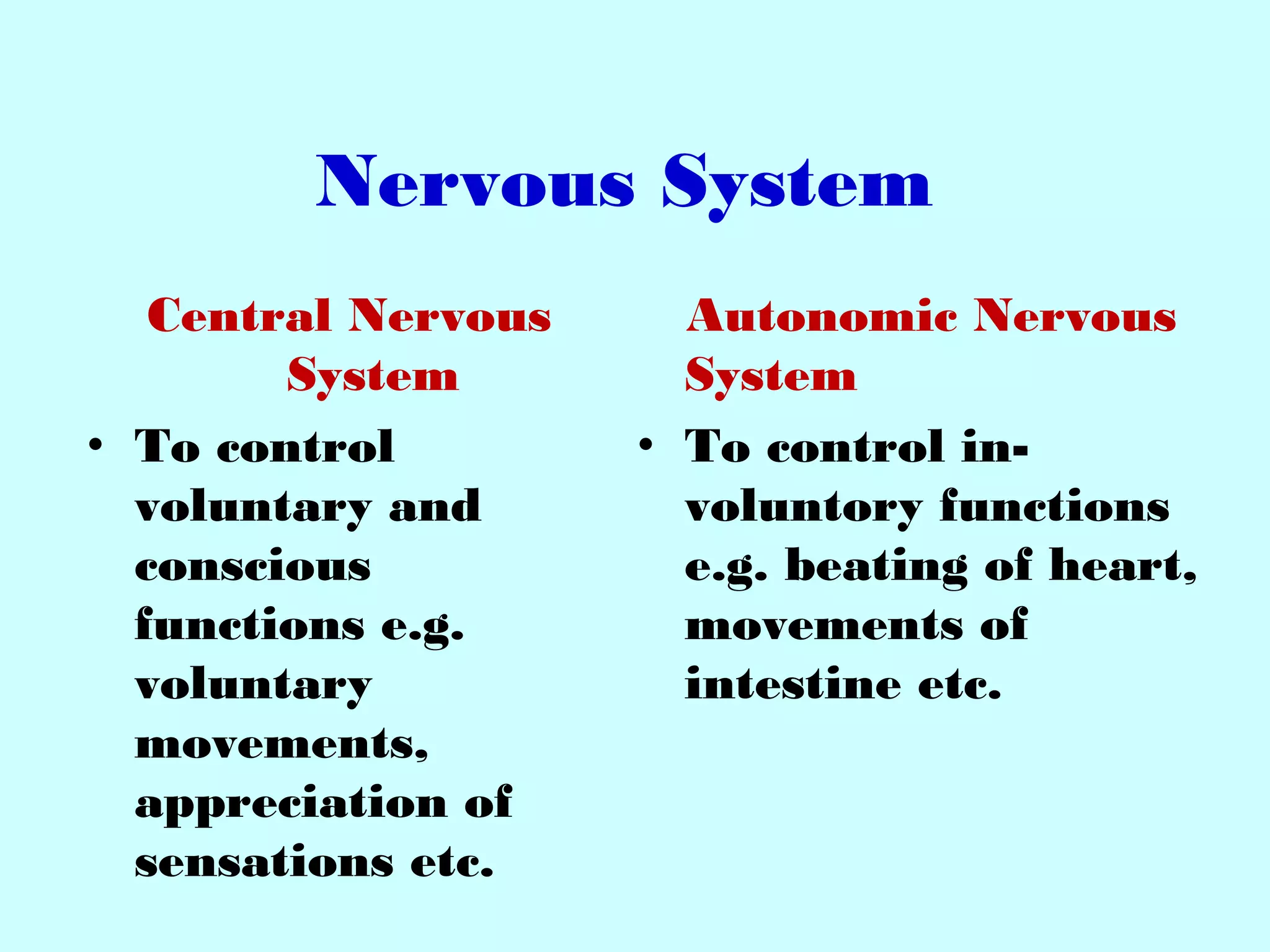
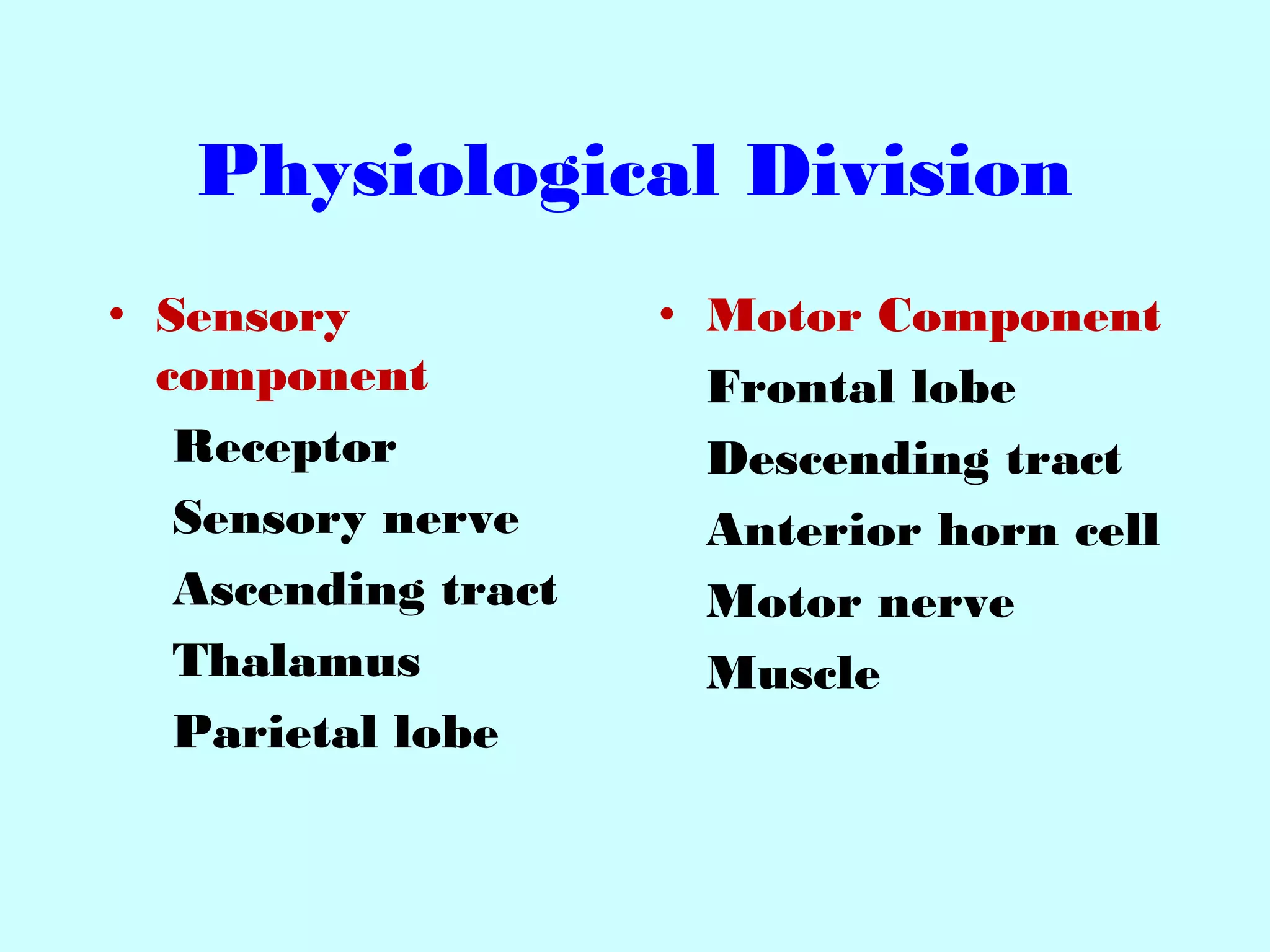
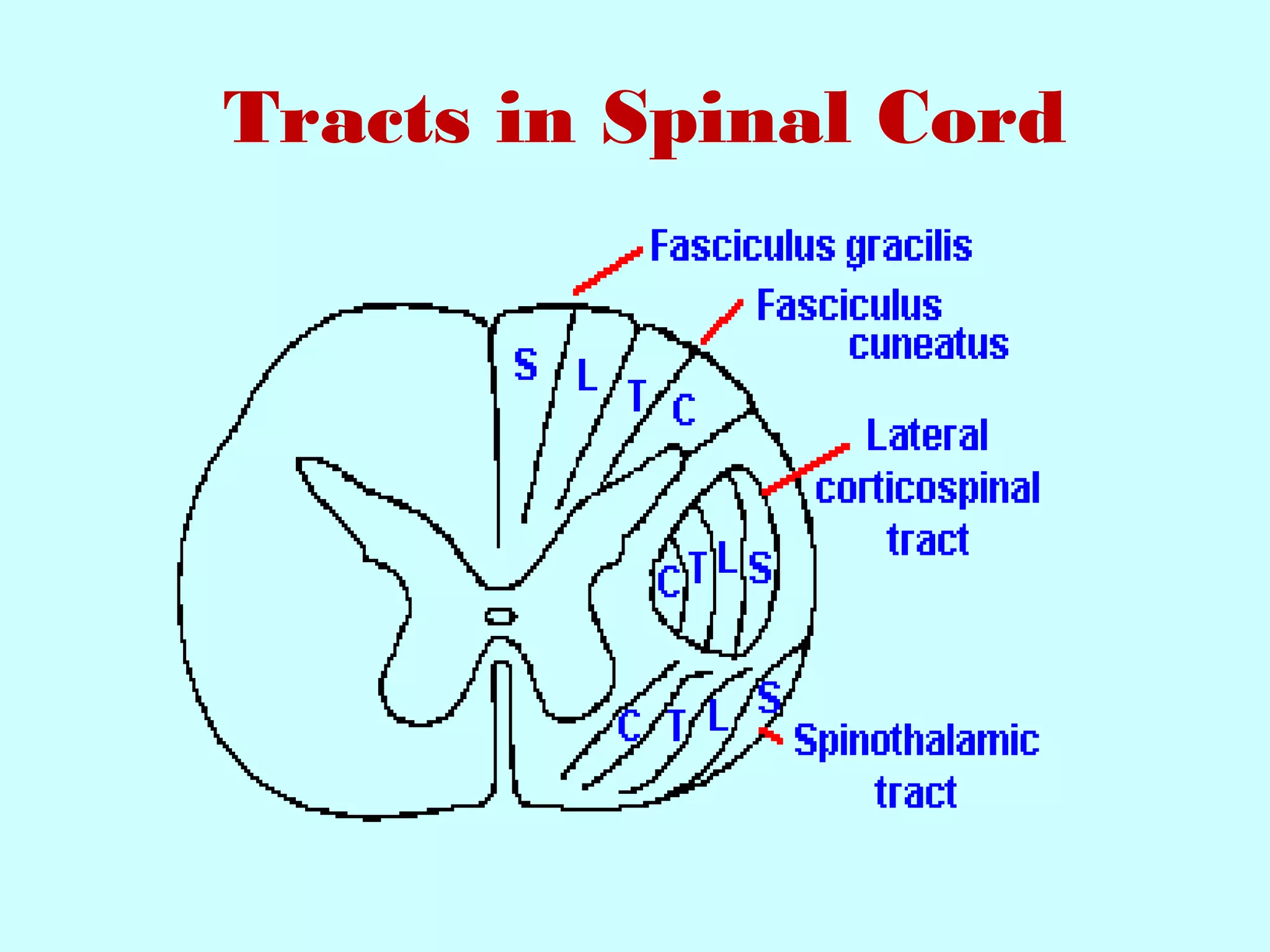
