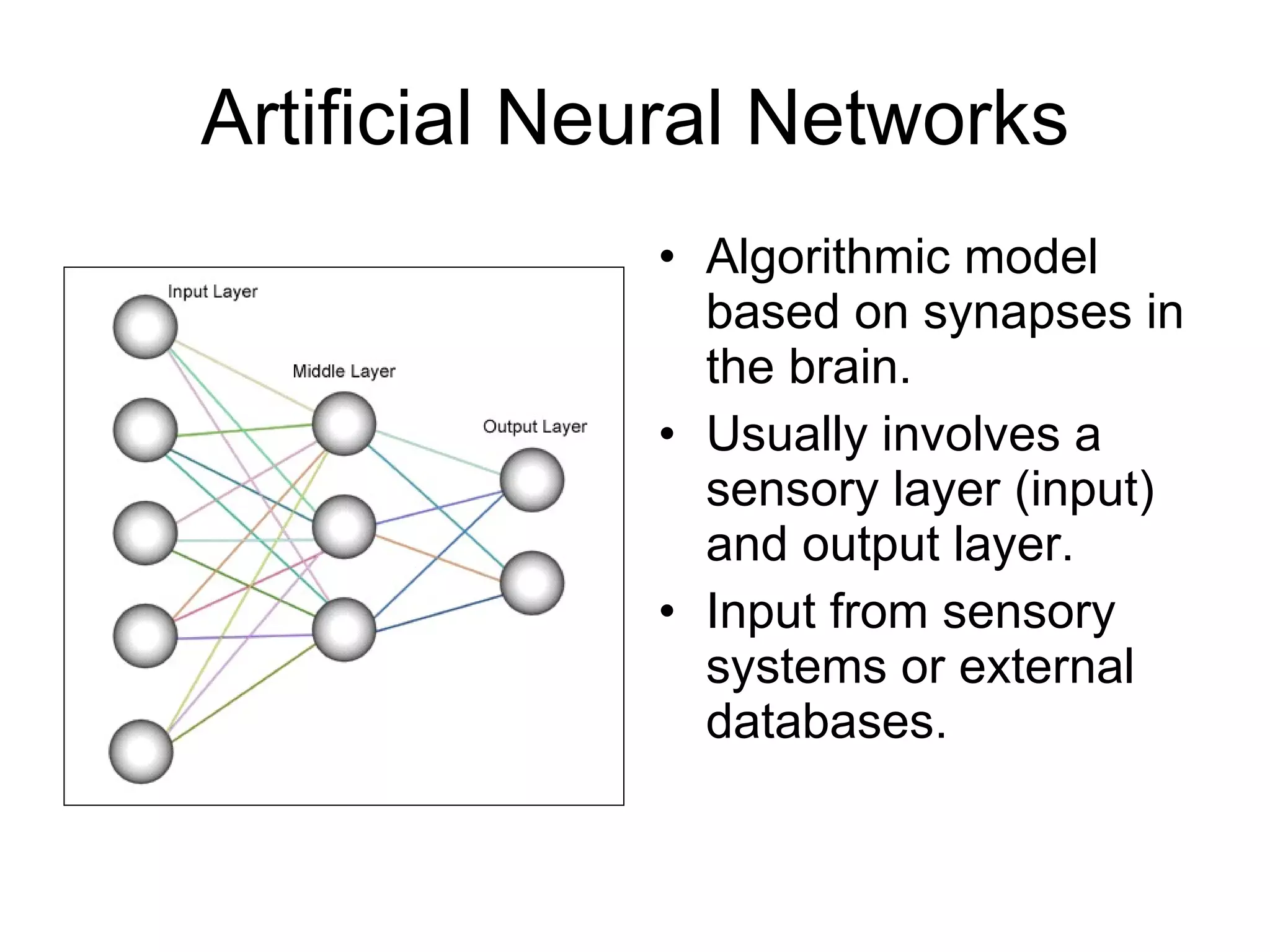
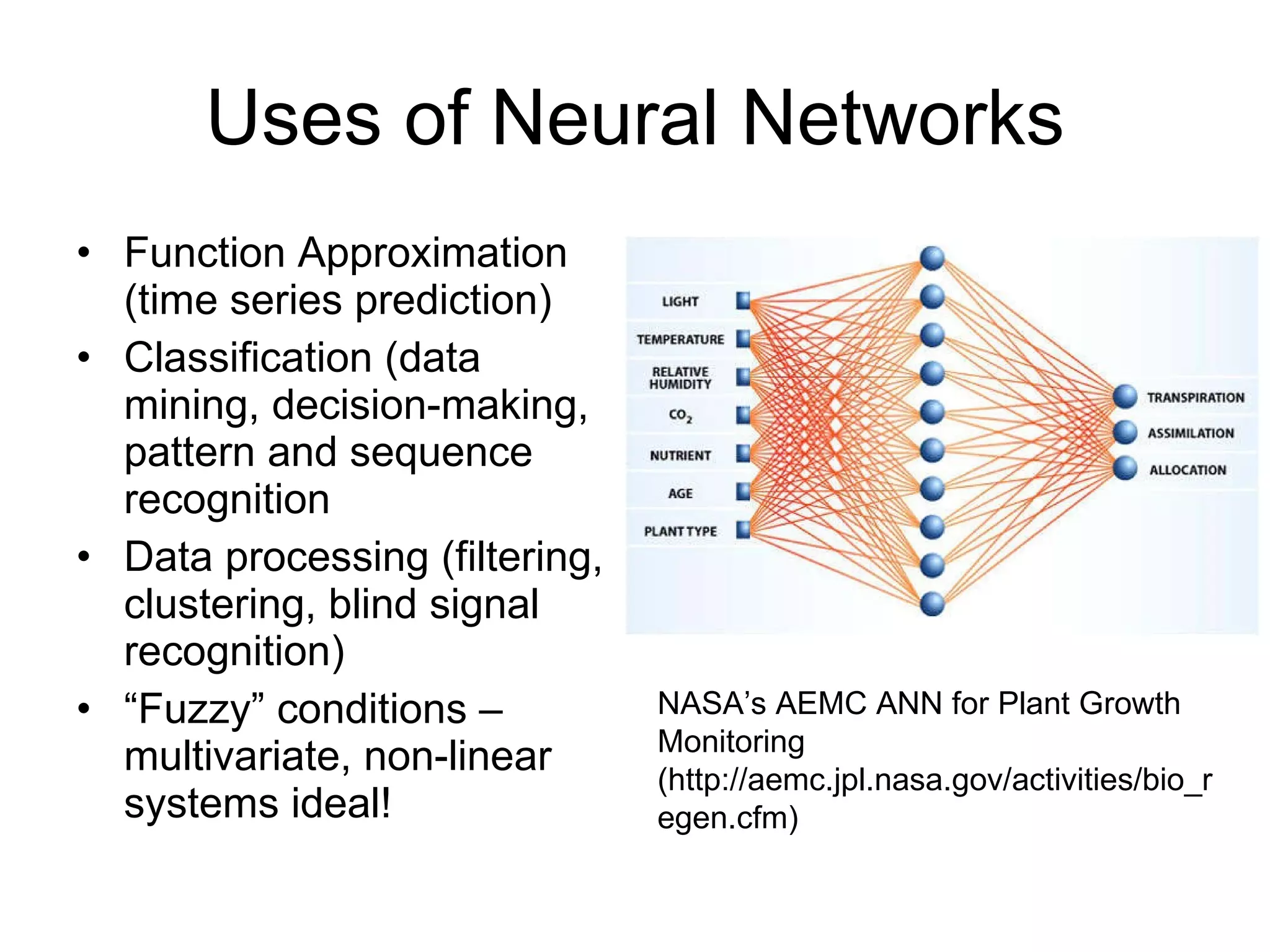
The document discusses the concept of neural networks and machine learning as extensions of the mind in artificial intelligence, presenting ideas from the philosophy of mind. It explores how machines learn from sensory data and environmental cues, comparing this to biological cognition and the implications for hard AI. The author argues that neural networks exemplify the extended mind by processing external information and shaping cognitive responses.