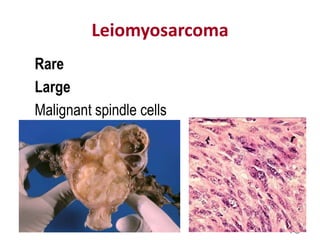
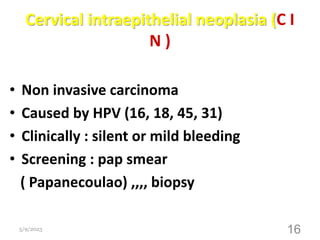
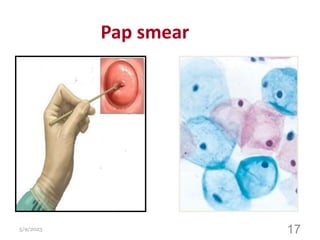
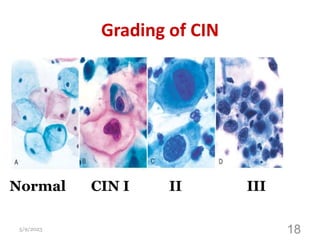
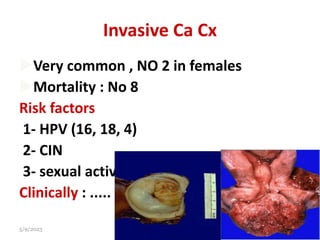
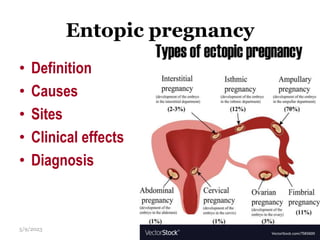
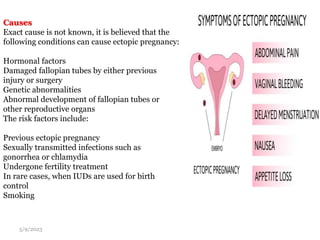
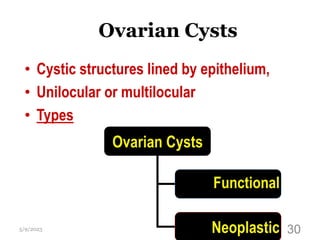
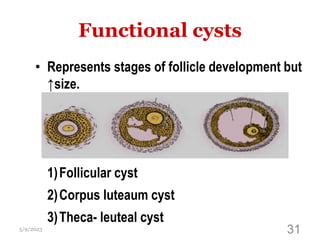
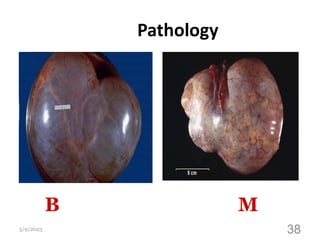
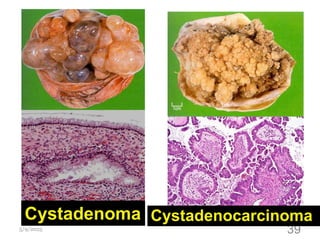
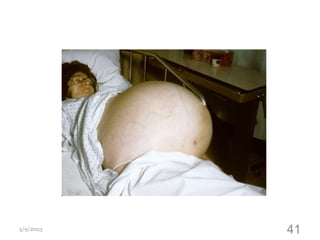
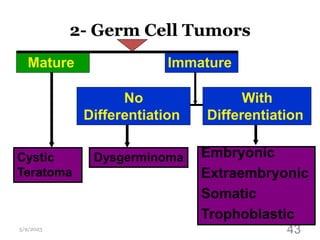
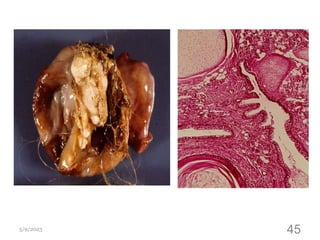
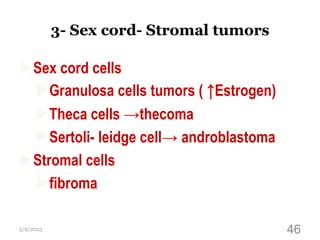
This document provides an overview of the female reproductive system, including common pathologies that can affect each organ. It discusses disorders of the lower genital tract and cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and pregnancy-related conditions. Some key topics covered include infections, endometrial diseases, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, ovarian cysts and tumors, and trophoblastic diseases. The document aims to describe the clinical presentations, risk factors, pathological findings, and management considerations for various female reproductive system disorders.