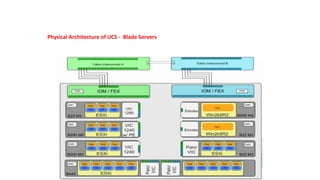
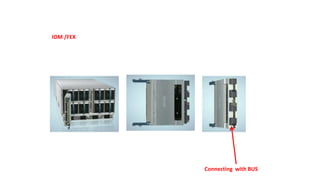
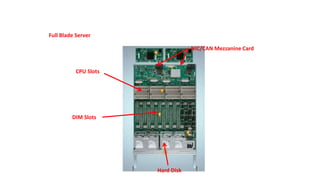
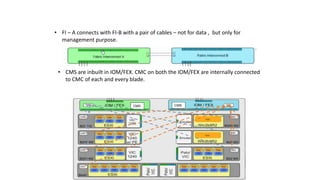
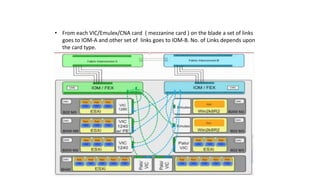
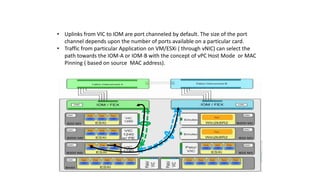
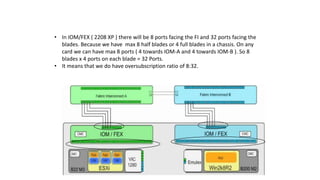
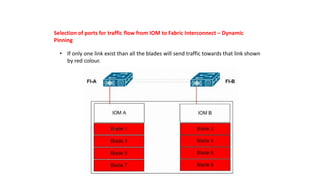
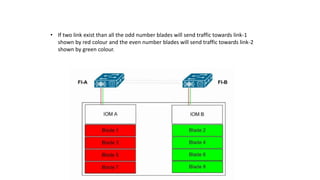
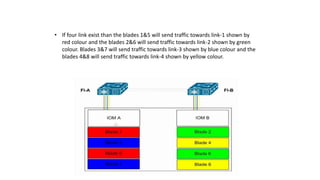
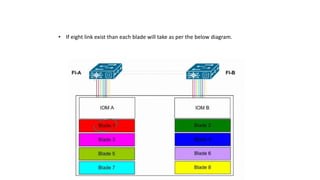
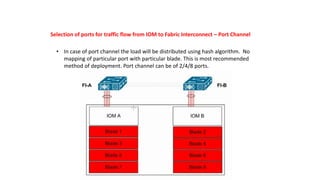
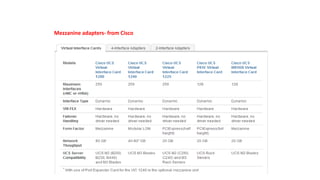
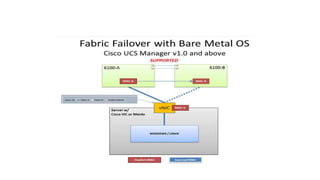
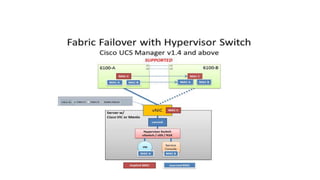
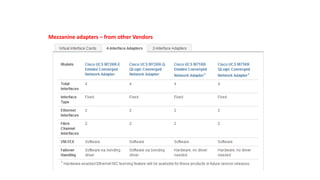
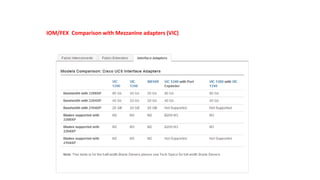
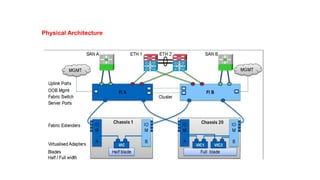
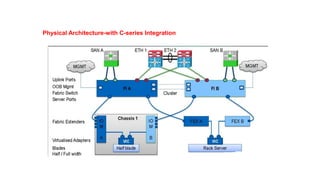
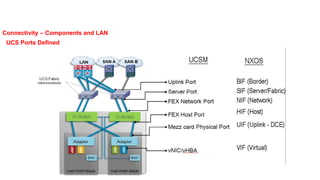
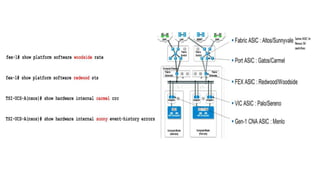
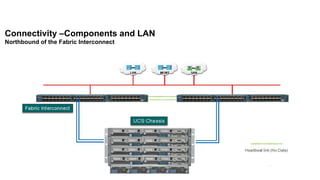
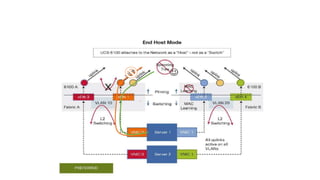
