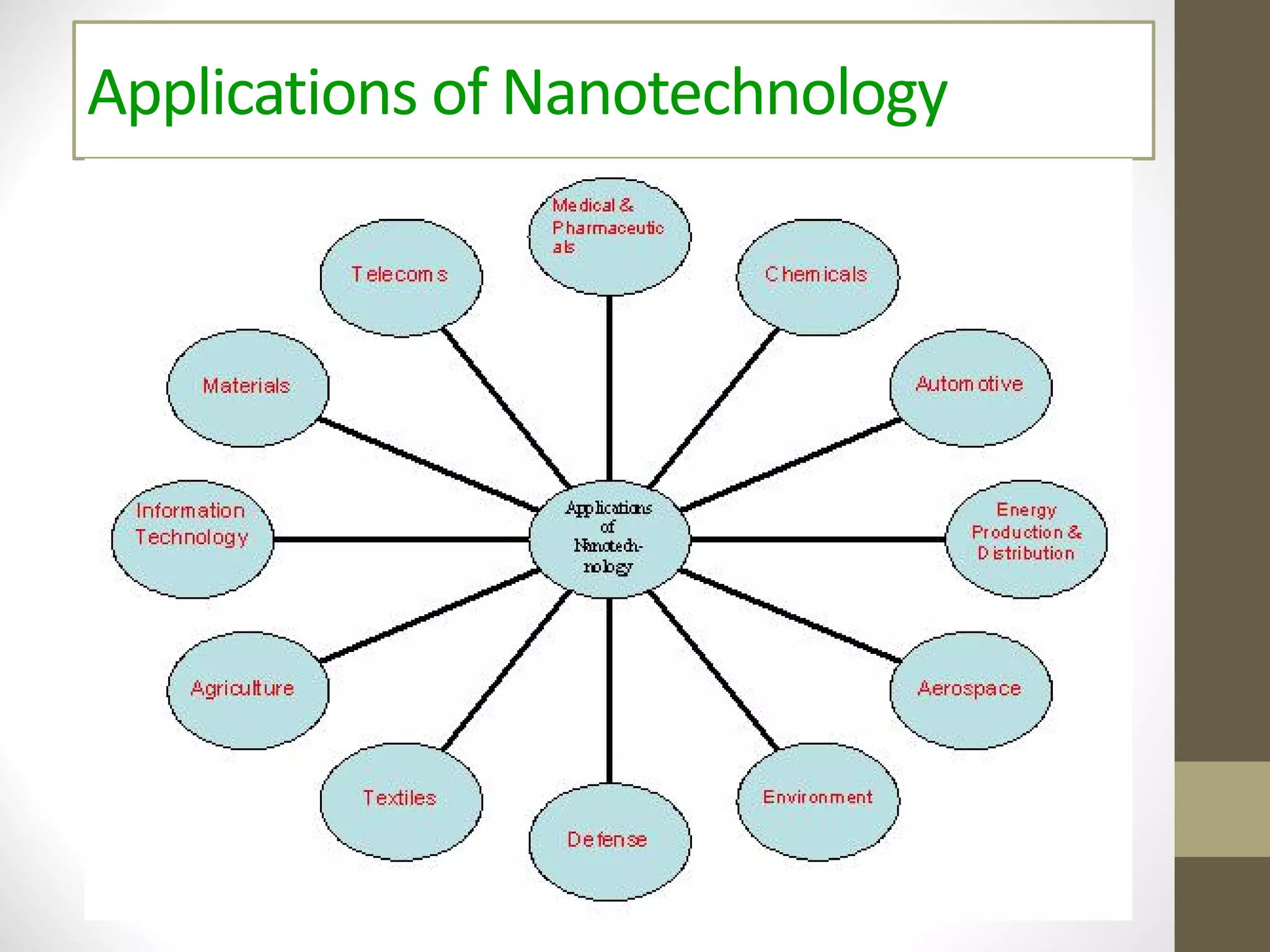
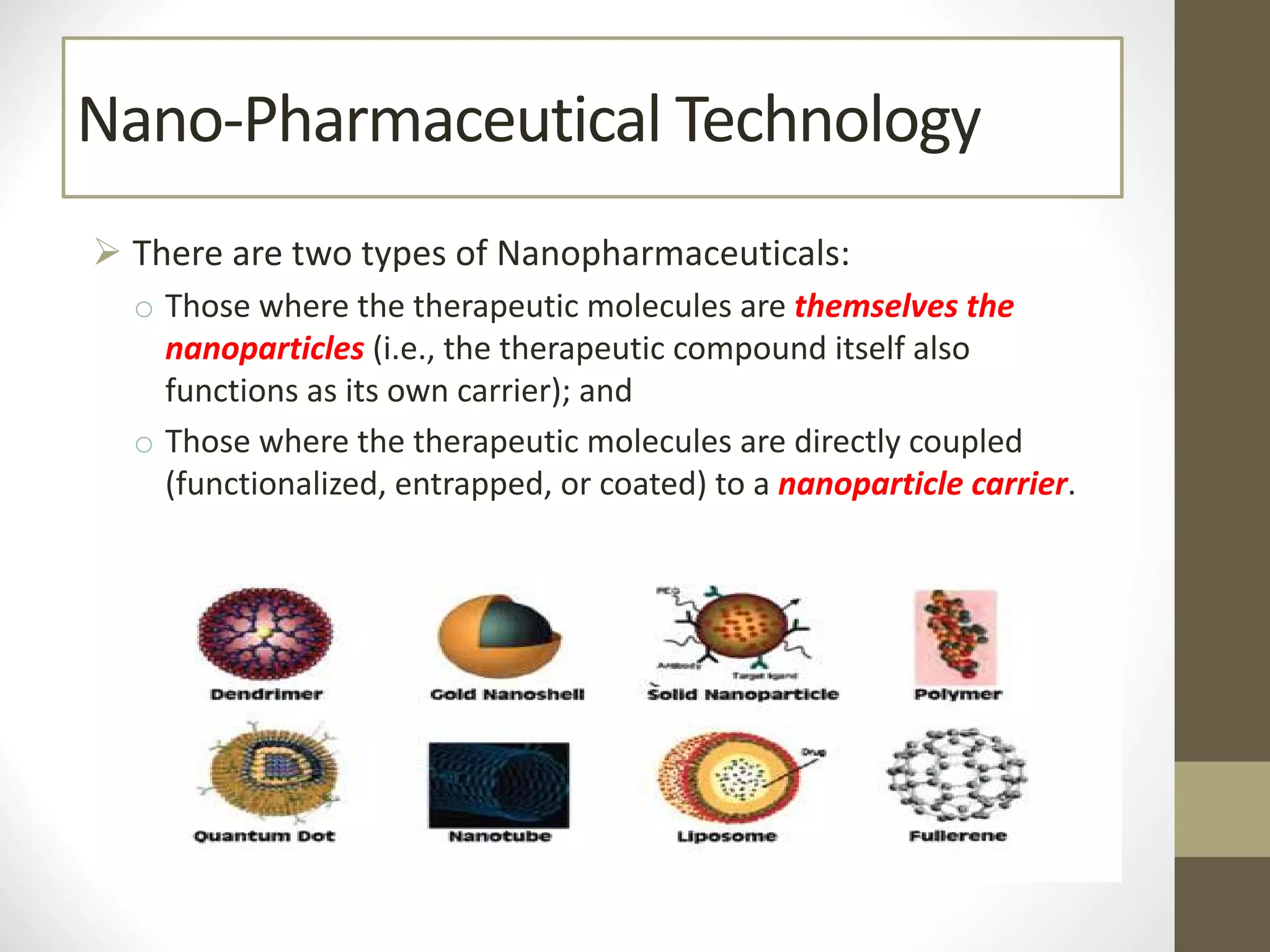