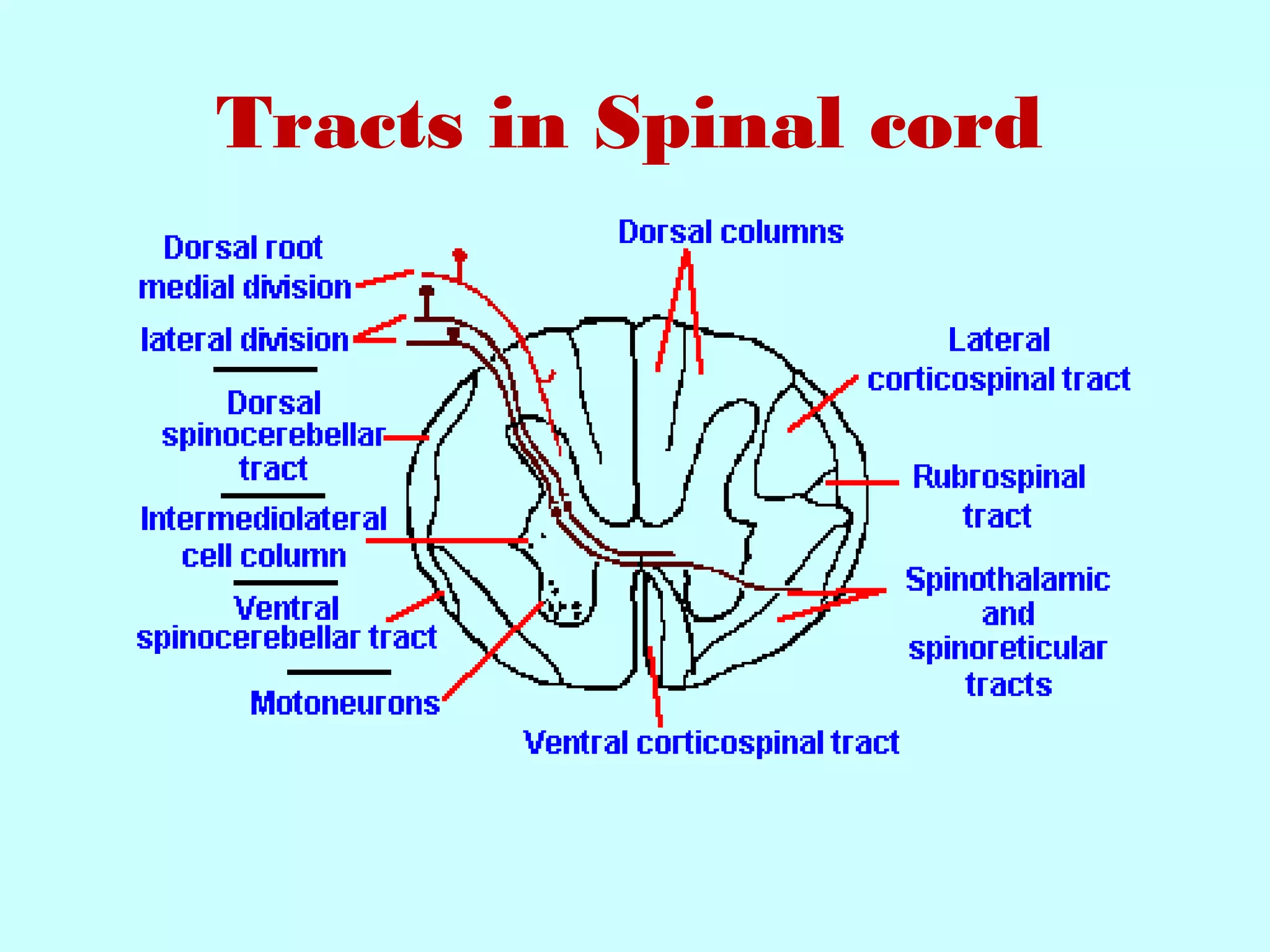
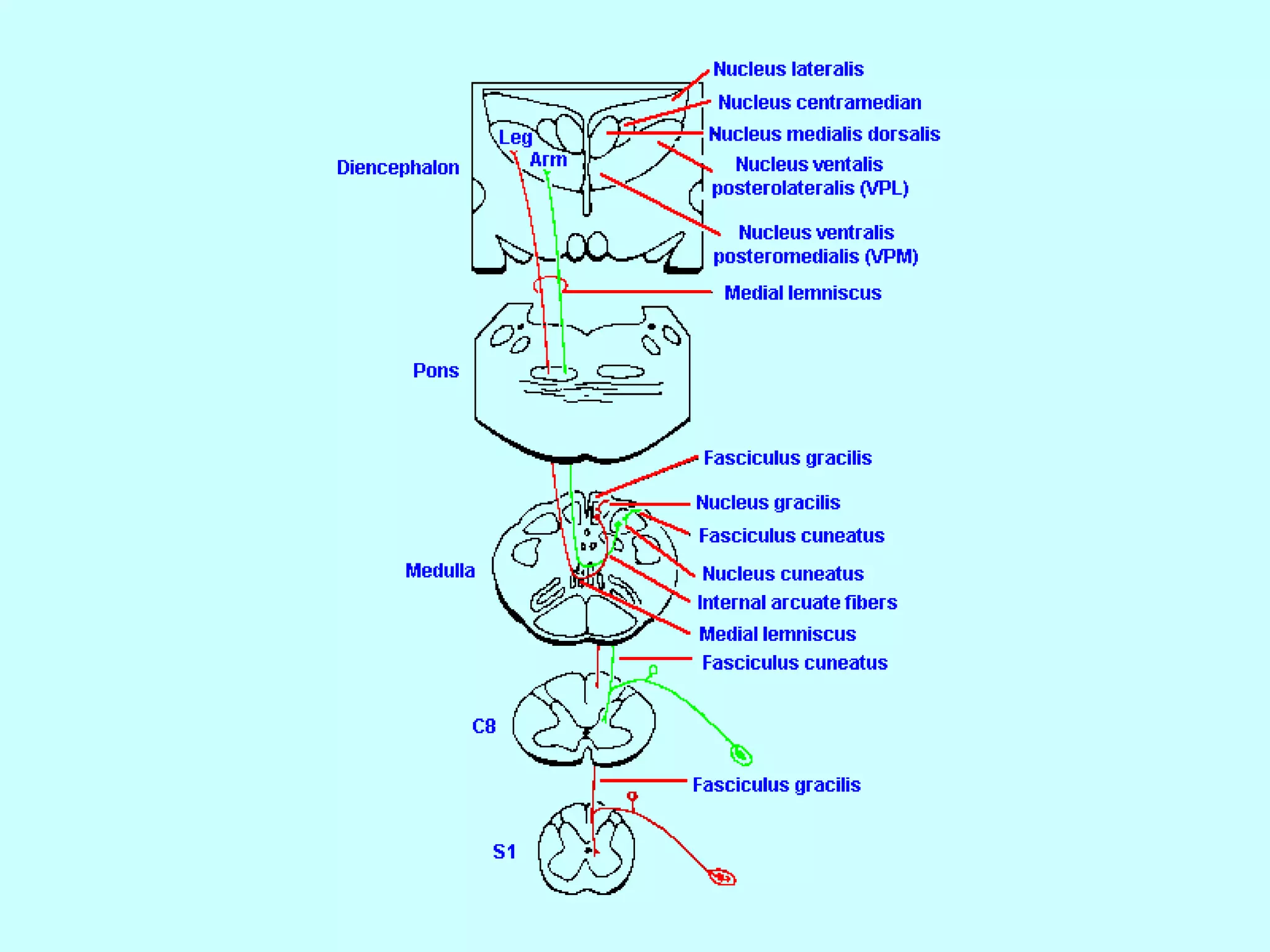
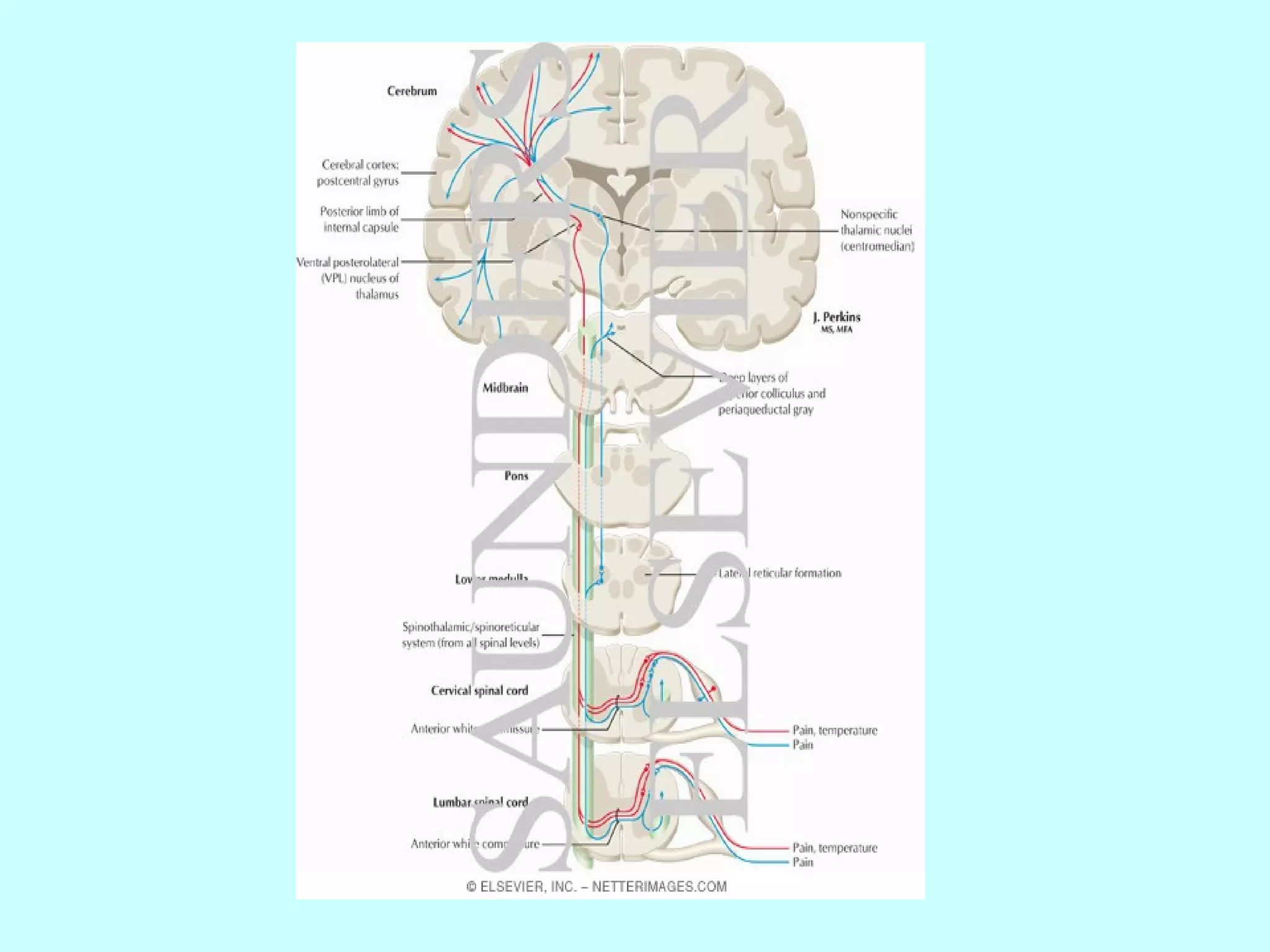
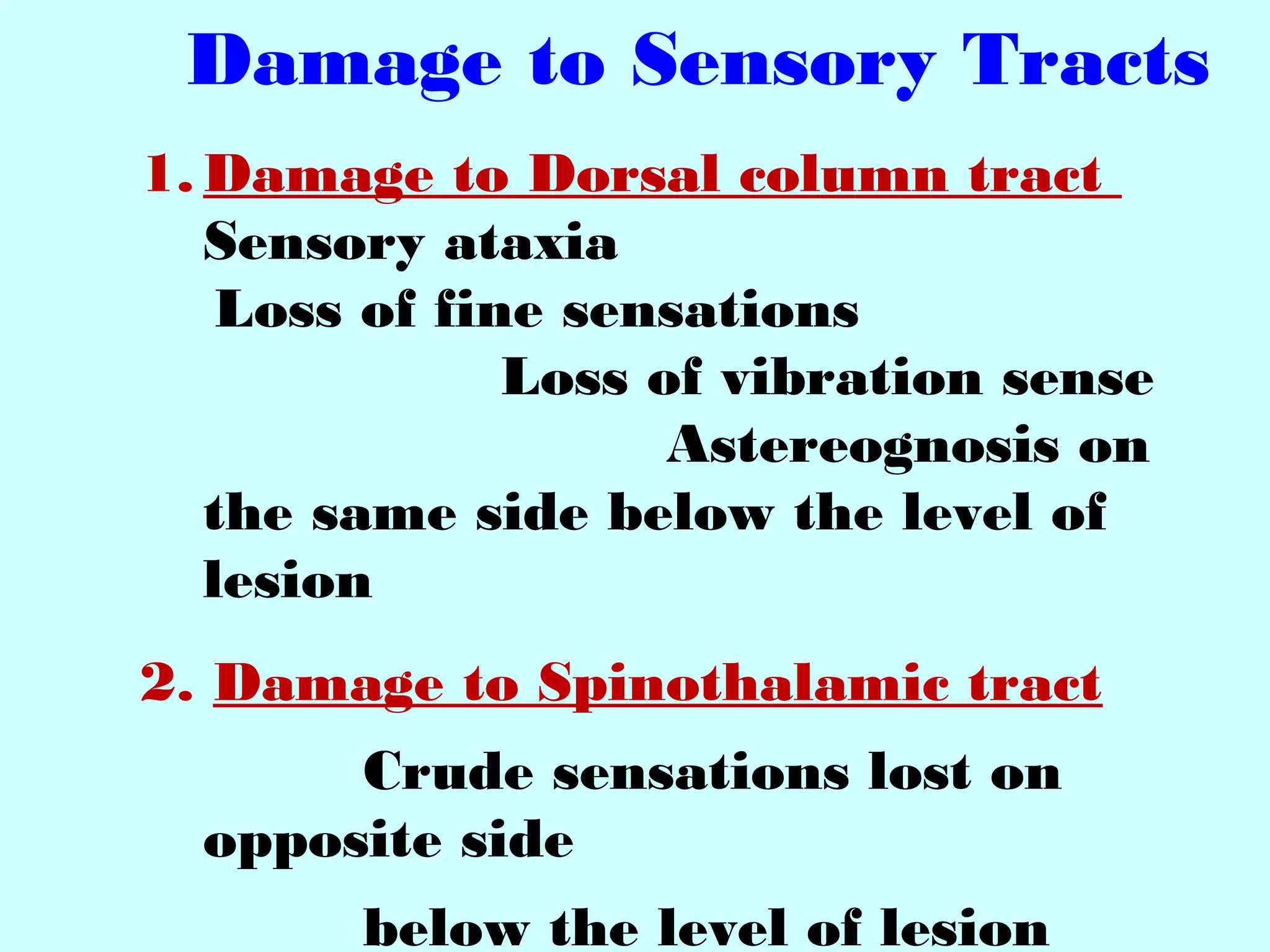
