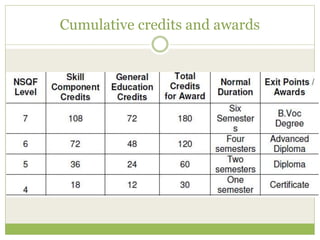
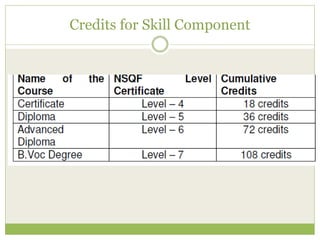
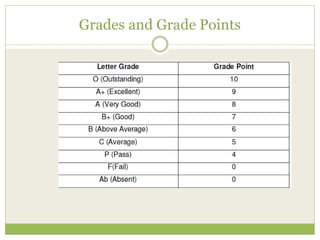
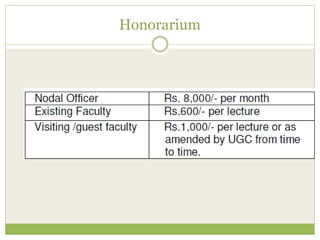
The document outlines the National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF) in India, addressing the demand-supply gap for skilled workforce and emphasizing the importance of skill development for better employability. It discusses various frameworks and schemes, such as the National Vocational Educational Qualification Framework (NVEQF) and the establishment of Sector Skill Councils (SSCs) to develop qualification packs and national occupational standards. The NSQF aims to facilitate mobility between vocational and general education while offering flexible entry and exit points in education, with a certification system recognizing skills and knowledge through a structured credit framework.