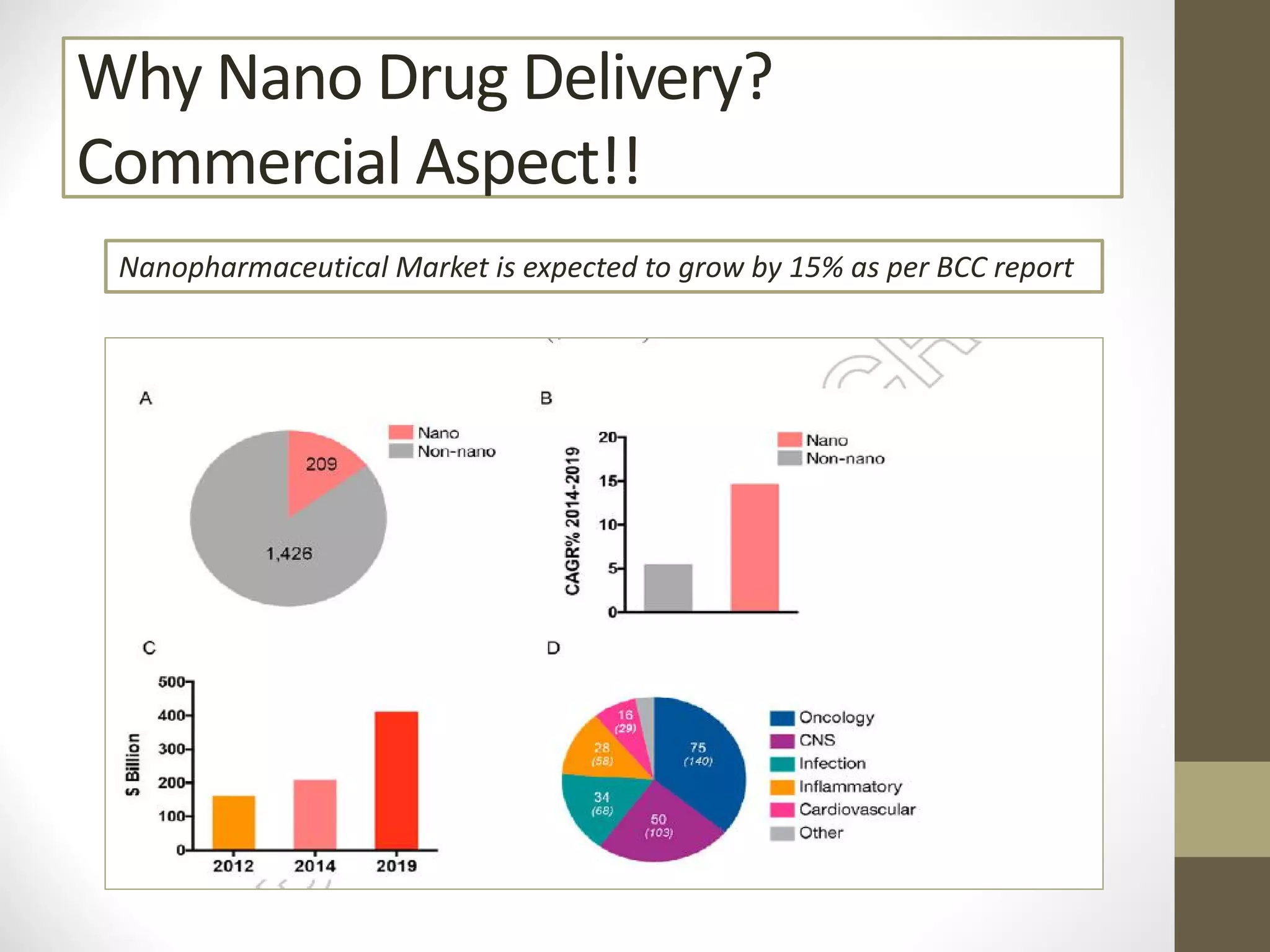