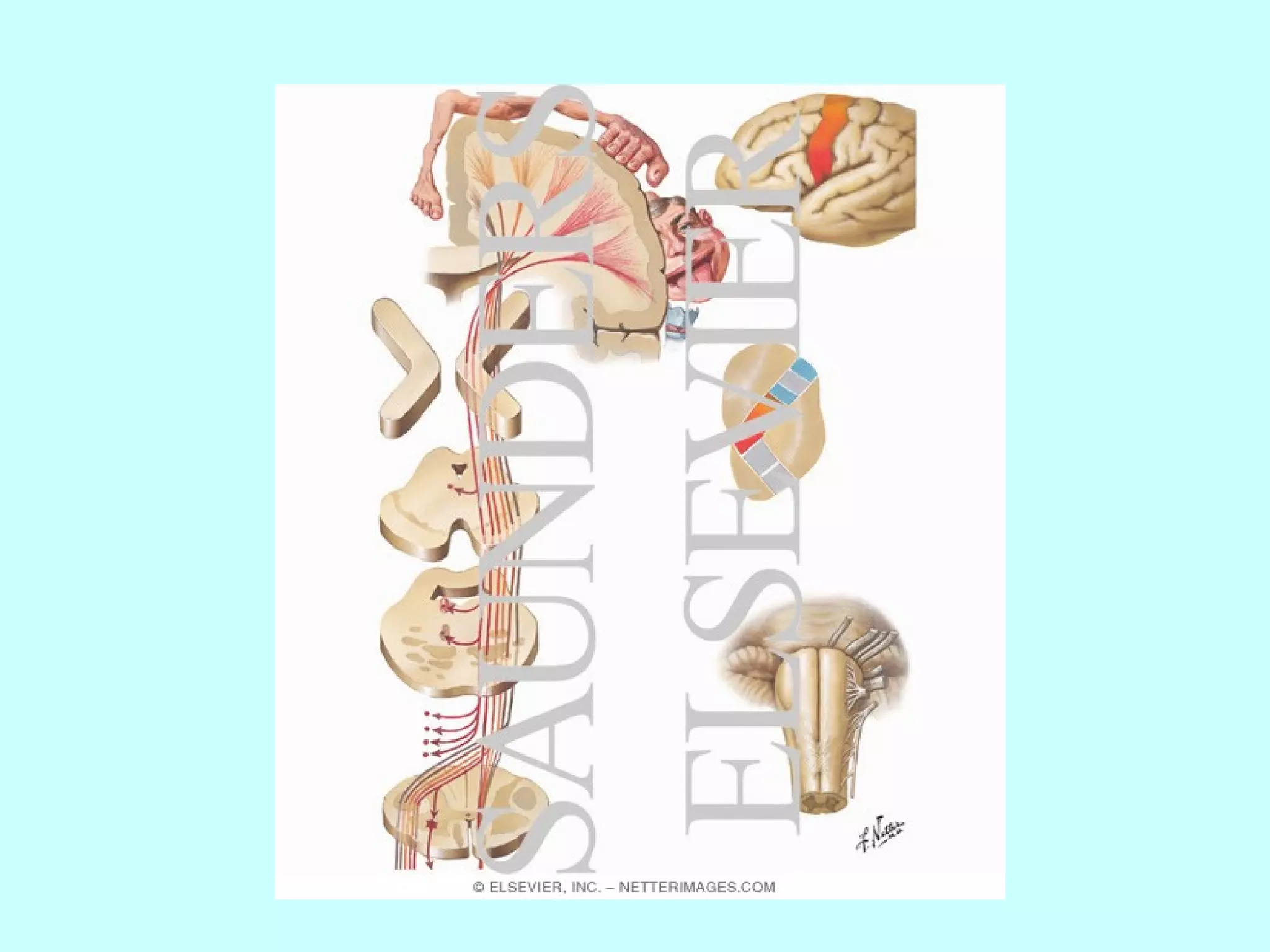
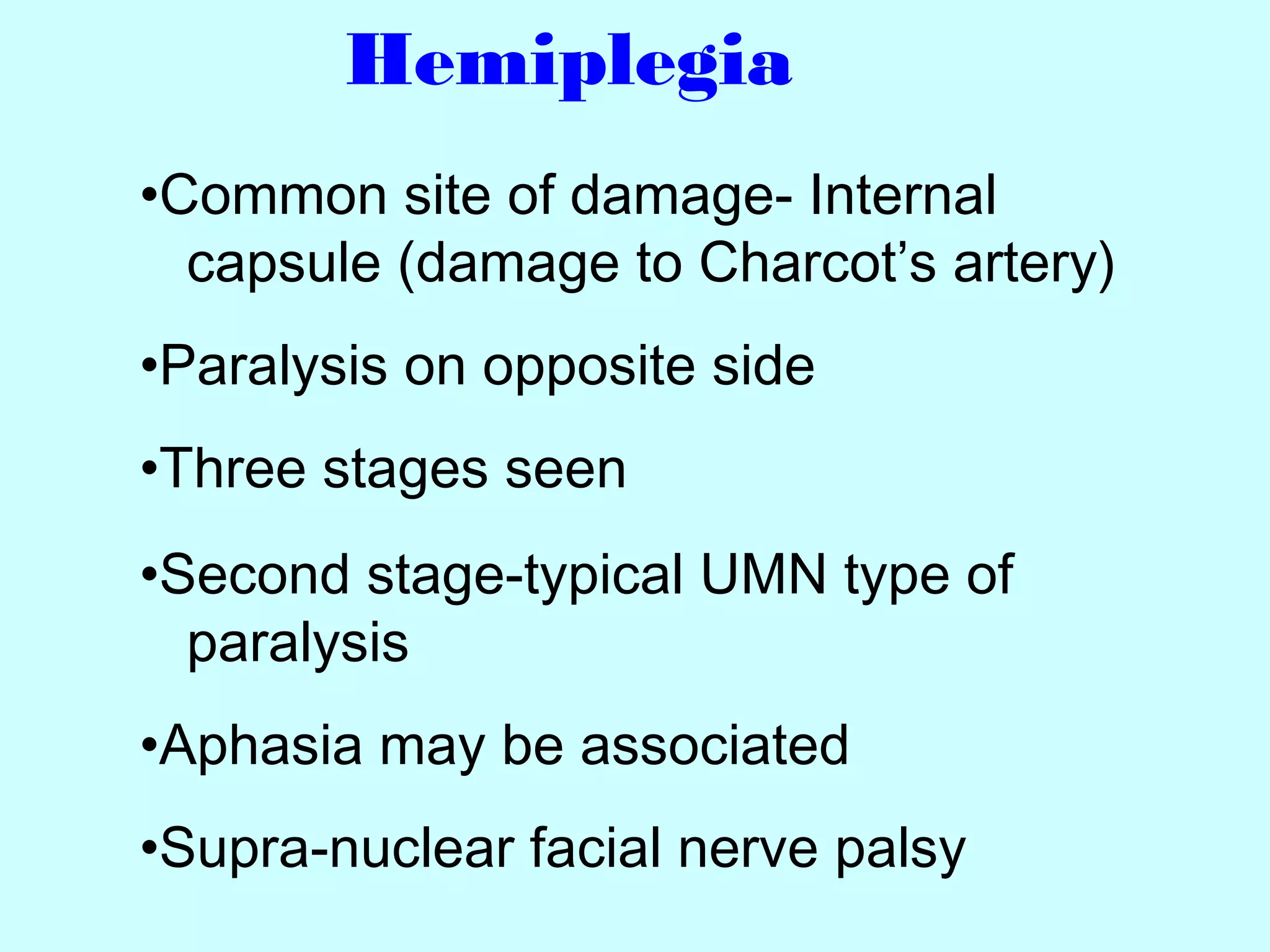
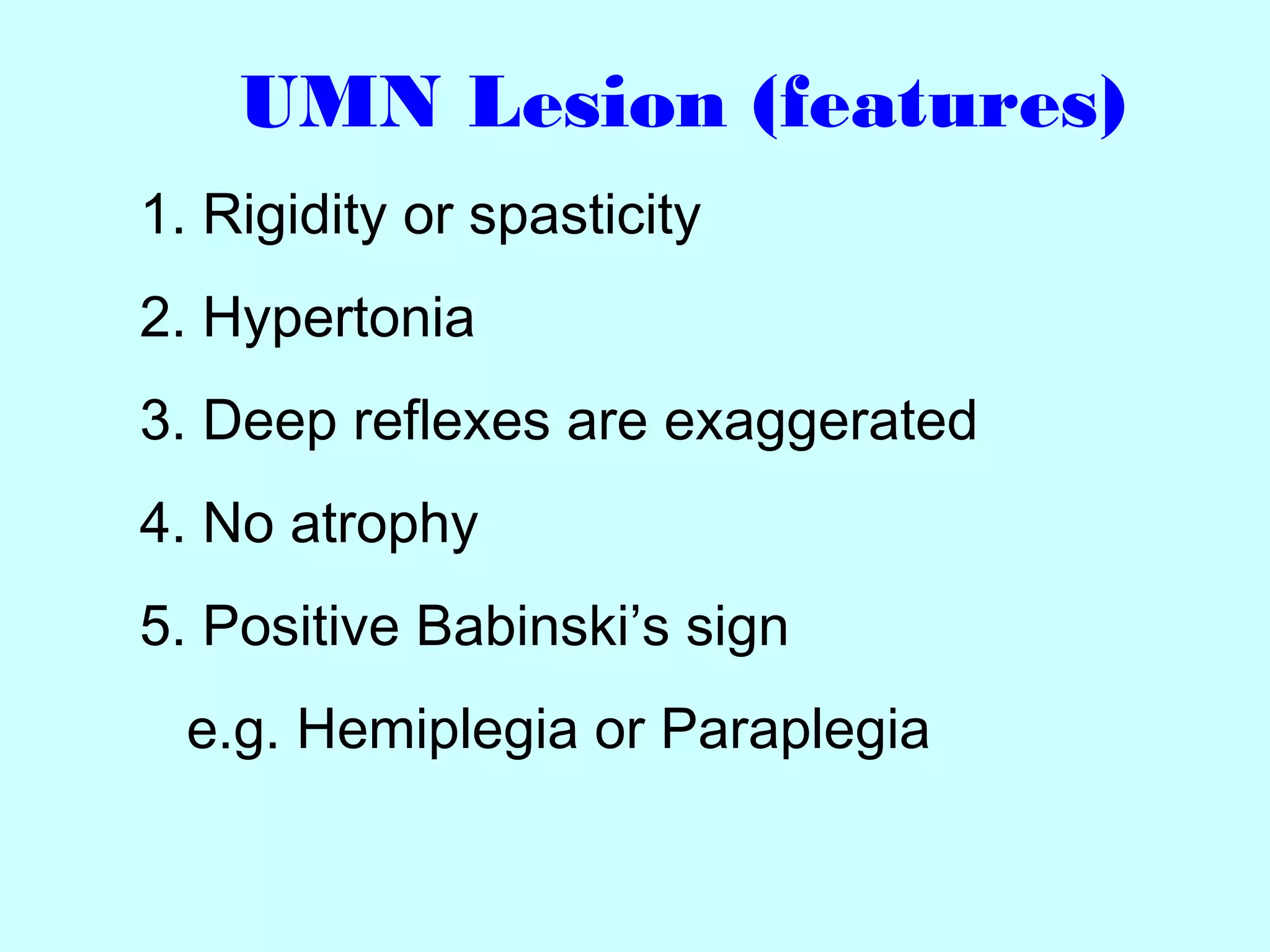
