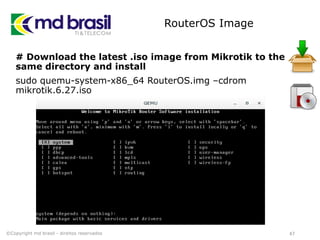
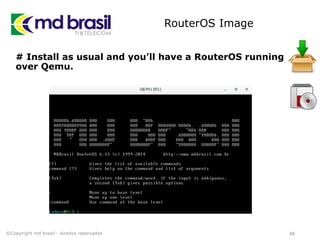
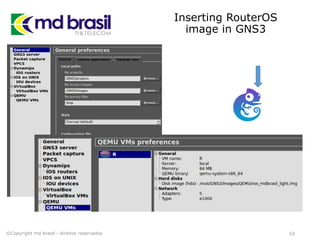
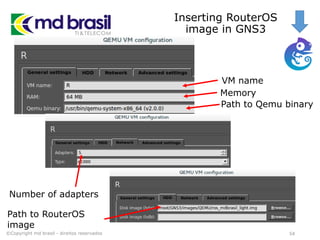
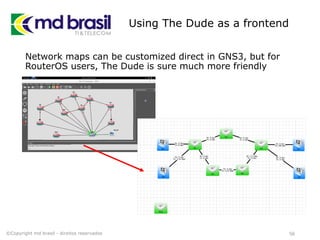
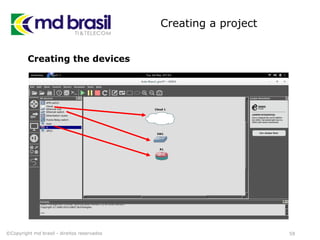
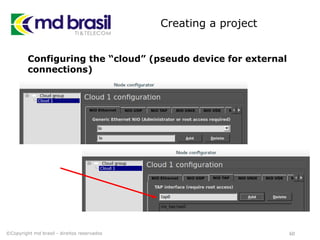
This document provides instructions for installing software to simulate networks using GNS3, Qemu, and the Dude. It discusses installing dependencies on Ubuntu, downloading and configuring GNS3, Qemu, Dynamips, IOU, and the Dude. It also describes creating a RouterOS image file and licensing it to use in simulations. The document aims to enable readers to set up the necessary tools to simulate IP networks and use RouterOS in their simulations.




























![Installation
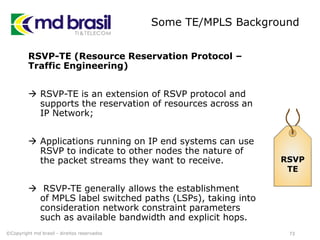
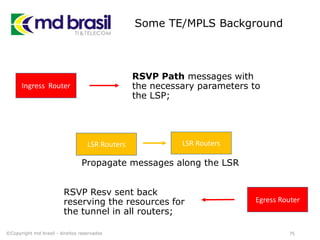
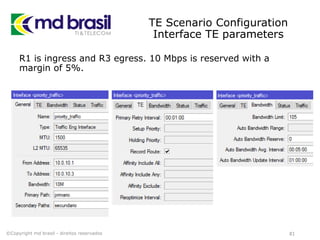
# Creating License file for Cisco (cont.)
# get the host id and host name to calculate the hostkey
hostid=os.popen("hostid").read().strip()
hostname = socket.gethostname()
ioukey=int(hostid,16)
for x in hostname:
ioukey = ioukey + ord(x)
print "hostid=" + hostid +", hostname="+ hostname + ", ioukey=" +
hex(ioukey)[2:]
39©Copyright md brasil - direitos reservados](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/network-simulation-maia-150411132607-conversion-gate01/85/Network-Simulation-Prague-2015-39-320.jpg)
![Installation
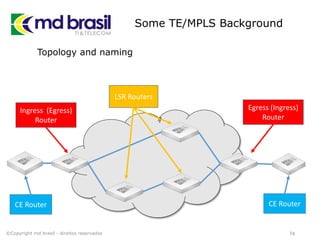
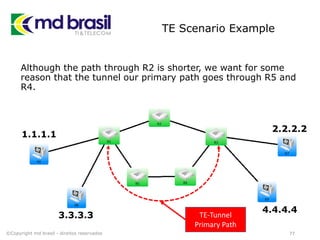
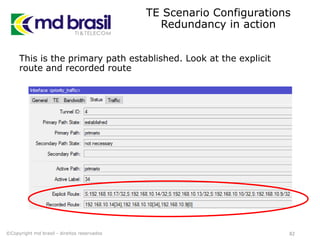
# Creating License file for Cisco (cont.)
# create the license using md5sum
iouPad1='x4Bx58x21x81x56x7Bx0DxF3x21x43x9Bx7ExAC
x1DxE6x8A'
iouPad2='x80' + 39*'0'
md5input=iouPad1 + iouPad2 + struct.pack('!L', ioukey) + iouPad1
iouLicense=hashlib.md5(md5input).hexdigest()[:16]
print "nAdd the following text to ~/.iourc:"
print "[license]n" + hostname + " = " + iouLicense + ";n"
print "You can disable the phone home feature with something like:"
print " echo '127.0.0.127 xml.cisco.com' >> /etc/hostsn"
40©Copyright md brasil - direitos reservados](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/network-simulation-maia-150411132607-conversion-gate01/85/Network-Simulation-Prague-2015-40-320.jpg)
![Installation
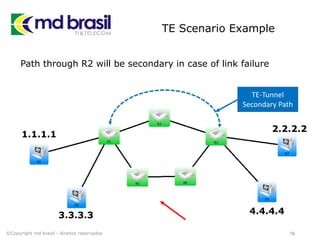
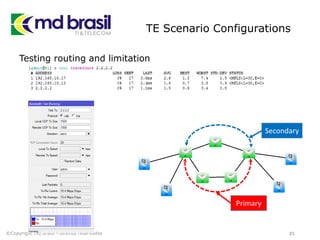
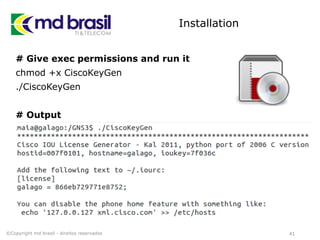
# Add license to iourc.txt
pico iourc.txt
[license]
galago = 866eb729771e8752;
# Disable the phone feature
echo '127.0.0.127 xml.cisco.com' >> /etc/hosts
42©Copyright md brasil - direitos reservados](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/network-simulation-maia-150411132607-conversion-gate01/85/Network-Simulation-Prague-2015-42-320.jpg)