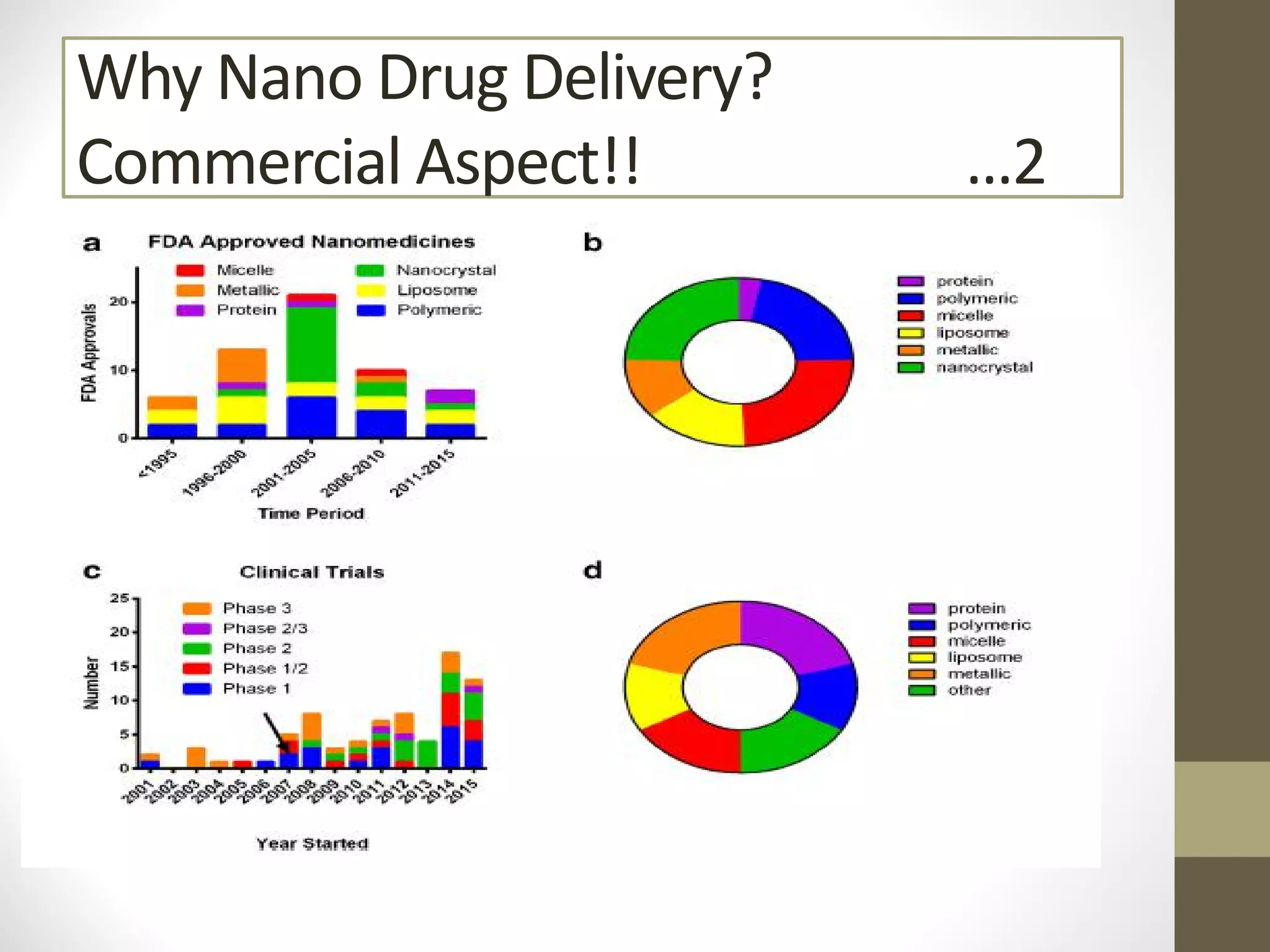
