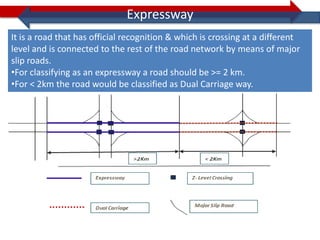
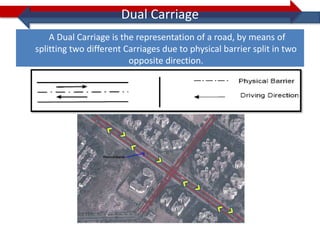
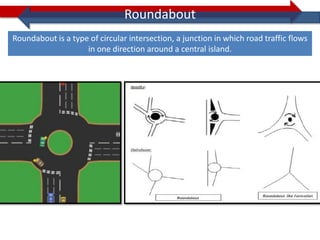
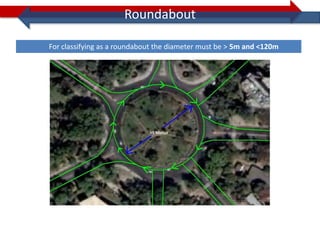
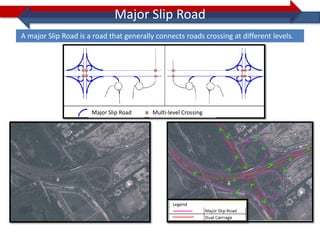
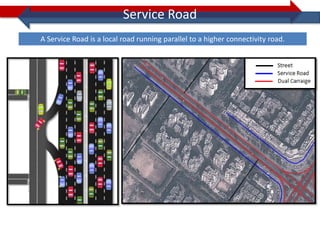
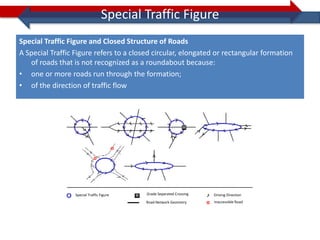
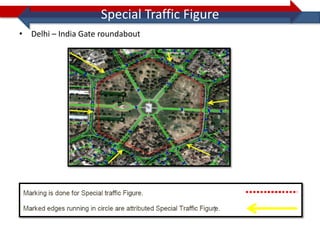
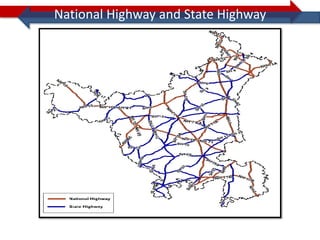
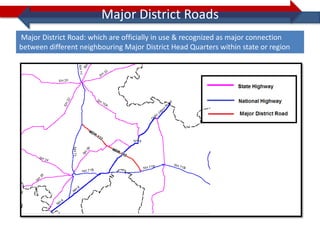
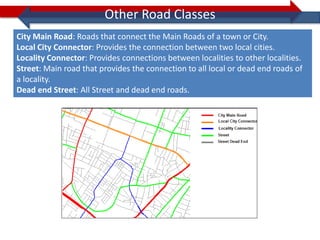
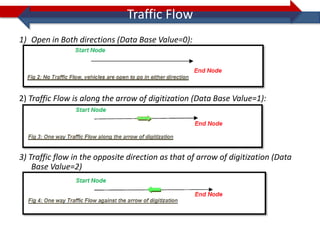
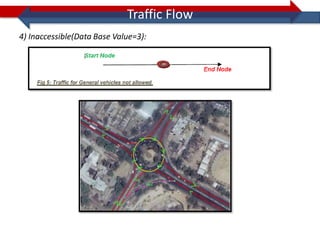
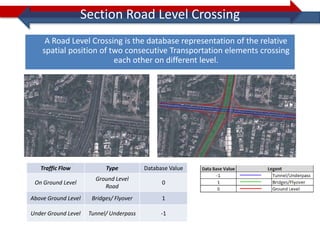
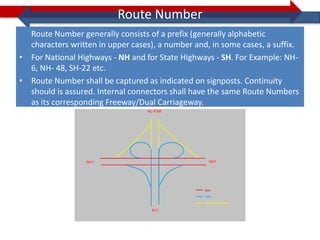
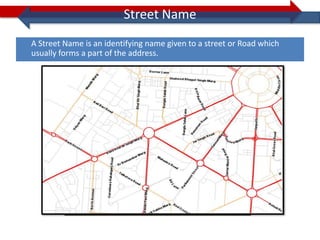
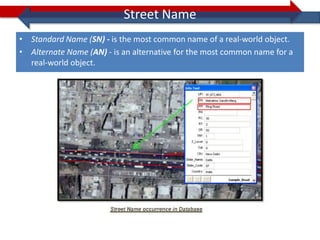
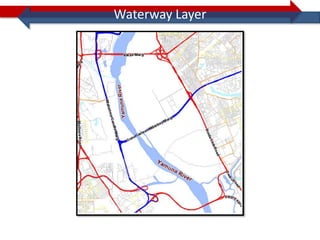
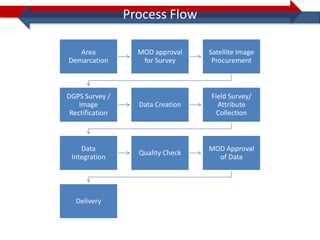
This document provides information on navigation maps including road network coverage in India, road types, and other transportation features. It details that the maps cover 658 cities in India with road network data on over 22 million km of roads, including 69,825 km of national highways. The maps also include railway coverage of 65,762 km of track. Road types classified include expressways, dual carriageways, roundabouts, and slip roads. Additional information covered includes road class, traffic flow, route numbers, and other transportation layers like railways and waterways.