1. Vocational education in India faces challenges in meeting the large demand for skilled labor. With a young population and over 70% of the workforce unskilled, only 2-10% receive formal vocational training.
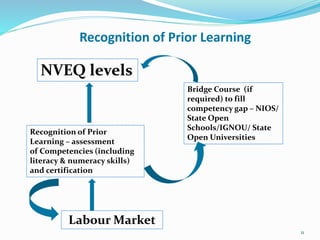
2. A National Vocational Education Qualifications Framework is being developed to standardize qualifications across institutions and improve recognition, mobility and credibility of vocational education. Industry involvement is key to making training demand-driven and competency-based.
3. Reforms aim to strengthen existing vocational schools, introduce new courses aligned with industry needs through public-private partnerships, and improve teacher training. National institutions also provide vocational education opportunities through open schools and distance learning programs.