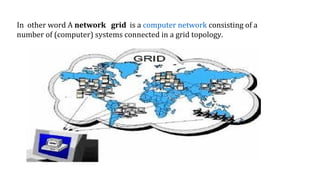
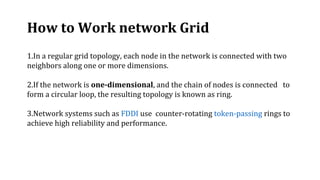
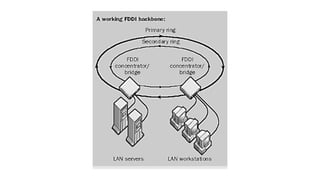
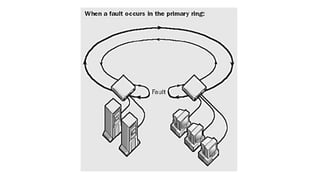
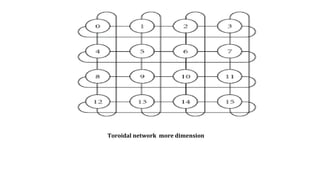
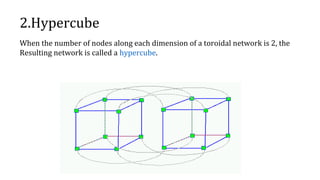
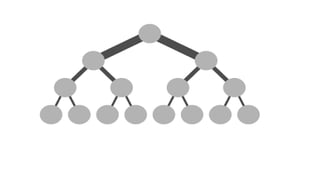
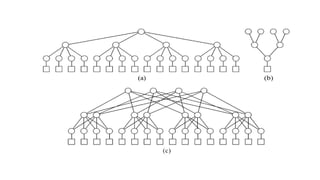
A grid network is defined as a fault-tolerant computer network that facilitates resource sharing and problem-solving across various institutions, featuring nodes that serve as data routers. Various topologies, such as toroidal networks, hypercubes, fat trees, and hypertrees, are explored, each offering unique structures for data transmission. Specifically, the fiber distributed data interface (FDDI) employs dual token-passing rings to ensure high reliability and a data transmission rate of up to 100 Mbit/s.
![Grid Network
Presented by
Gamit Jaysing
[Eno:201504100120256]
[TYMCA-C]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkgrid-160928202302/75/Network-grid-1-2048.jpg)