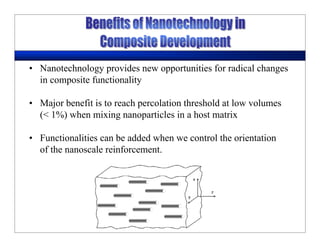
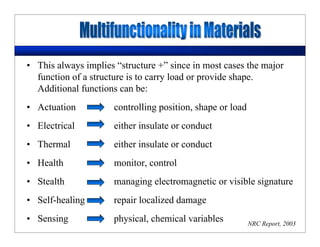
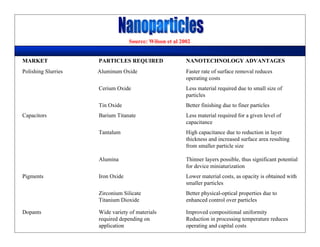
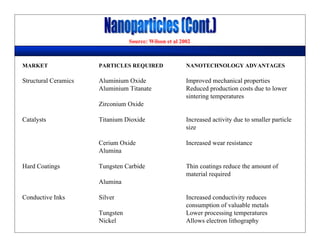
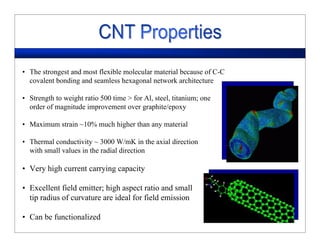
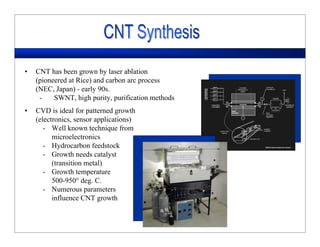
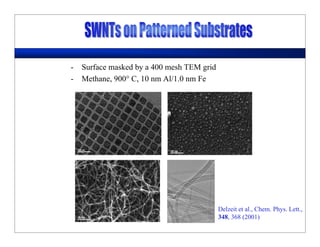
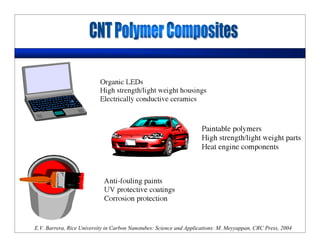
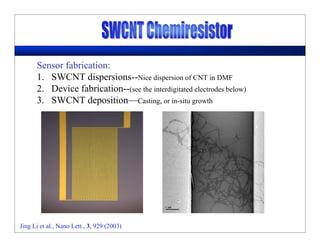
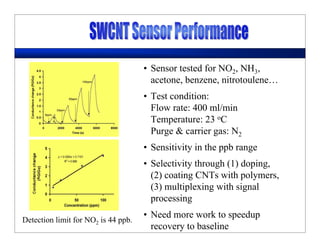
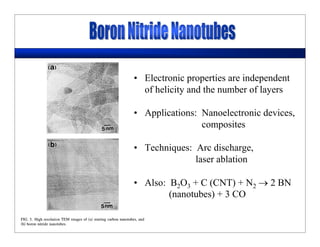
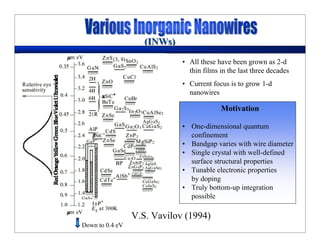
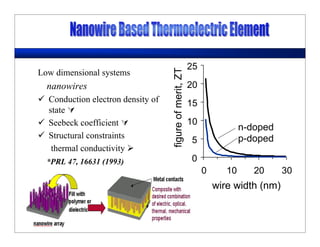
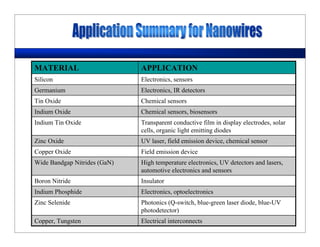
This lecture discusses nanotechnology applications in aerospace, focusing on carbon nanotubes. Carbon nanotubes have excellent mechanical and electrical properties and are being investigated for use in high-strength, lightweight composites for aircraft. The lecture will cover the properties of carbon nanotubes and their current and potential uses in aerospace composites, sensors, coatings and other applications. It will also discuss challenges in dispersing carbon nanotubes uniformly in composite matrices.