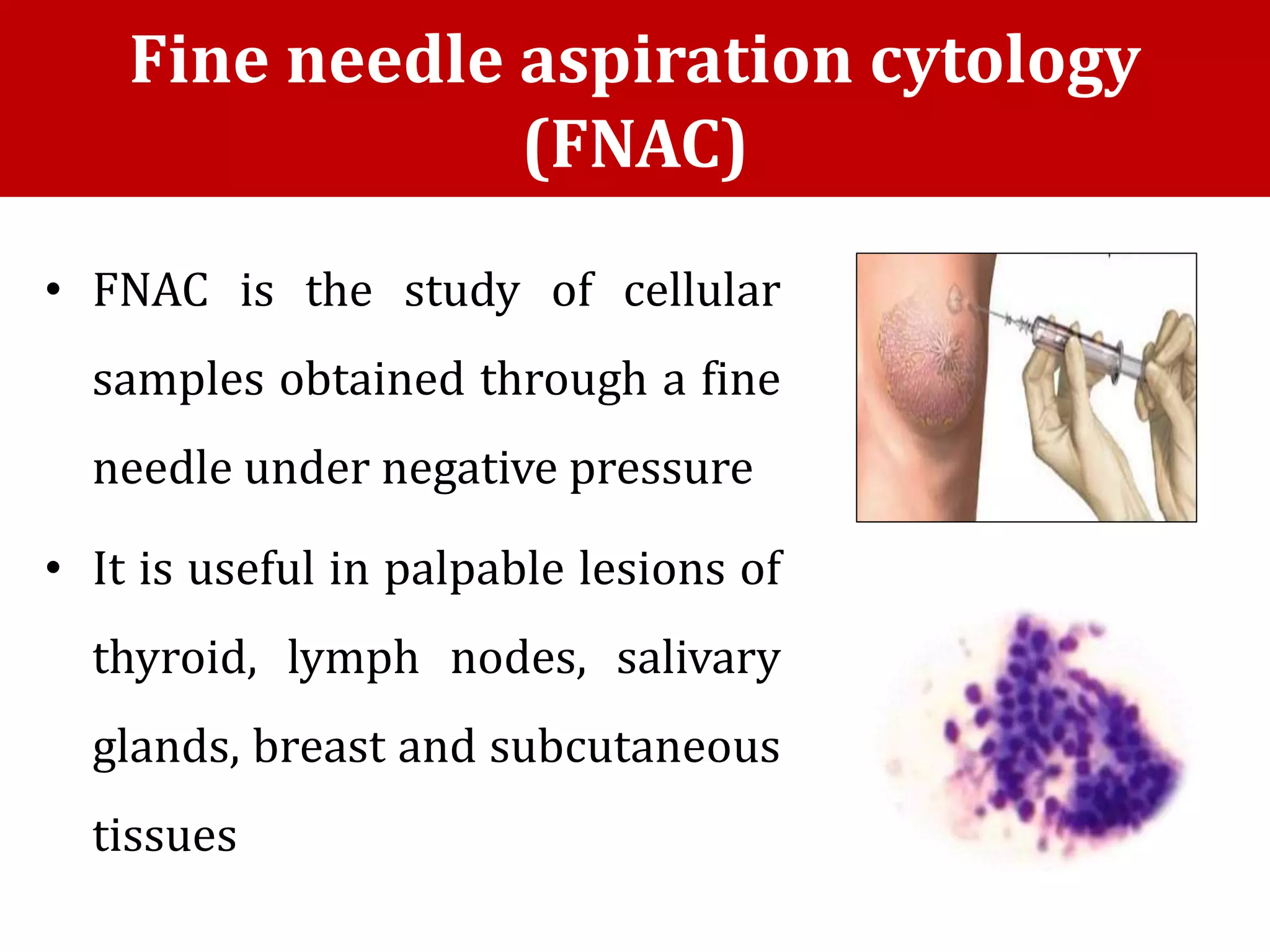
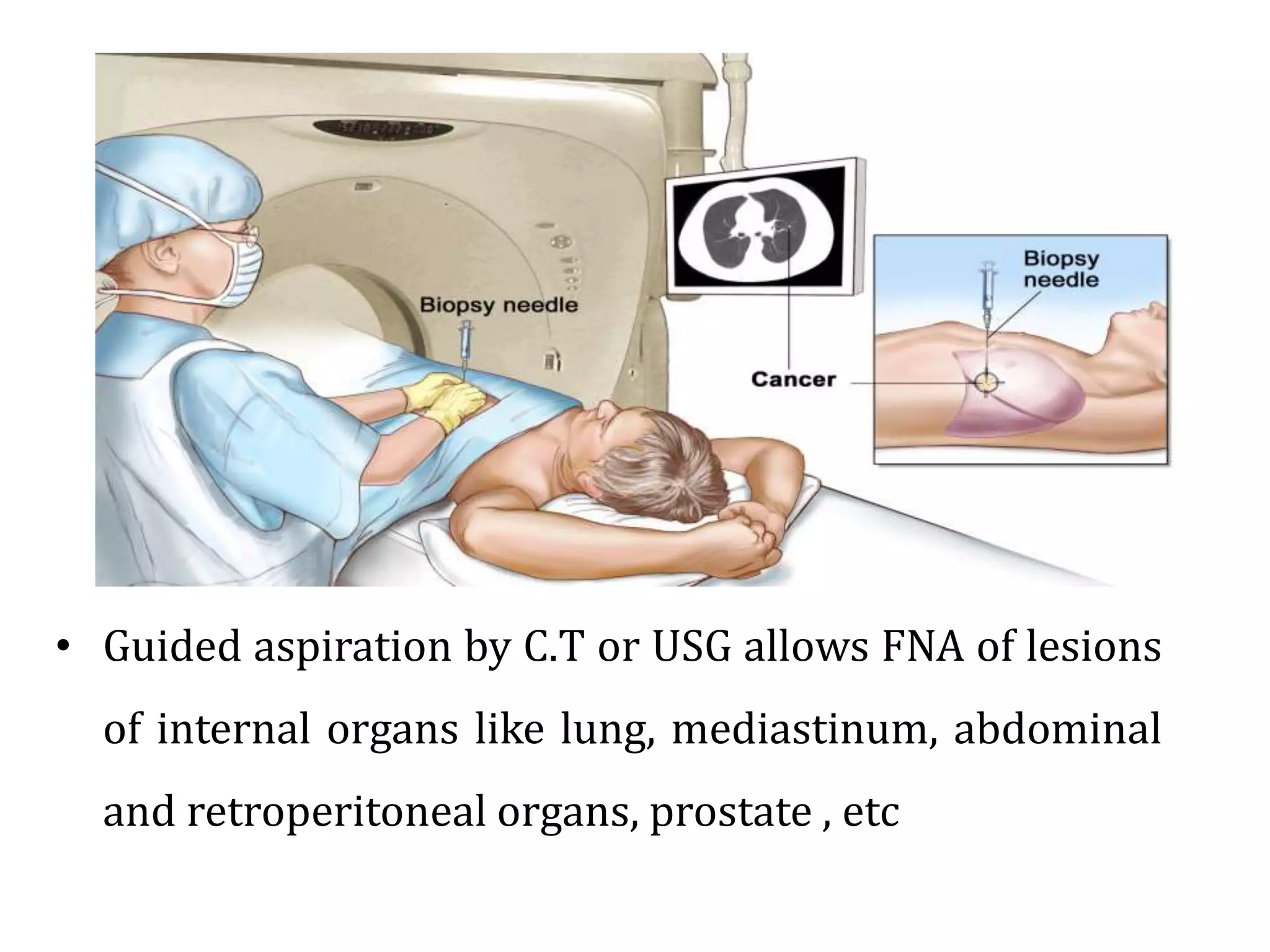
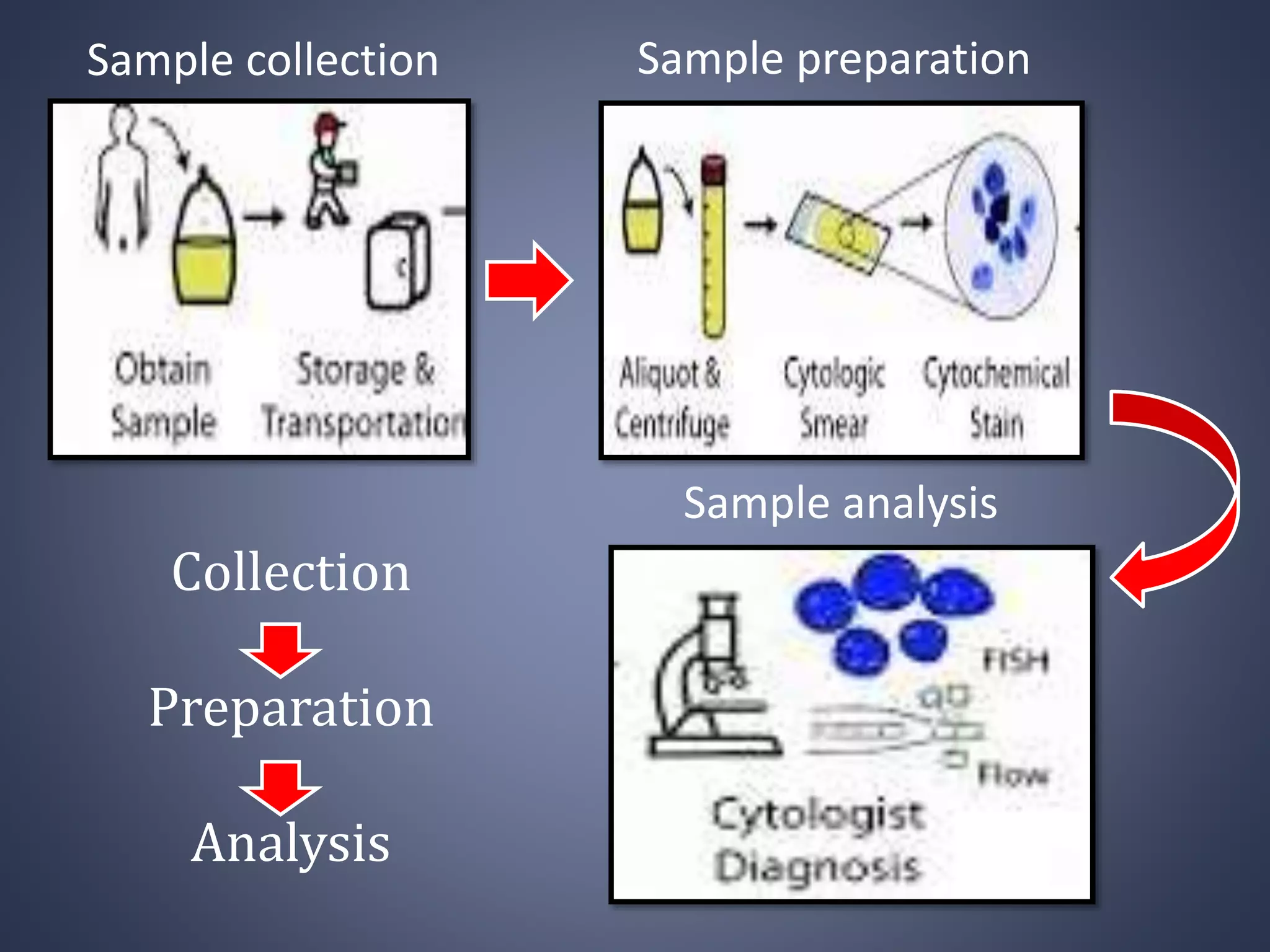