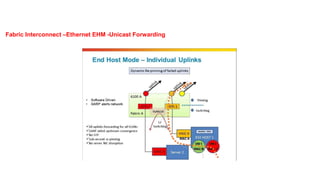
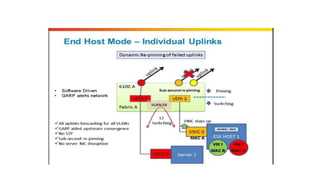
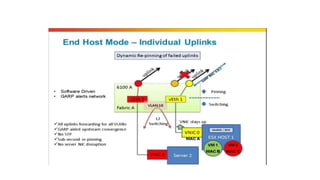
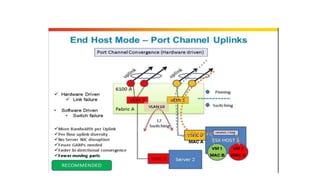
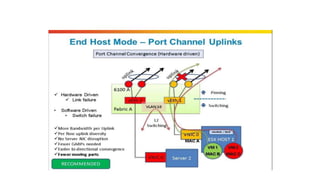
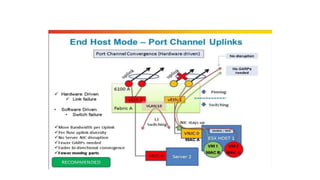
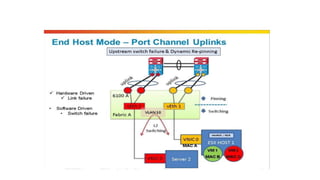
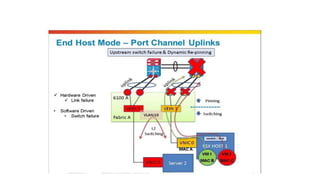
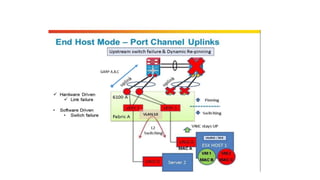
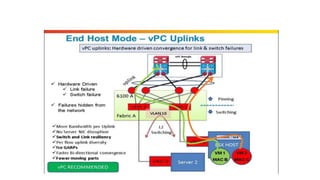
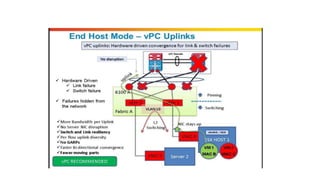
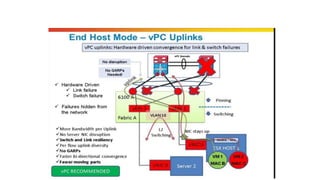
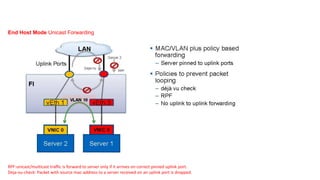
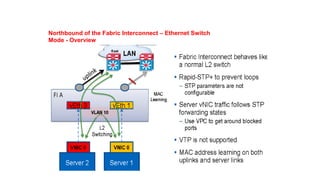
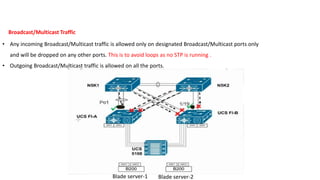
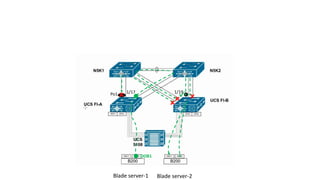
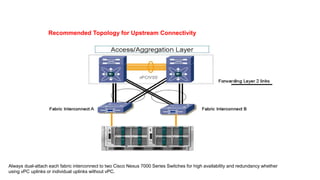
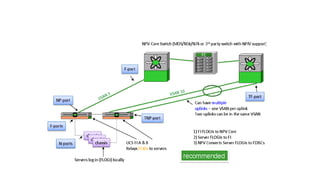
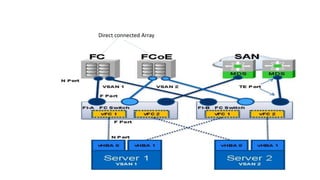
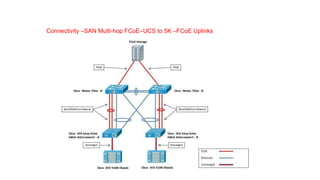
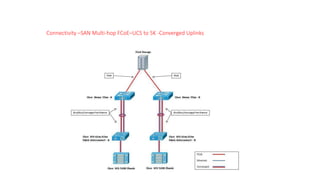
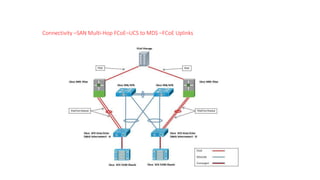
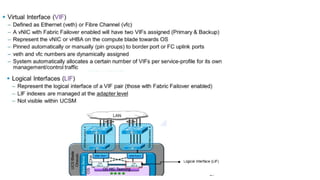