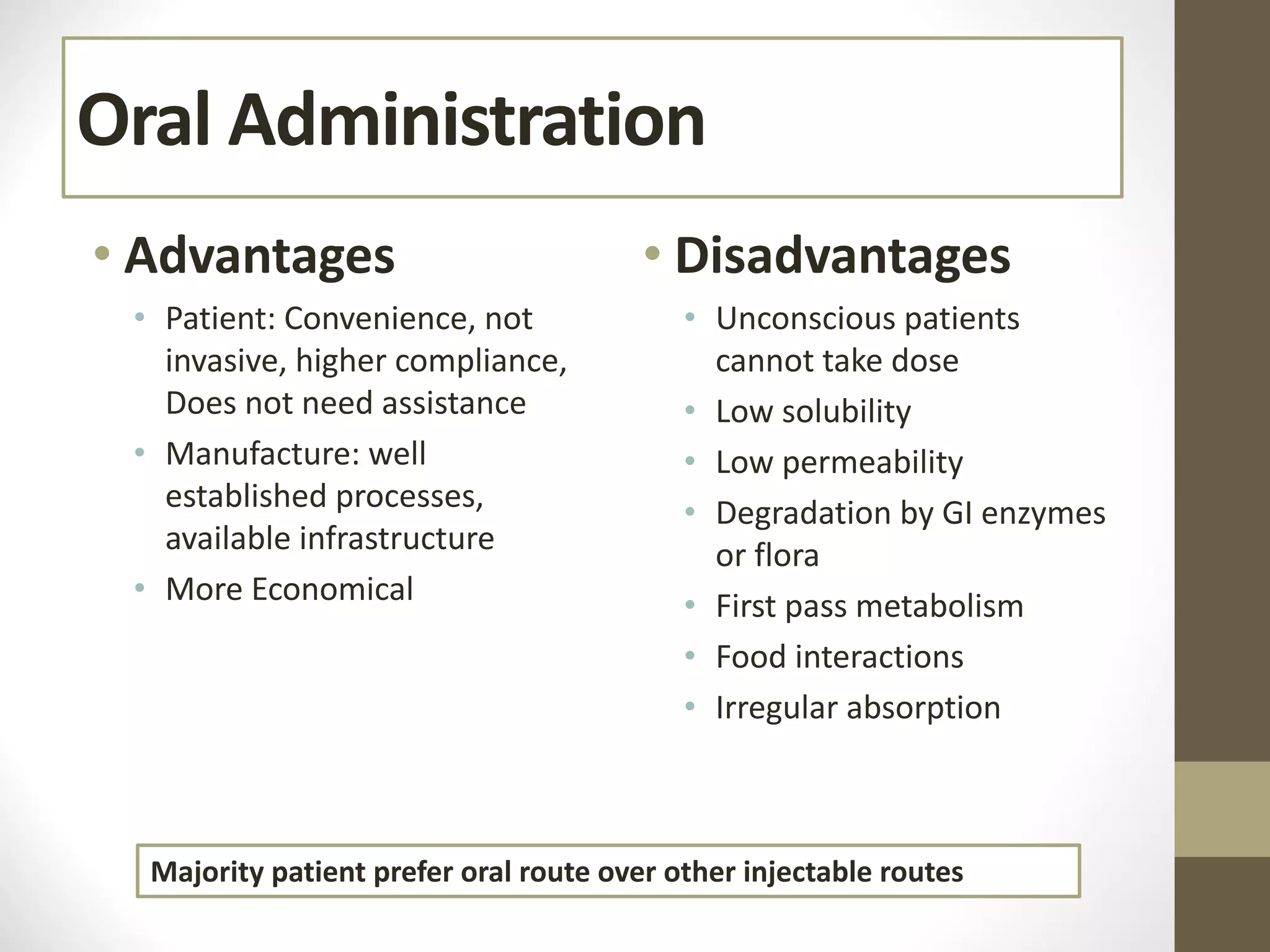
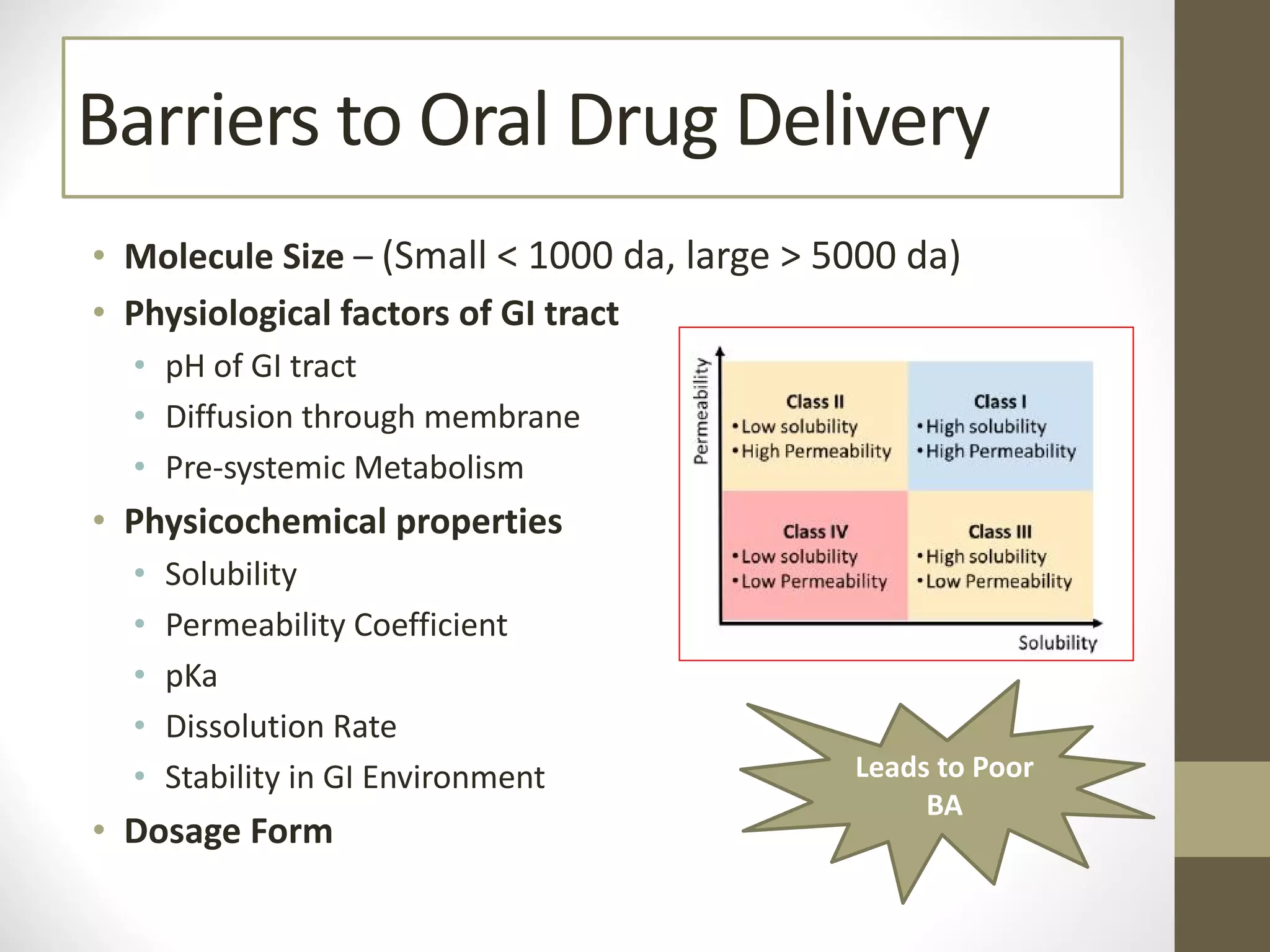