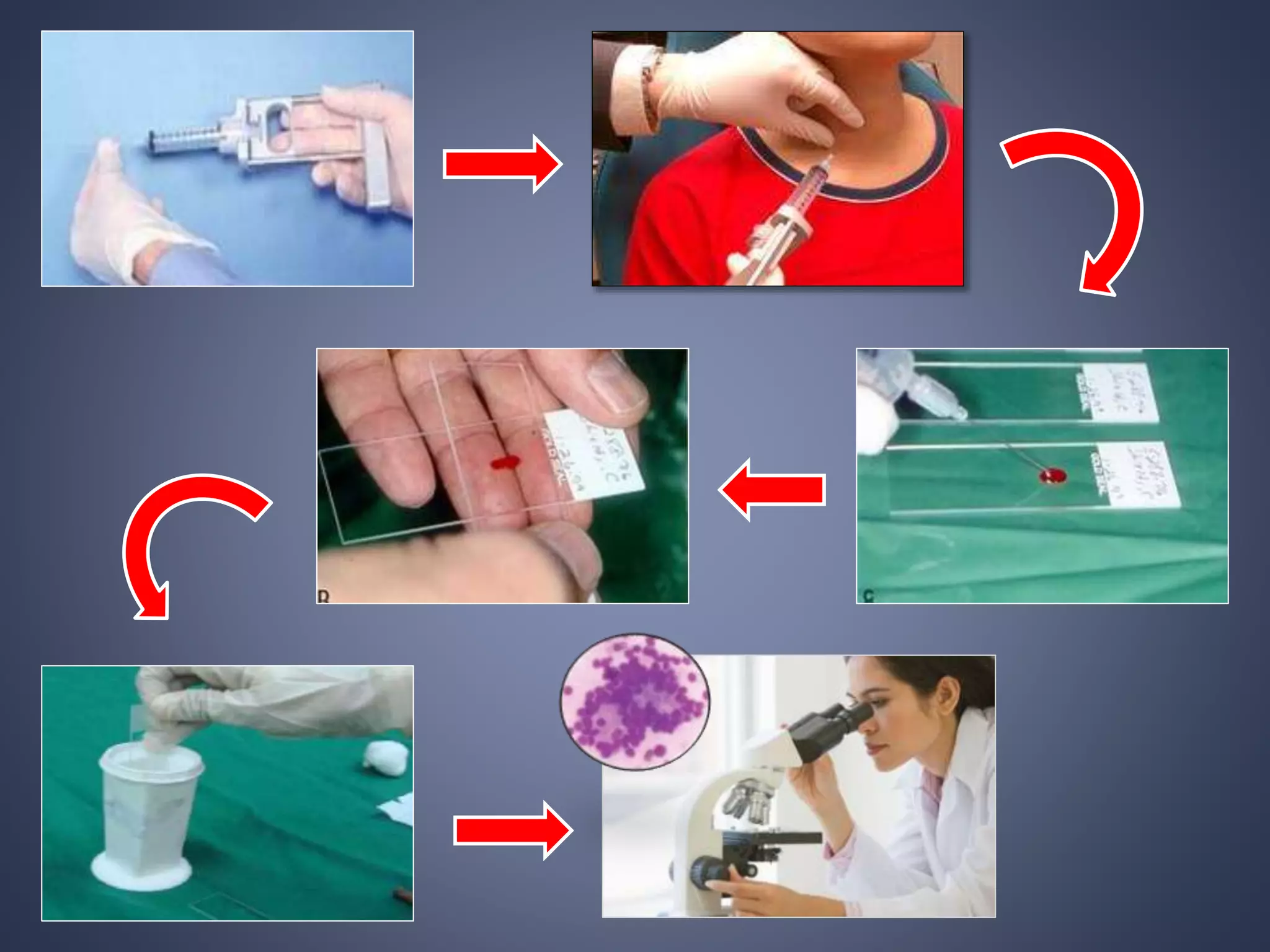
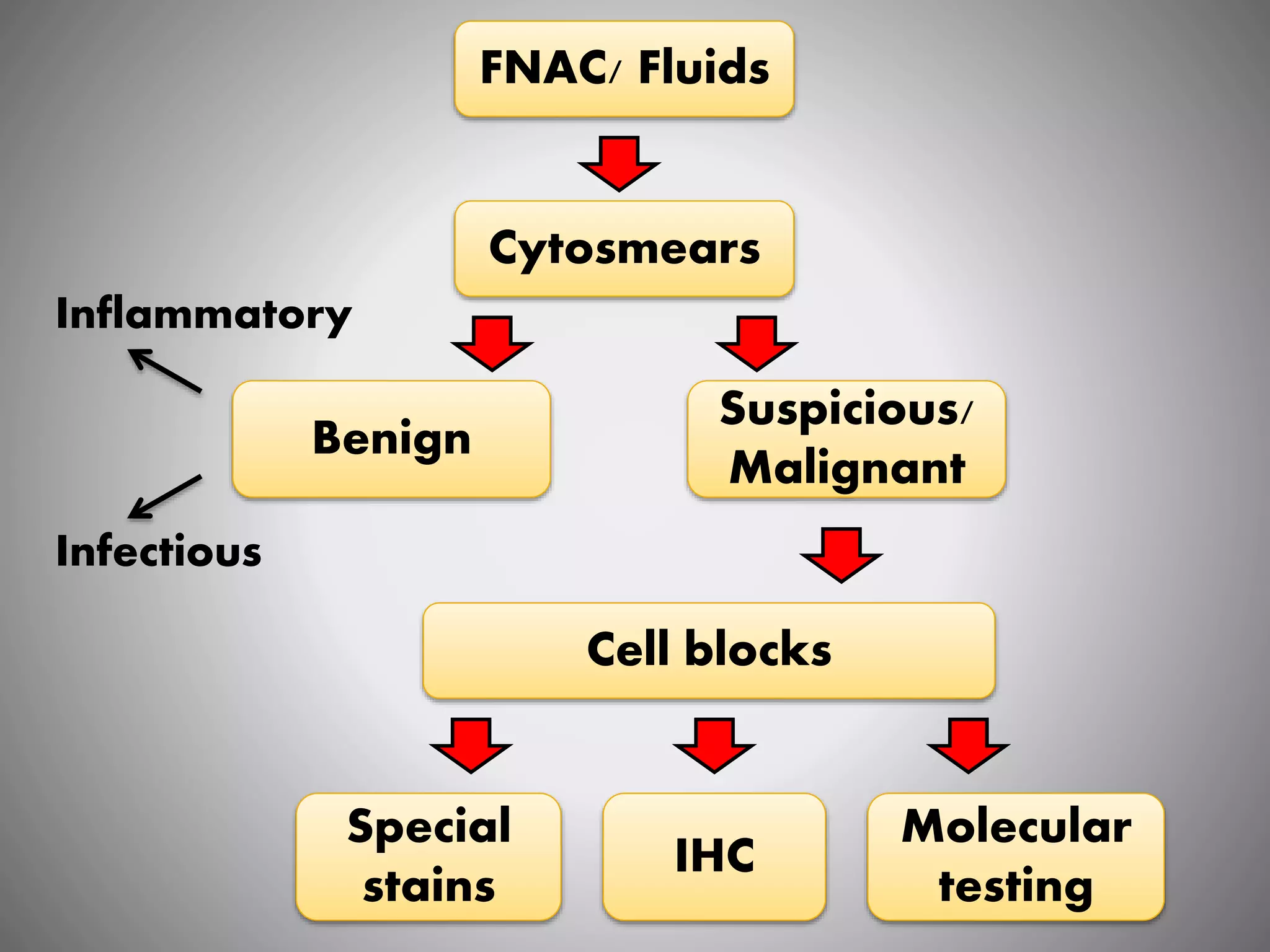
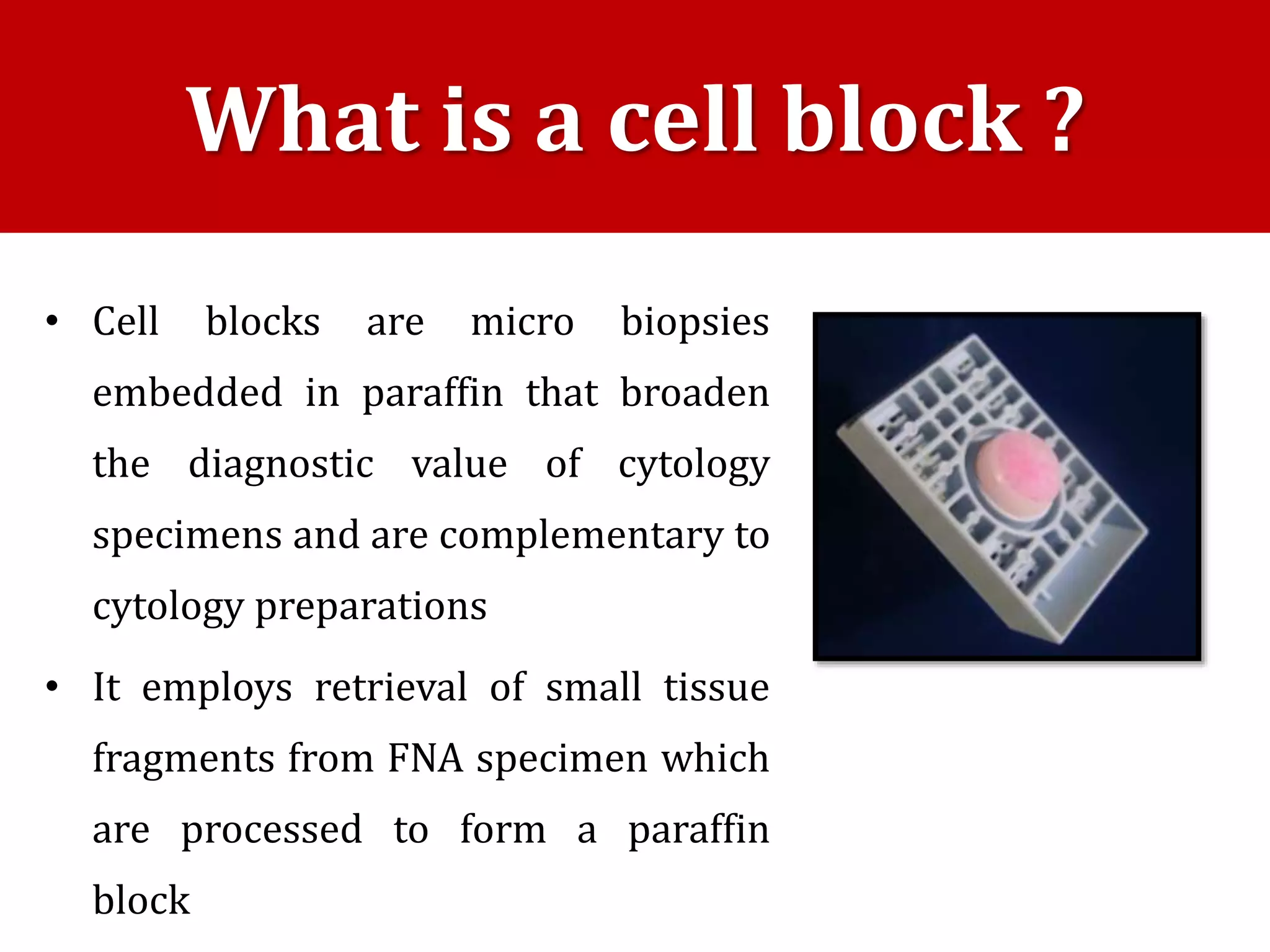
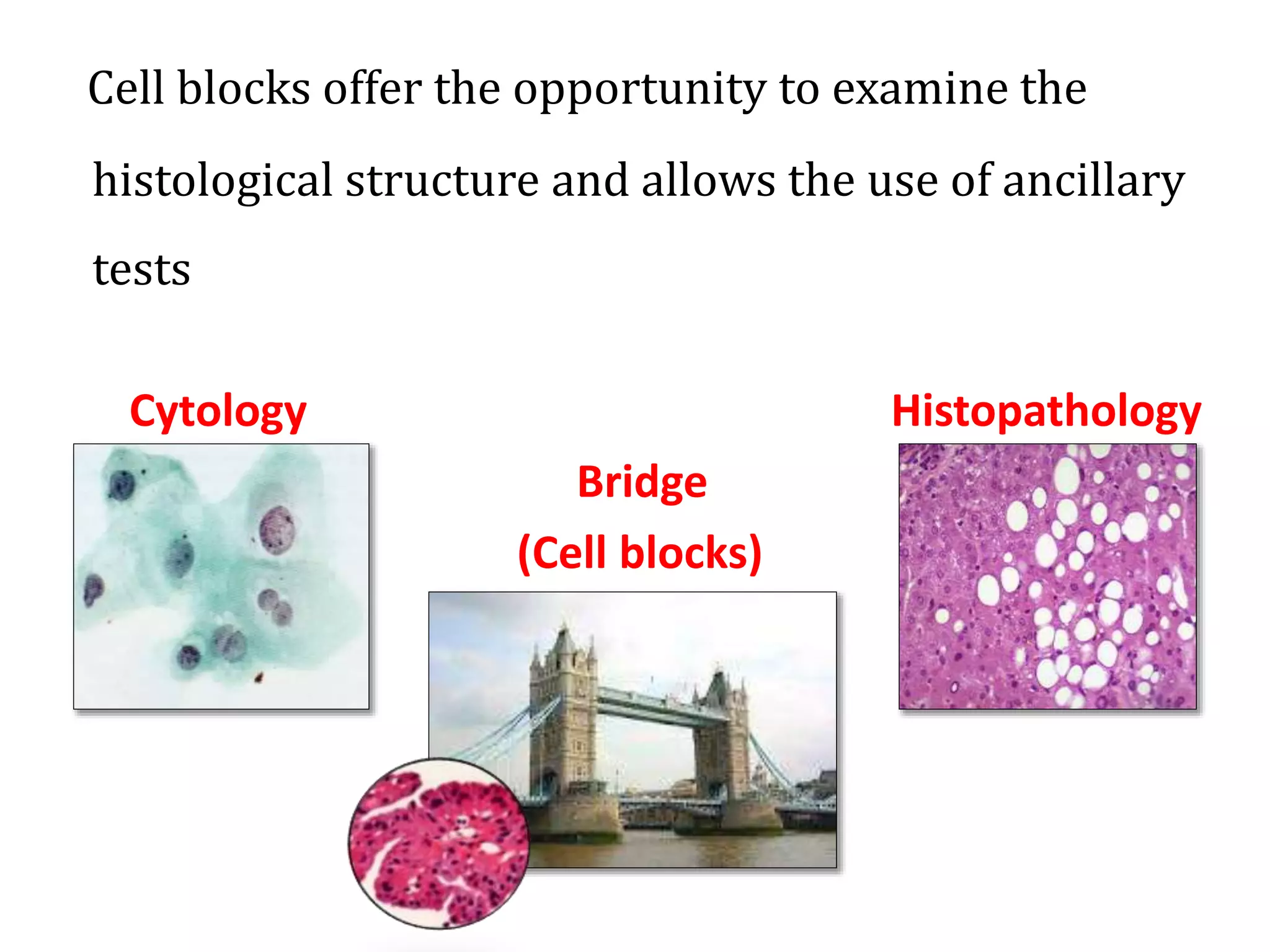
