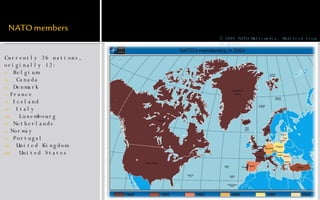
NATO is a political and military alliance between 26 North American and European countries formed in 1949. It was originally formed as a response to the threat of Soviet aggression and aimed to establish collective security. NATO is headquartered in Brussels and led by the Secretary General and Chairman of the Military Committee. Key functions include collective defense if a member country is attacked and stabilization of security conditions through economic and political cooperation. NATO has been involved in military operations in Bosnia, Kosovo, Afghanistan and elsewhere.


![Aimed at “promot[ing] stability and well-being in the North Atlantic area” Sought to unite efforts for collective defence Sought to use peaceful means where possible Sought to stabilize various international conditions through economic policies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nato-1217368548124474-9/85/NATO-5-320.jpg)
![Aimed at “develop[ing] their individual and collective capacity to resist armed attack” Established a military alliance between militarily mighty nations including the US, the UK, France Authorized use of force to aid other member nations, or in retaliation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nato-1217368548124474-9/85/NATO-6-320.jpg)