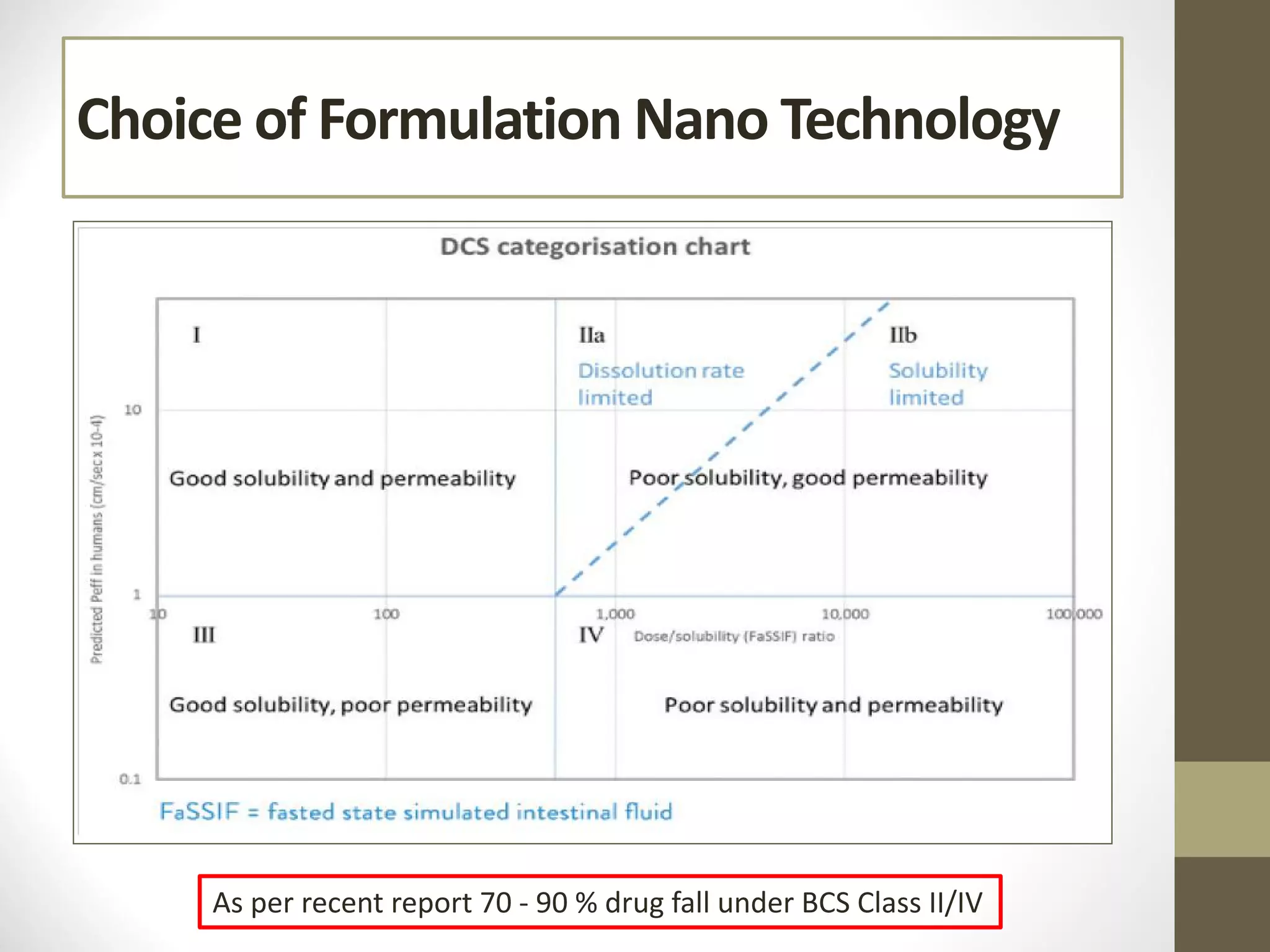
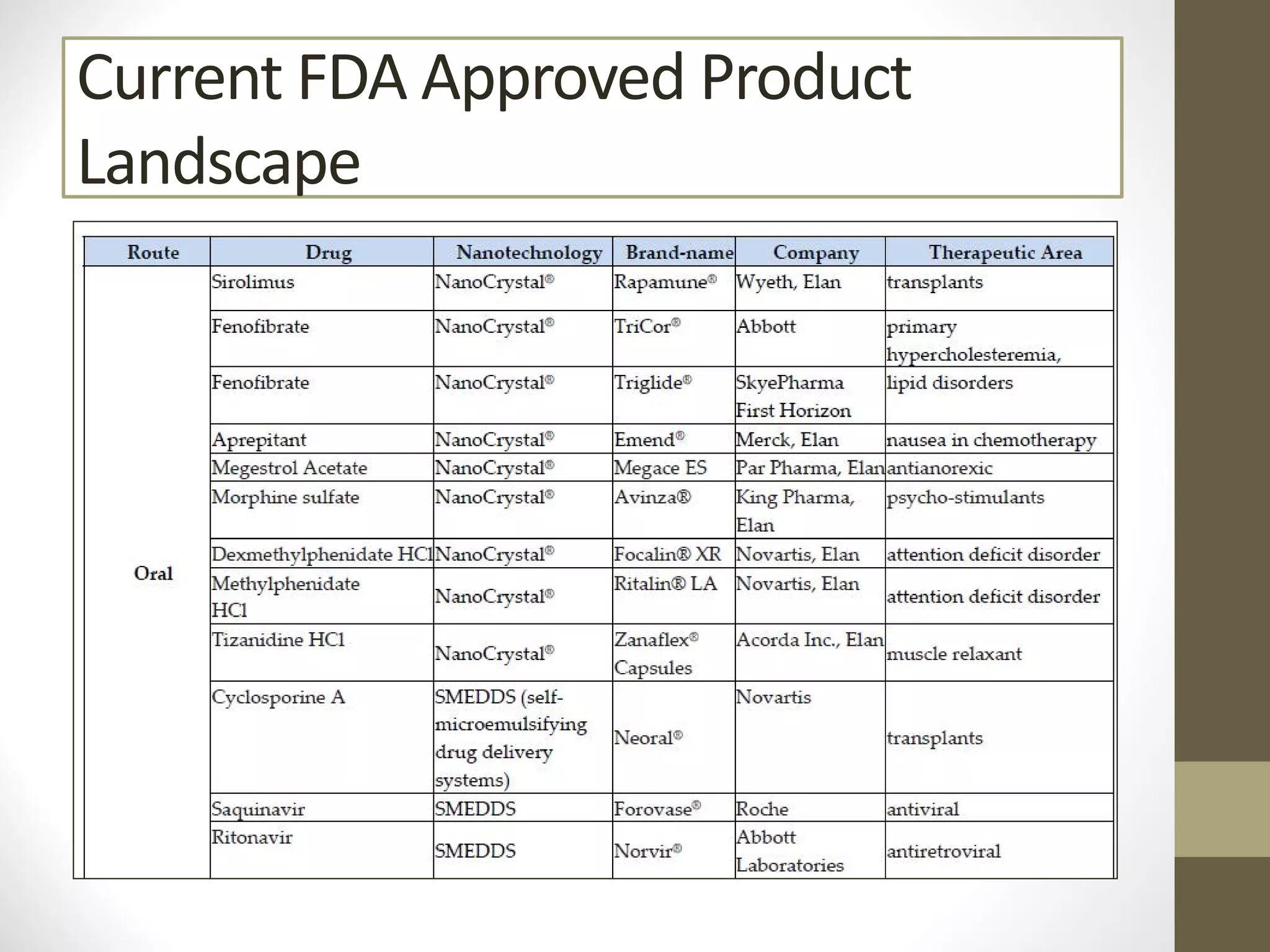
