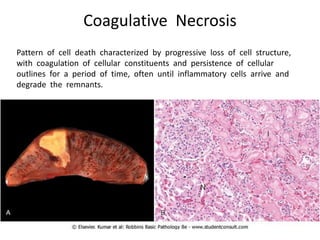
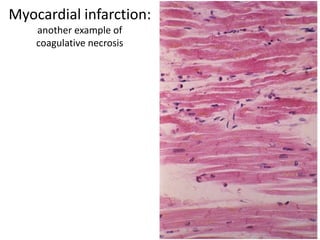
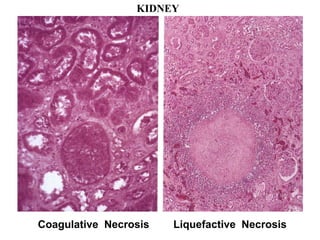
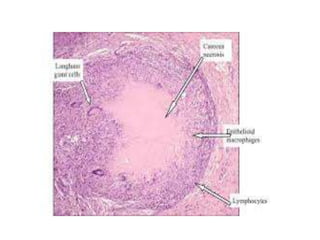
There are several patterns of tissue necrosis:
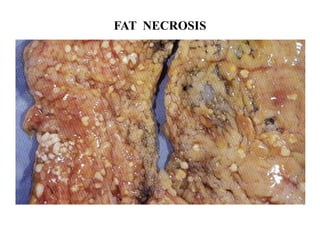
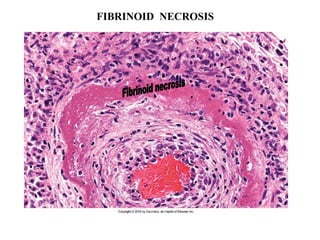
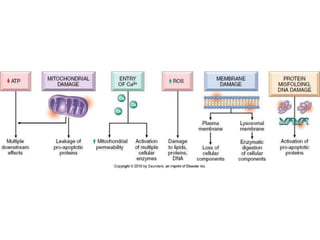
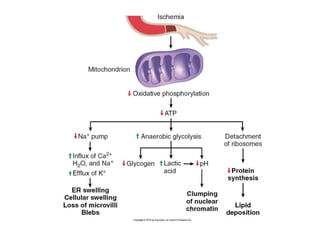
Coagulative necrosis is characterized by loss of cell structure and persistence of outlines. Liquefactive necrosis causes cell dissolution and pus formation. Caseous necrosis occurs in tuberculosis granulomas, forming debris resembling cottage cheese. Fat necrosis occurs when lipases cleave triglycerides, forming chalky calcium deposits. Fibrinoid necrosis is seen in vasculitis, with necrosis of artery wall muscle and fibrin deposition. Cell injury depends on the nature, duration and severity of the insult.