jpg)
![CONTD.
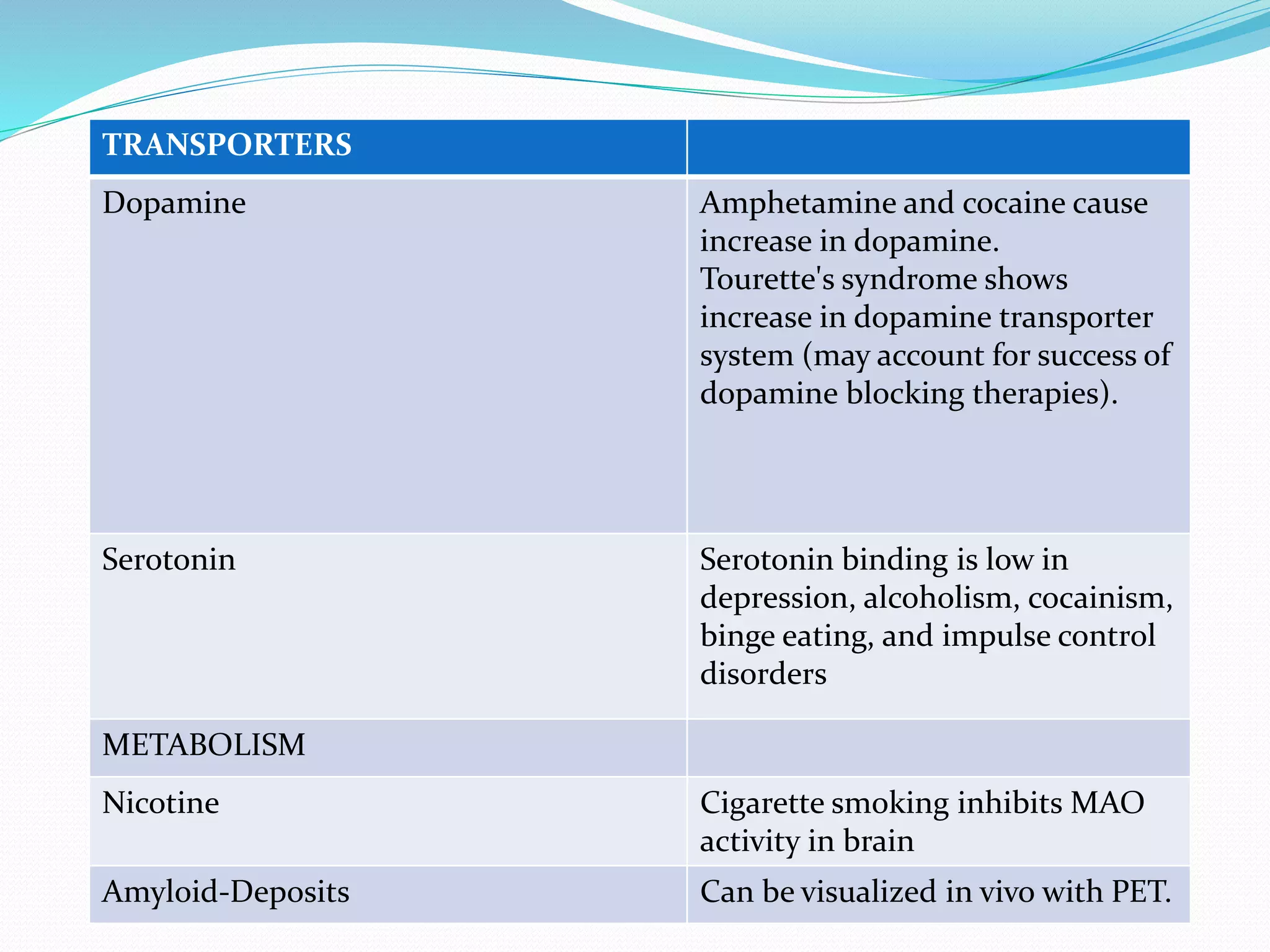
Glucose is by far the predominant energy source
available to brain cells, and its use is thus a highly
sensitive indicator of the rate of brain metabolism.
[18F]-labeled 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA), the
fluorinated precursor to dopamine, has been used to
localize dopaminergic neurons.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuroimaginganditsimplicationsinpsychiatry-141201080814-conversion-gate01/75/Neuroimaging-and-its-implications-in-psychiatry-27-2048.jpg)