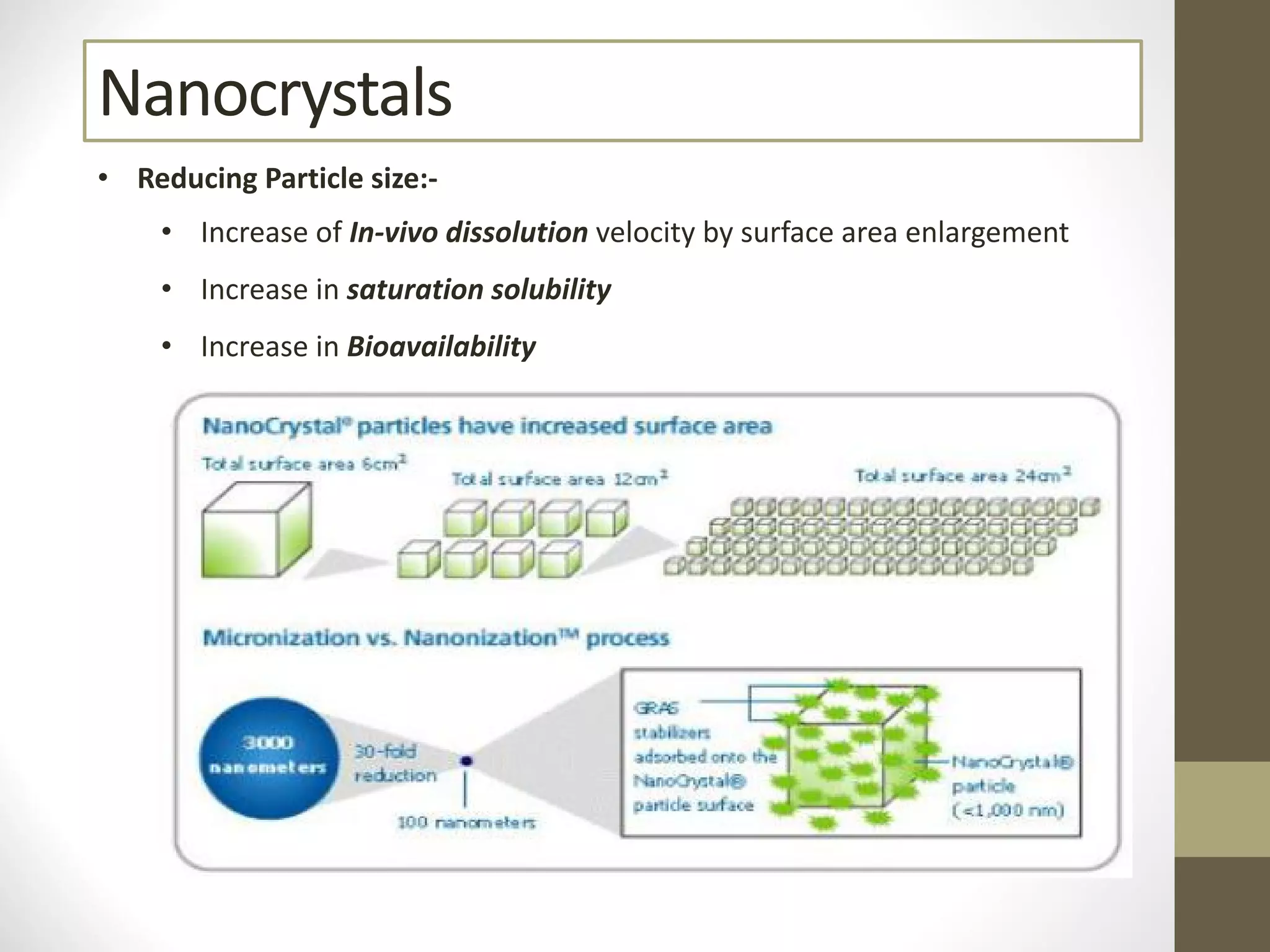
