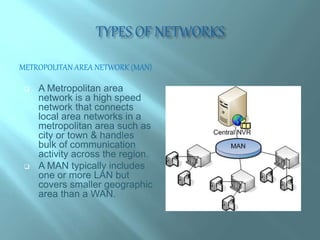
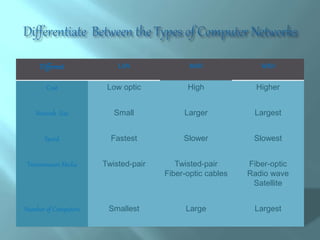
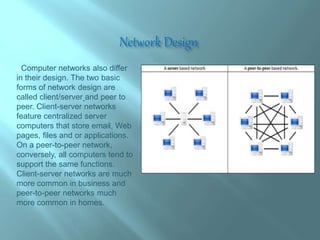
Networking involves connecting computing devices together to share data and communicate. The main advantages are easy and efficient communication, ability to share files and data, and rapid transfer of information. However, there are also disadvantages like network breakdowns causing loss of resources, high costs of building large networks, and security threats from hackers. Networks can be categorized based on their geographic reach, with local area networks (LANs) spanning a small area like a home or office, metropolitan area networks (MANs) connecting LANs across a city, and wide area networks (WANs) spanning countries or the entire world like the Internet. [/SUMMARY]