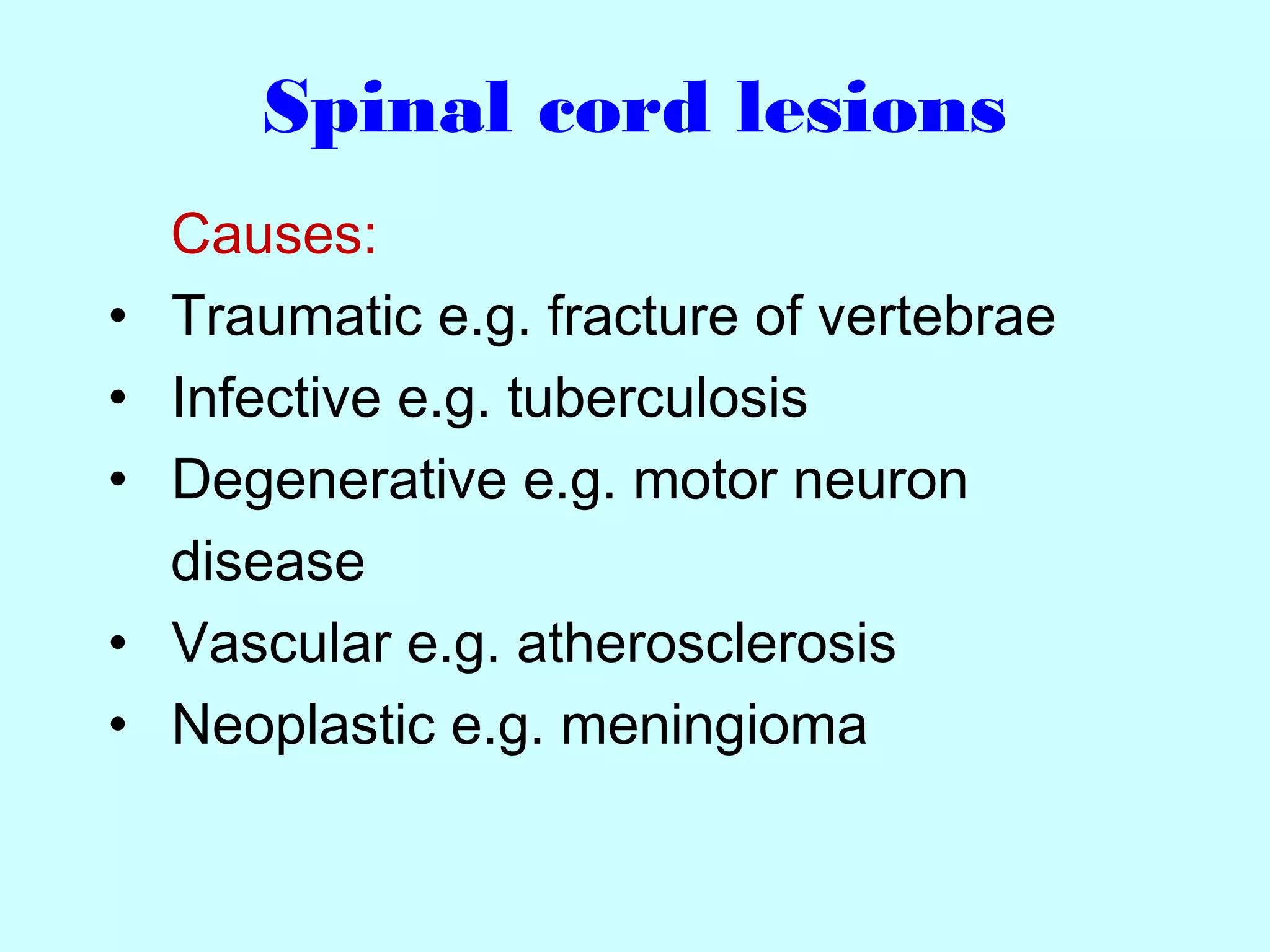
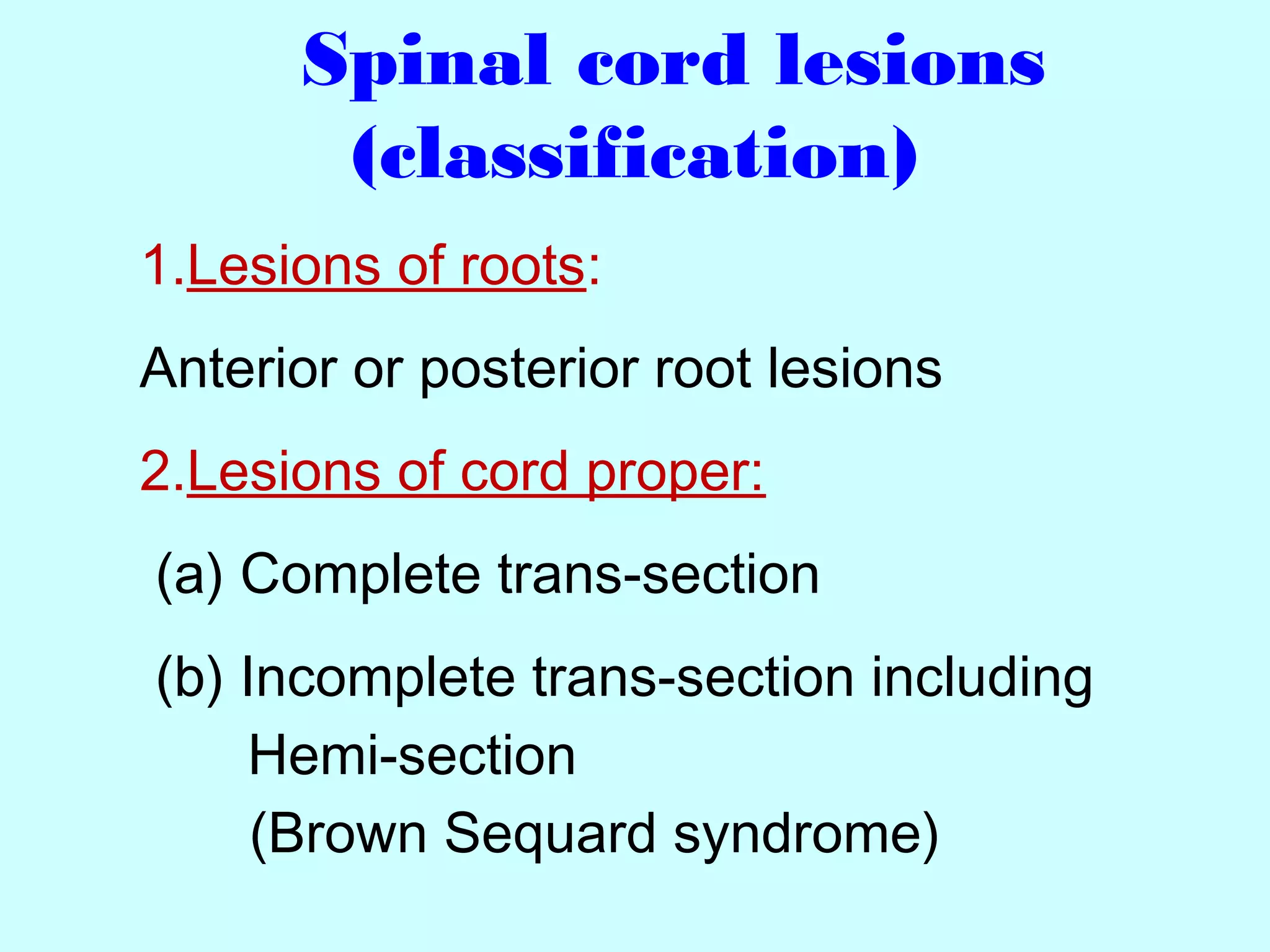
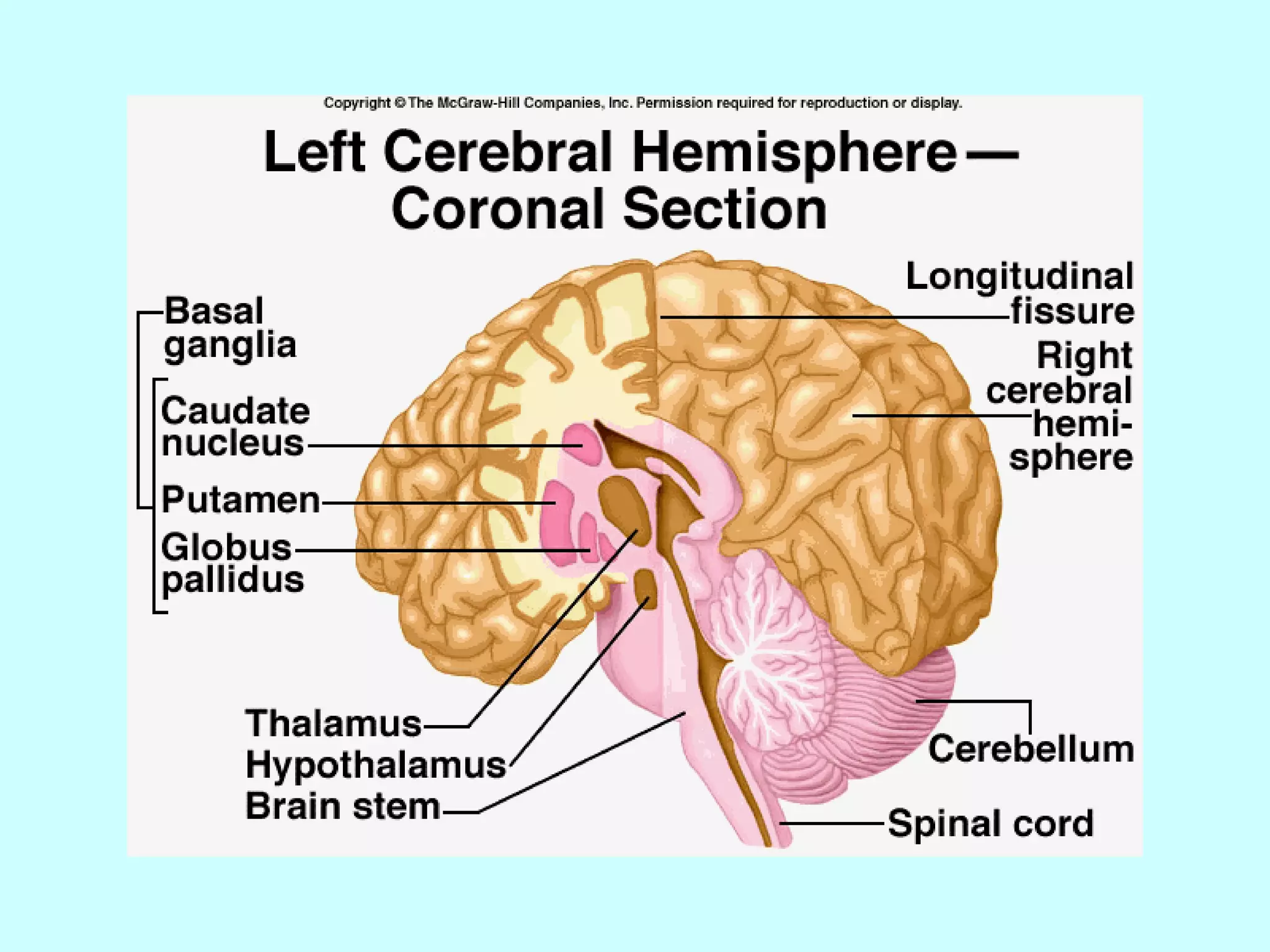
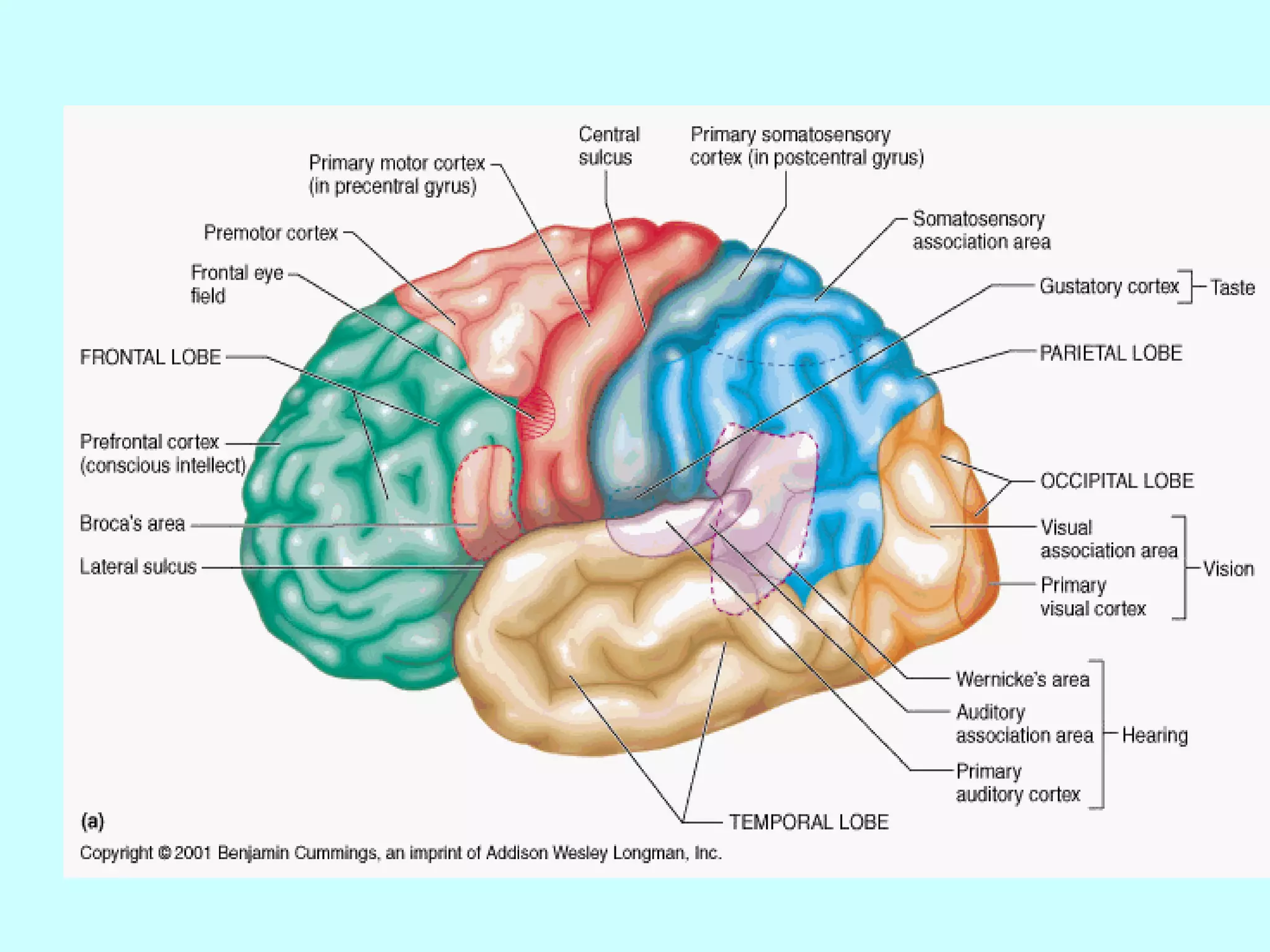