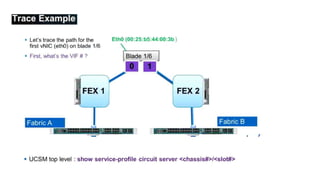
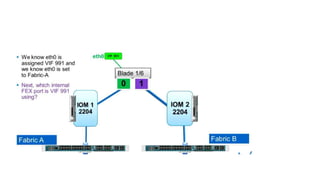
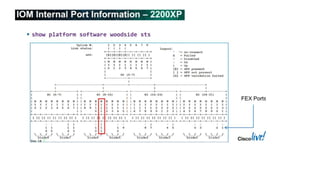
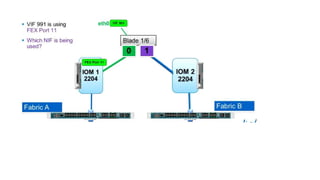
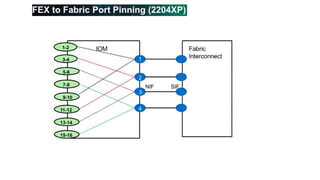
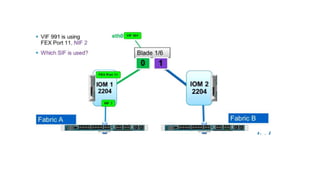
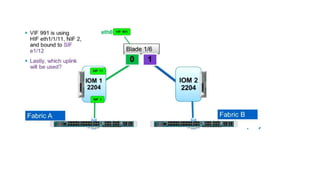
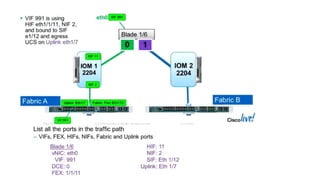
The document provides a detailed overview of Unified Computing System (UCS) architecture, including the two types of servers (rack-mountable and blade servers) and the components involved such as fabric interconnects and management interfaces. It describes the physical architecture and the function of various components, highlighting features like stateless computing, rapid server provisioning, and virtualization readiness. Additionally, it covers connectivity options, port selection for traffic flow, and specifics about the fabric interconnect and its operational modes for SAN connectivity.