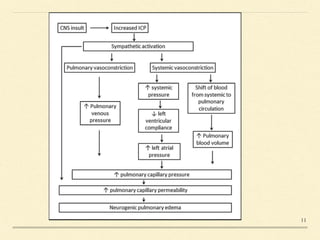
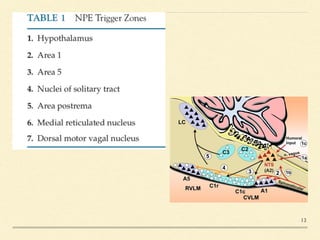
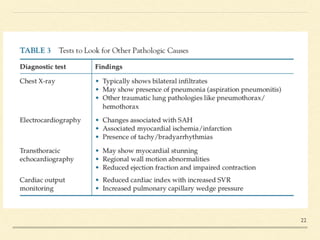
Neurogenic pulmonary edema (NPE) is a rare form of pulmonary edema that occurs following central nervous system (CNS) insults, characterized by fluid accumulation in the lungs due to increased pulmonary vascular permeability and interstitial fluid. The condition is associated with higher mortality rates, particularly in cases of subarachnoid hemorrhage and traumatic brain injury, and its management focuses primarily on supportive care while addressing the underlying CNS disorder. Symptoms may onset rapidly or be delayed, and diagnosis is primarily based on exclusion of other causes of pulmonary edema.