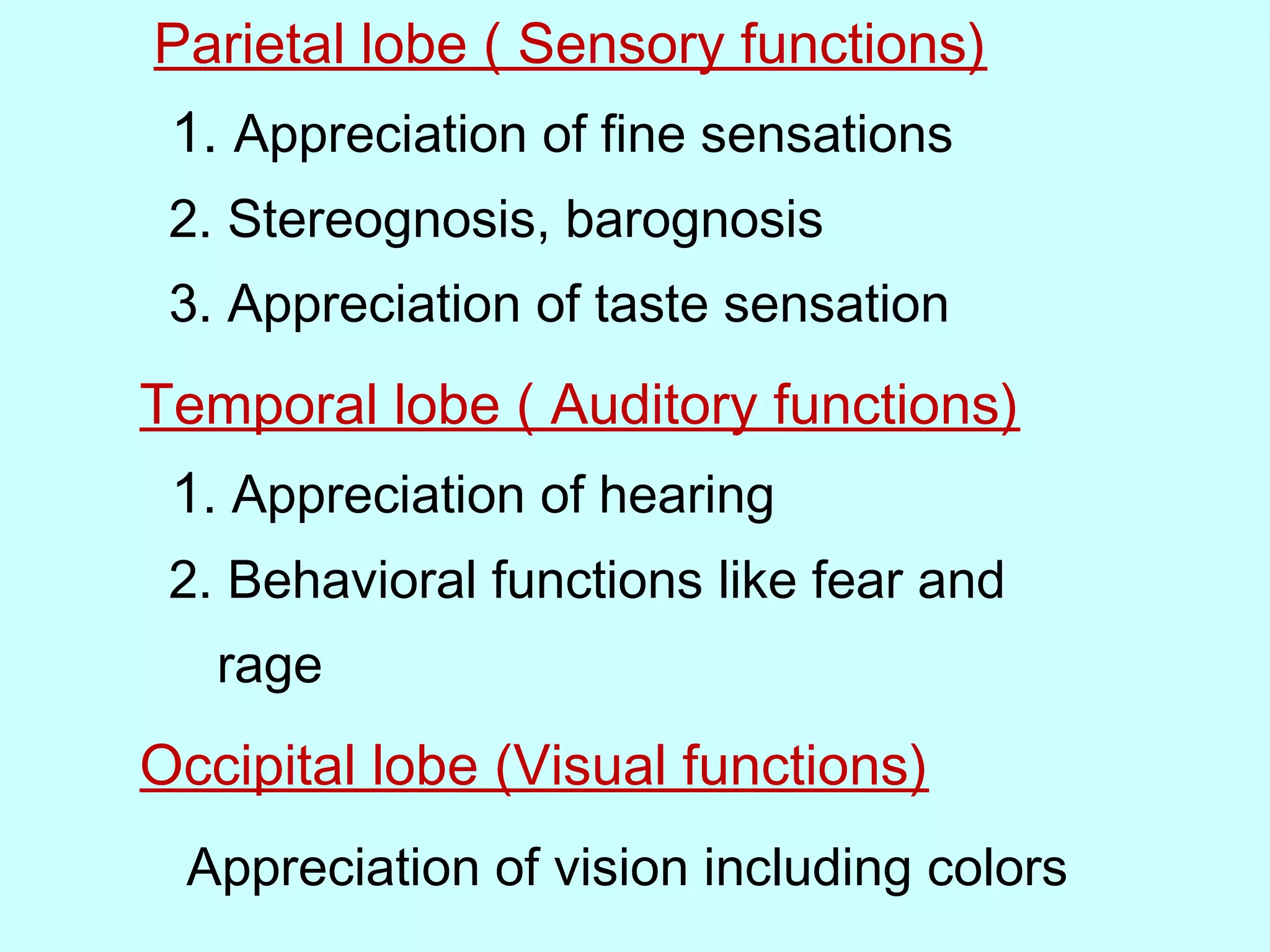
The document summarizes the structure and function of the nervous system. It describes the central nervous system including the brain and spinal cord. It discusses the divisions of the brain and spinal cord. It also describes neurons, synapses, tracts in the spinal cord including ascending sensory and descending motor tracts. The functions of various parts of the brain like hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cerebellum are summarized. Various neurological disorders are also briefly discussed.