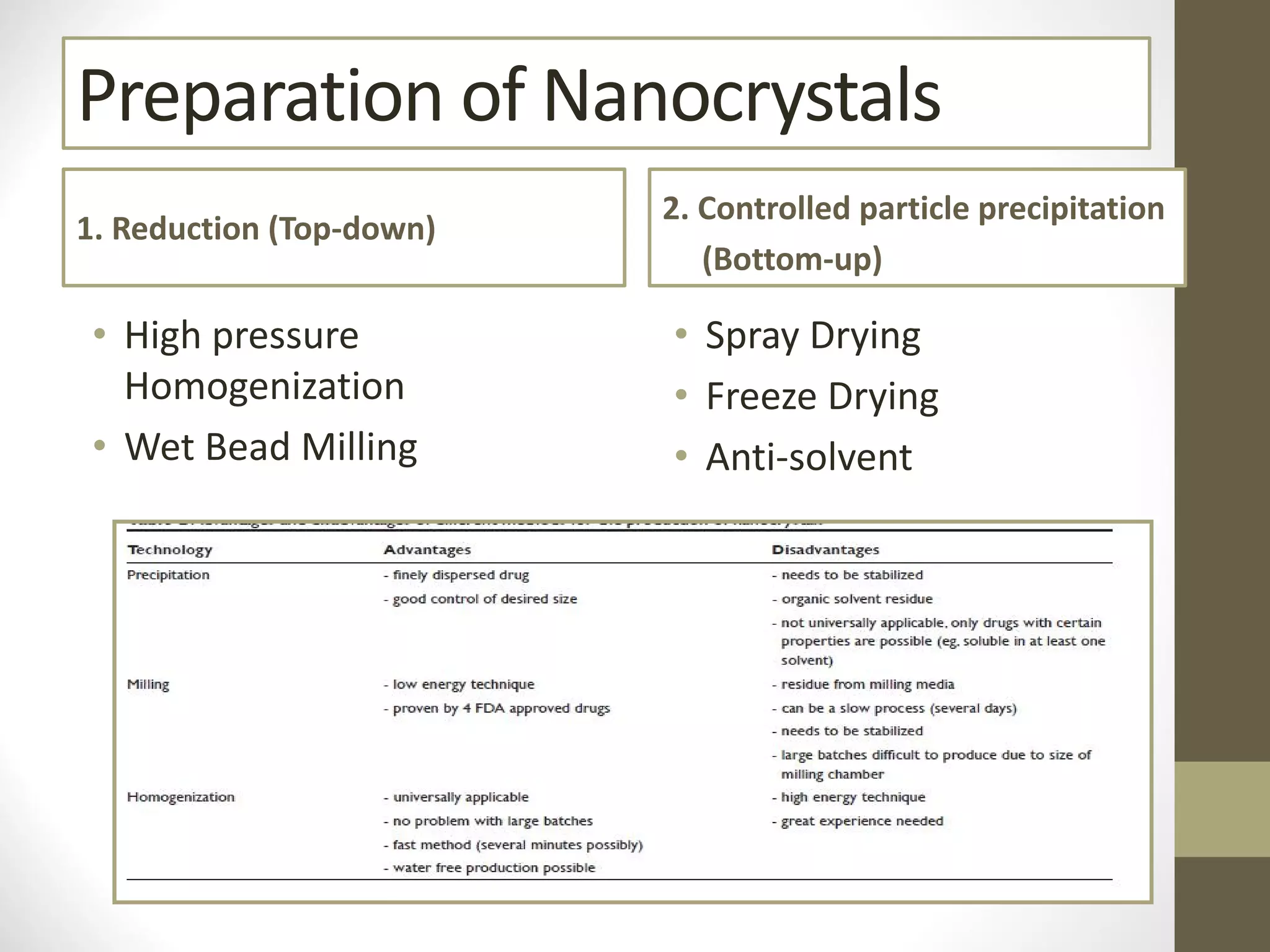
