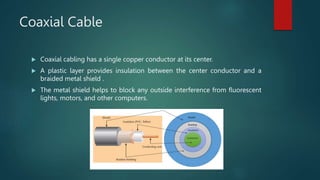
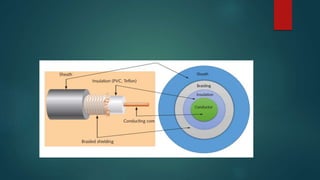
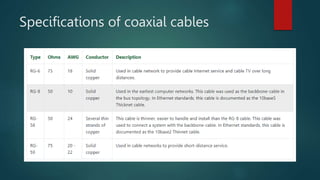
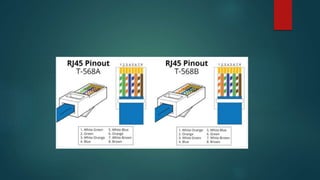
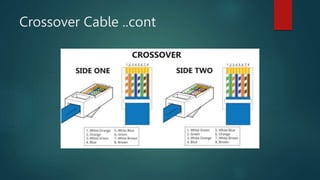
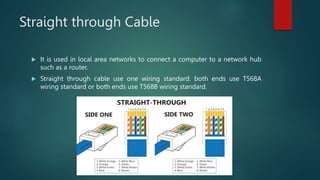
Network cabling includes coaxial cable, twisted-pair cable, and fiber optic cable. Coaxial cable uses a central conductor surrounded by insulation and a braided shield, and can be single-core or multi-core. Twisted-pair cable consists of multiple insulated copper wire pairs that can be shielded (STP) or unshielded (UTP). Fiber optic cable transmits data using light pulses through glass cores and is less susceptible to interference over longer distances than other cable types.