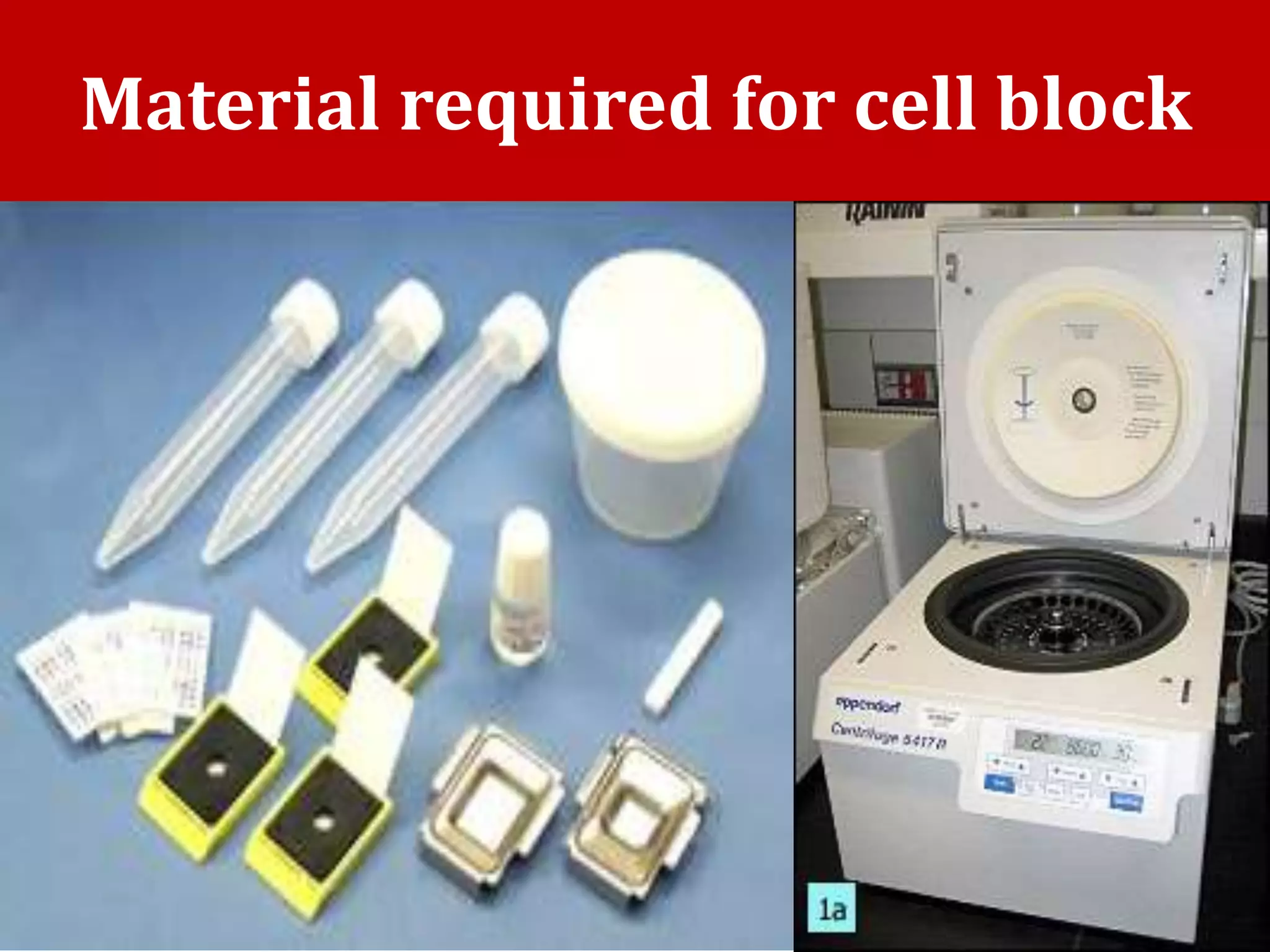
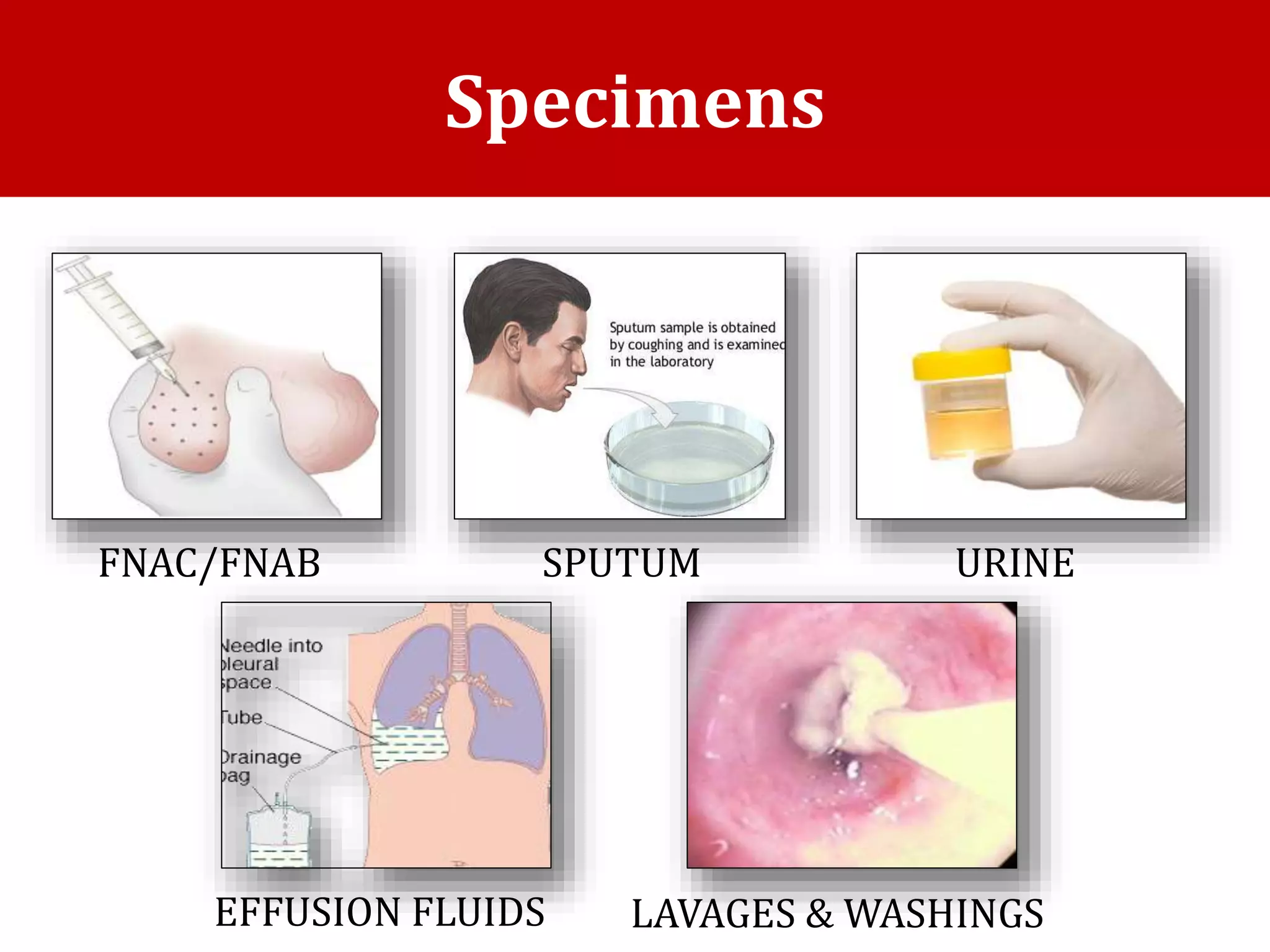
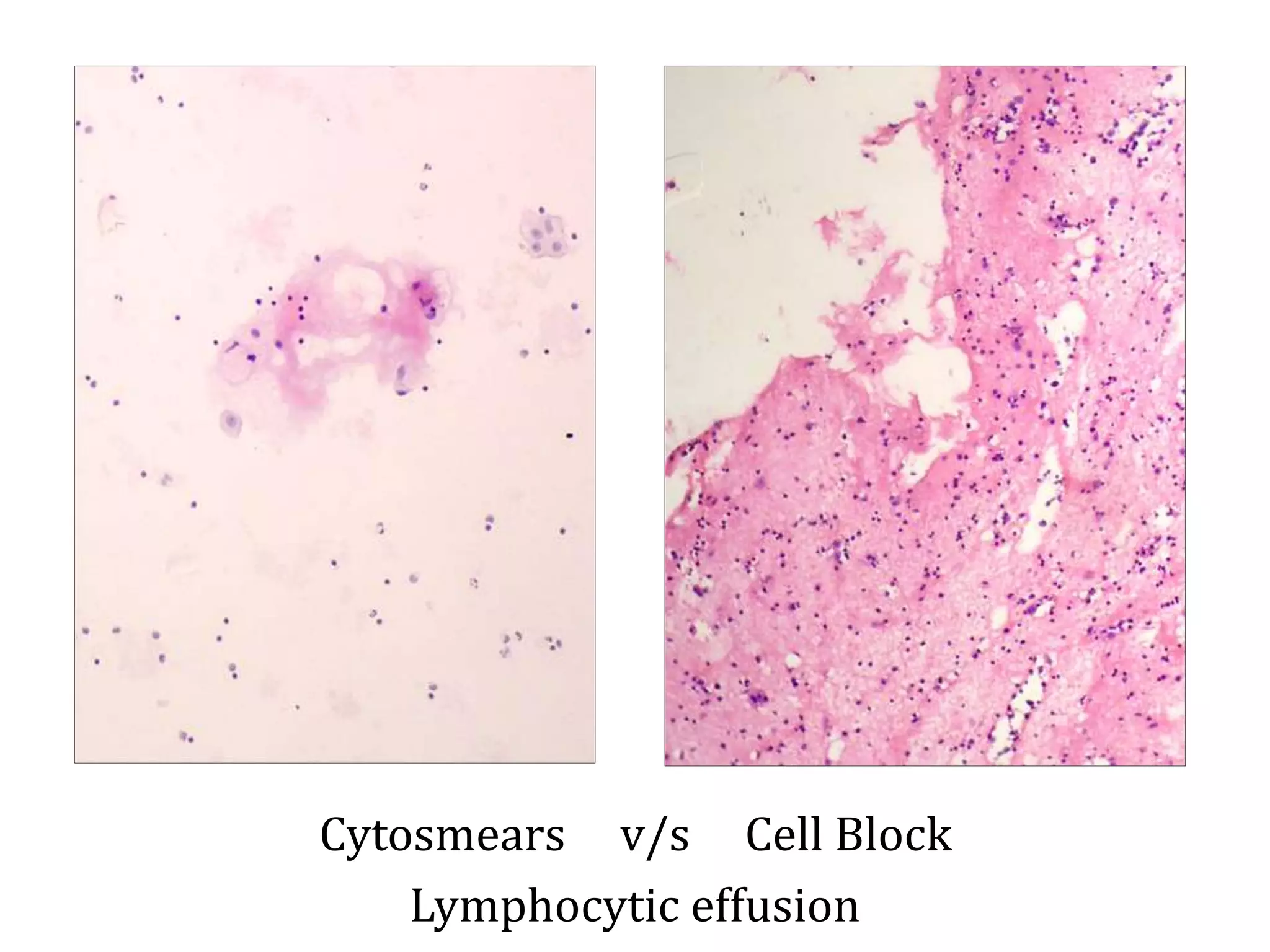
