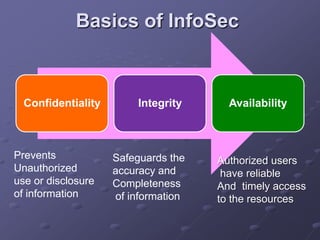
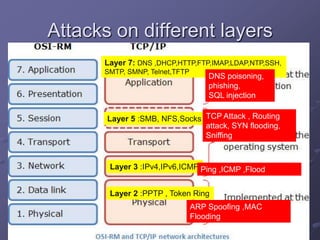
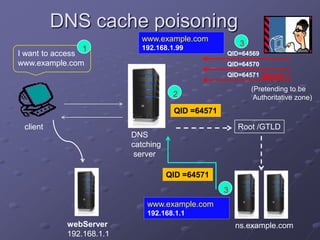
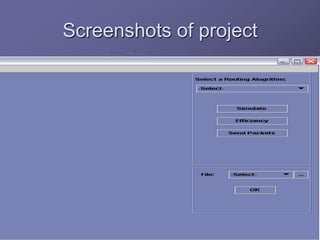
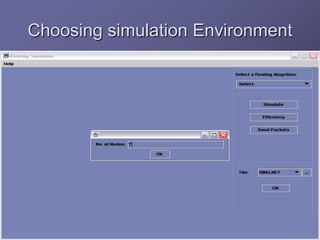
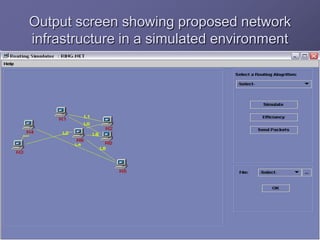
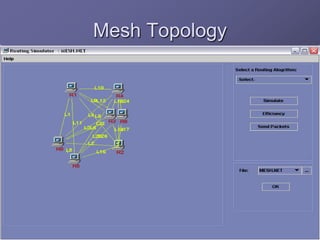
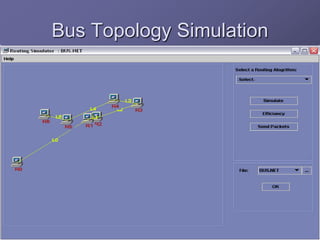
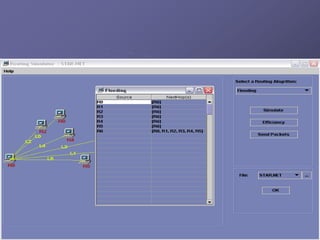
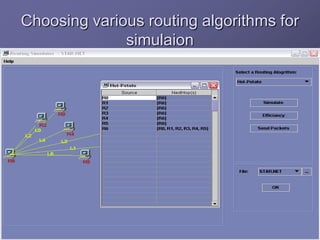
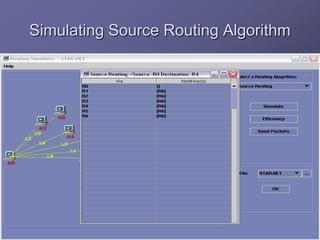
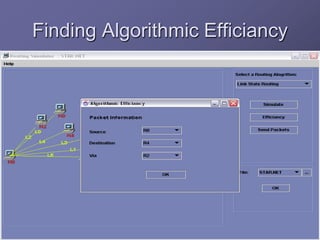
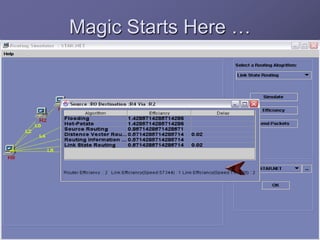
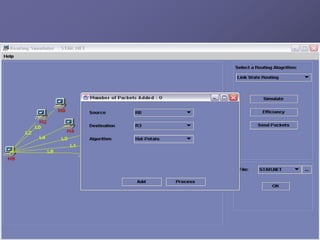
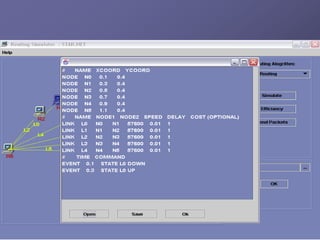
The document outlines a router simulation system designed to mitigate network security attacks by emphasizing the need for security measures in modern internet use. It discusses various types of cyber attacks, defensive technologies like firewalls and VPNs, and the importance of authentication and access control. The simulator aims to optimize routing efficiency and test configurations without disrupting production networks, providing benefits for networking service providers and designers.