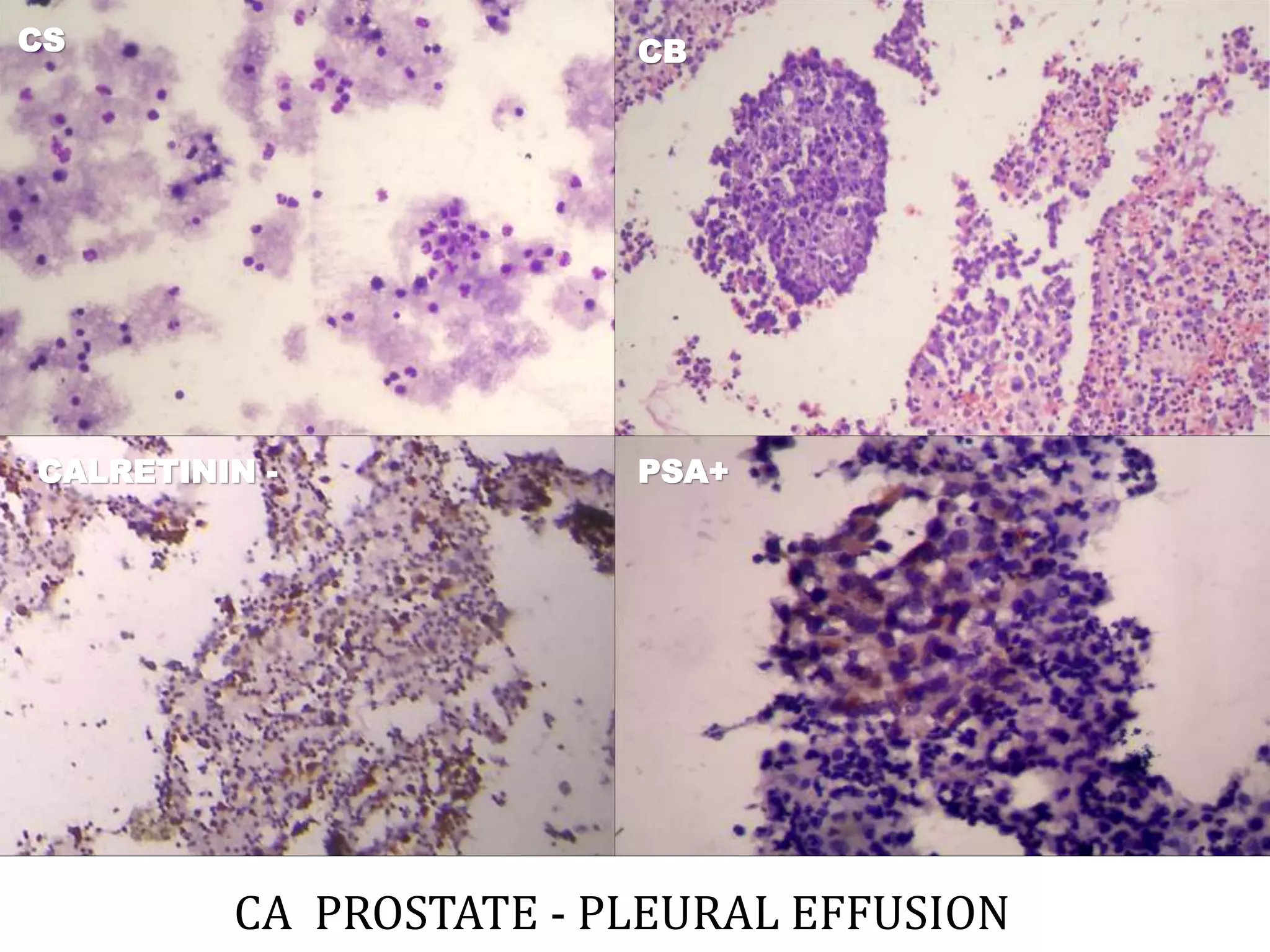
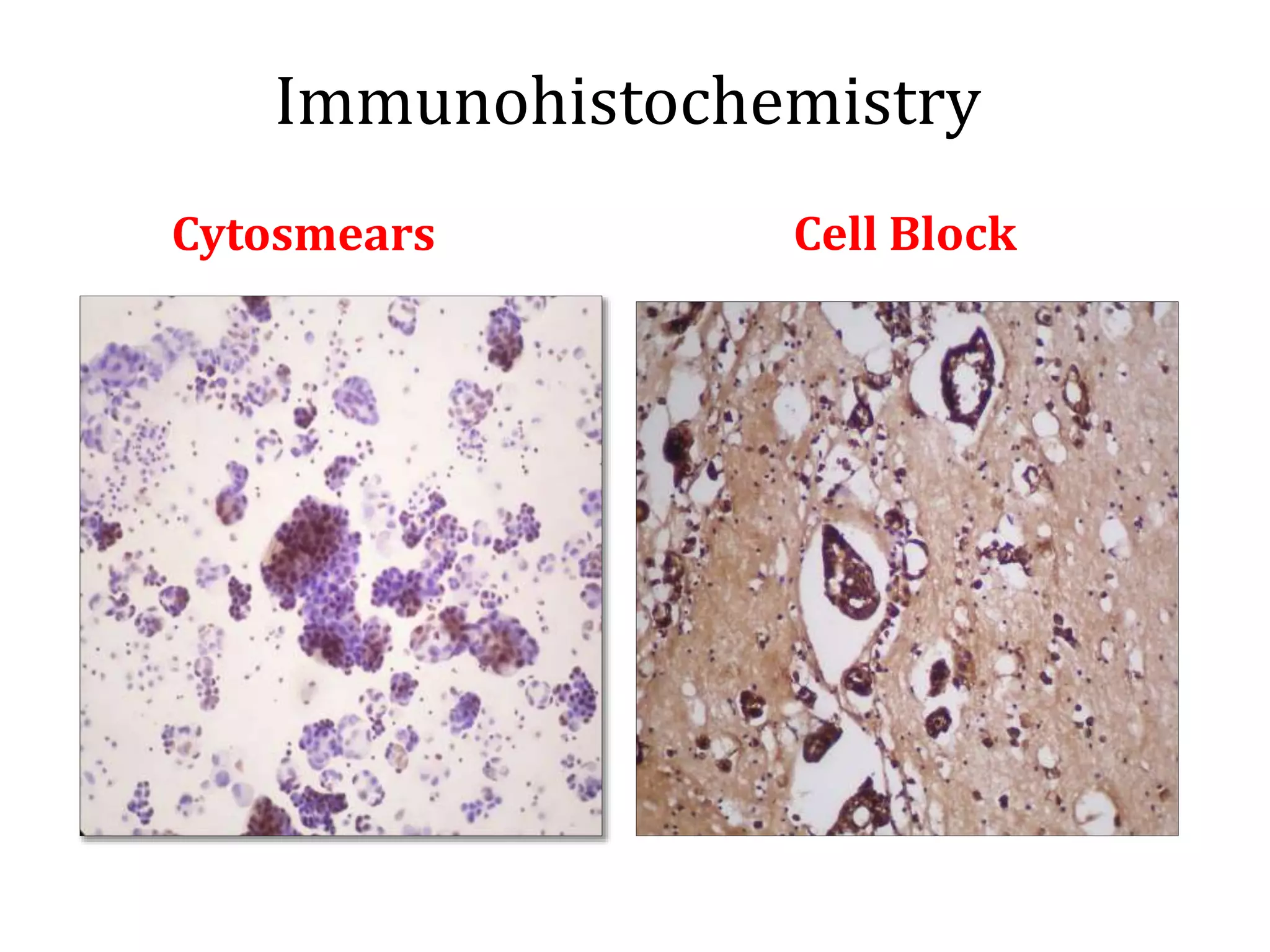
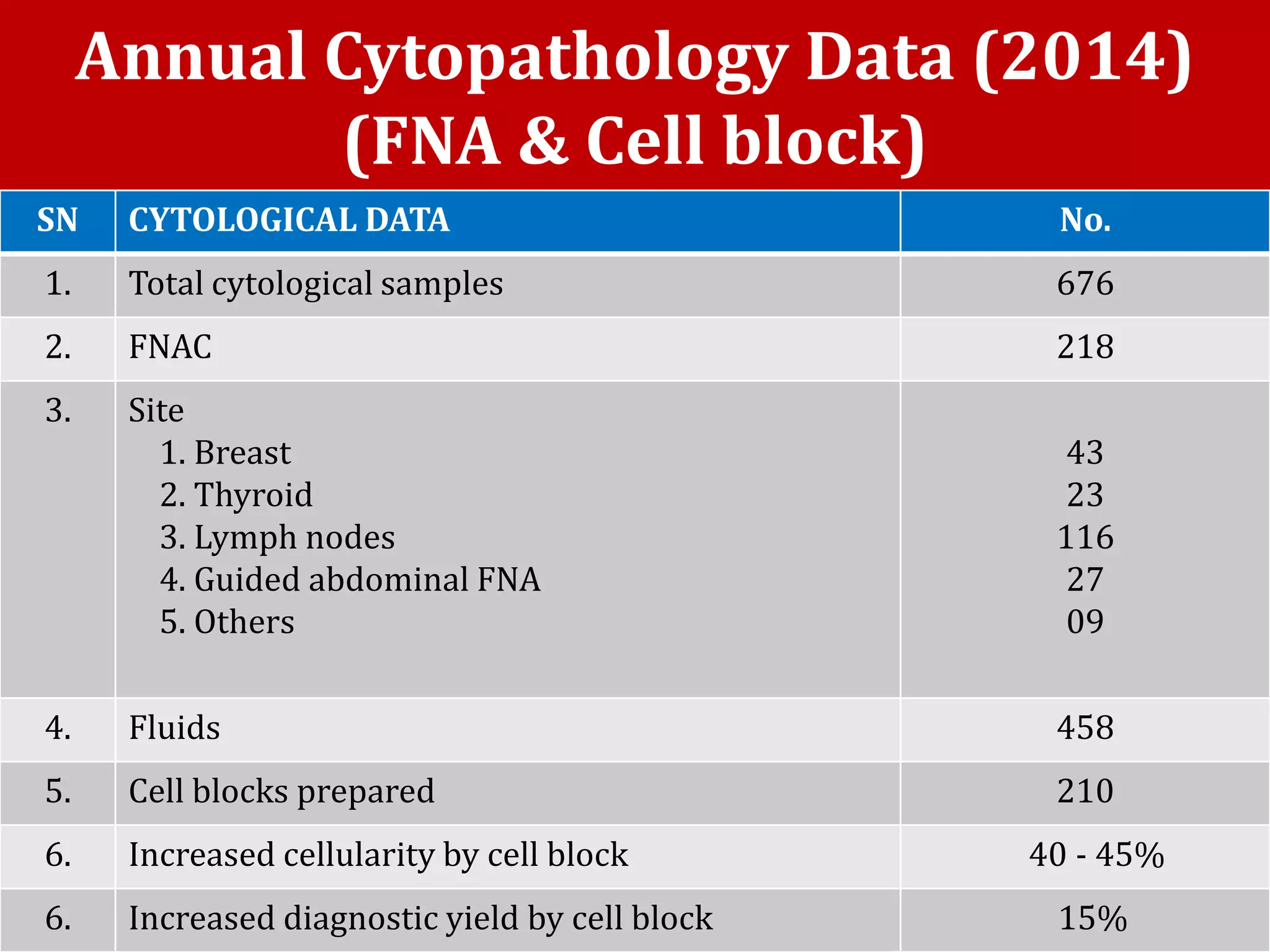
Cell blocks provide tissue fragments from FNA specimens that are processed into paraffin blocks. This allows examination of histological structure and use of ancillary tests like immunohistochemistry. Cell blocks increase diagnostic sensitivity and specificity compared to cytology alone. They require minimal effort and preserve tissue for second opinions without losing the original smears. The document discusses FNAC and cell block techniques, materials used, advantages like increased cellularity and diagnostic yield, and importance of clinical information for optimal diagnosis.