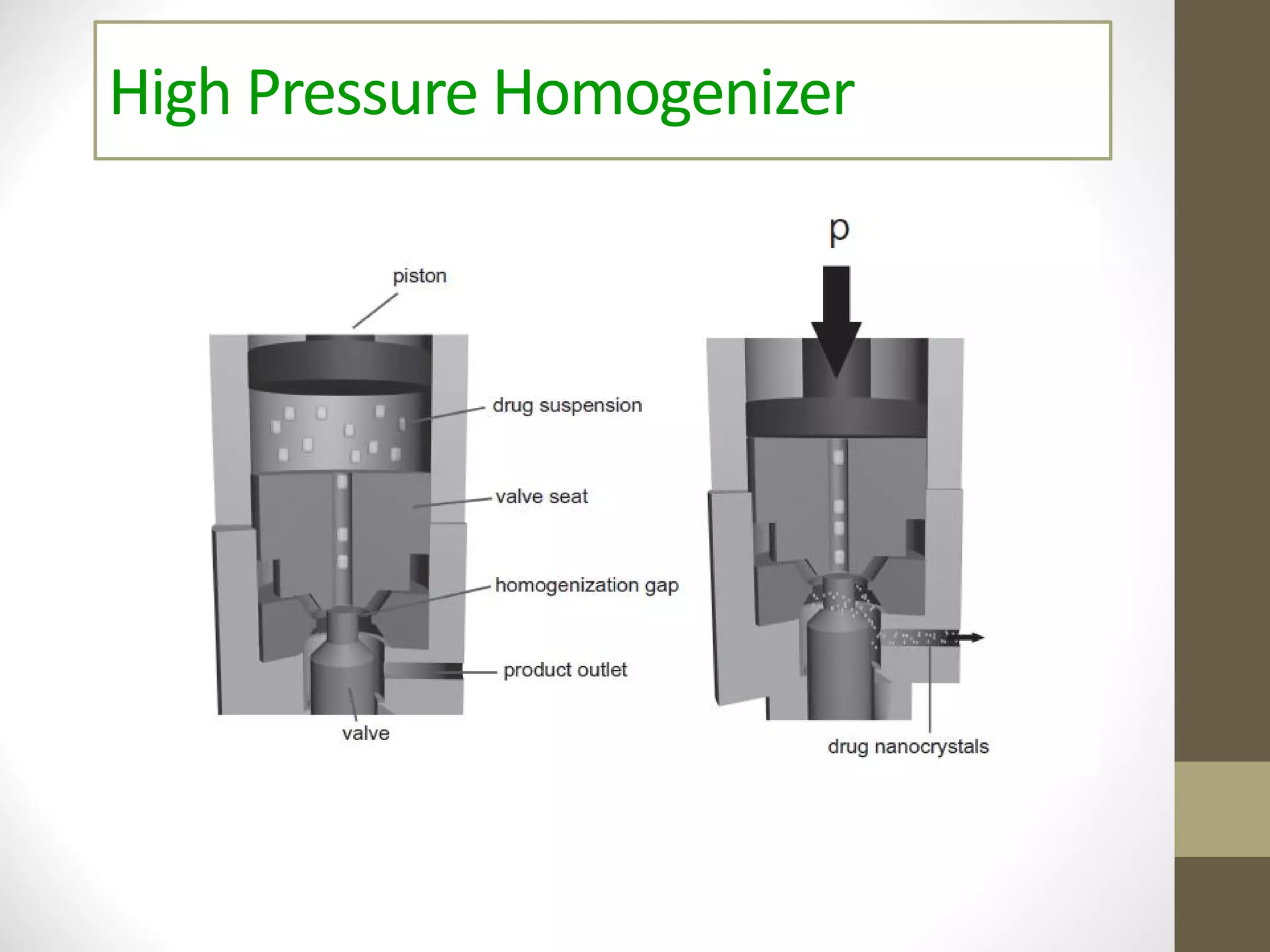
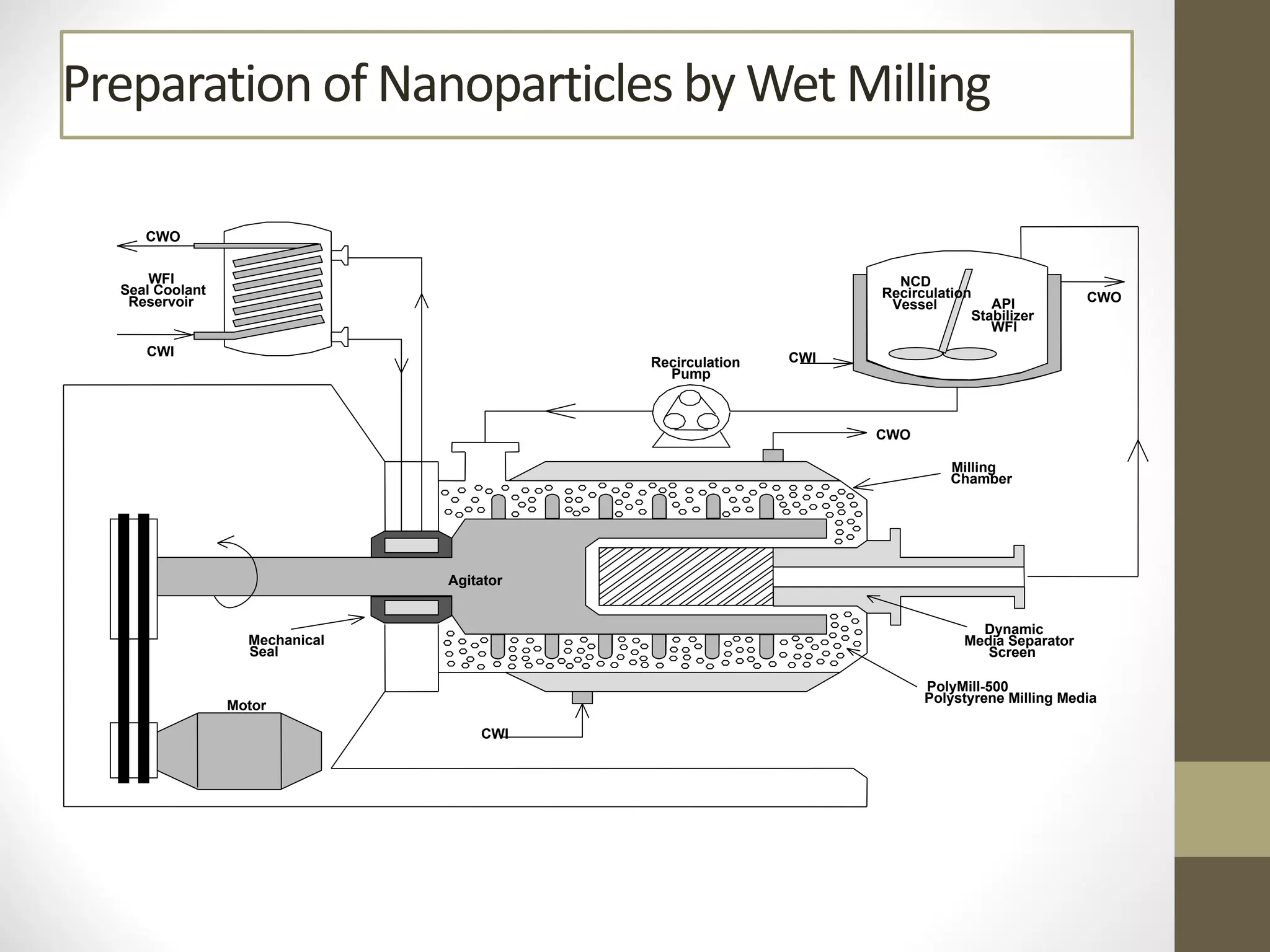
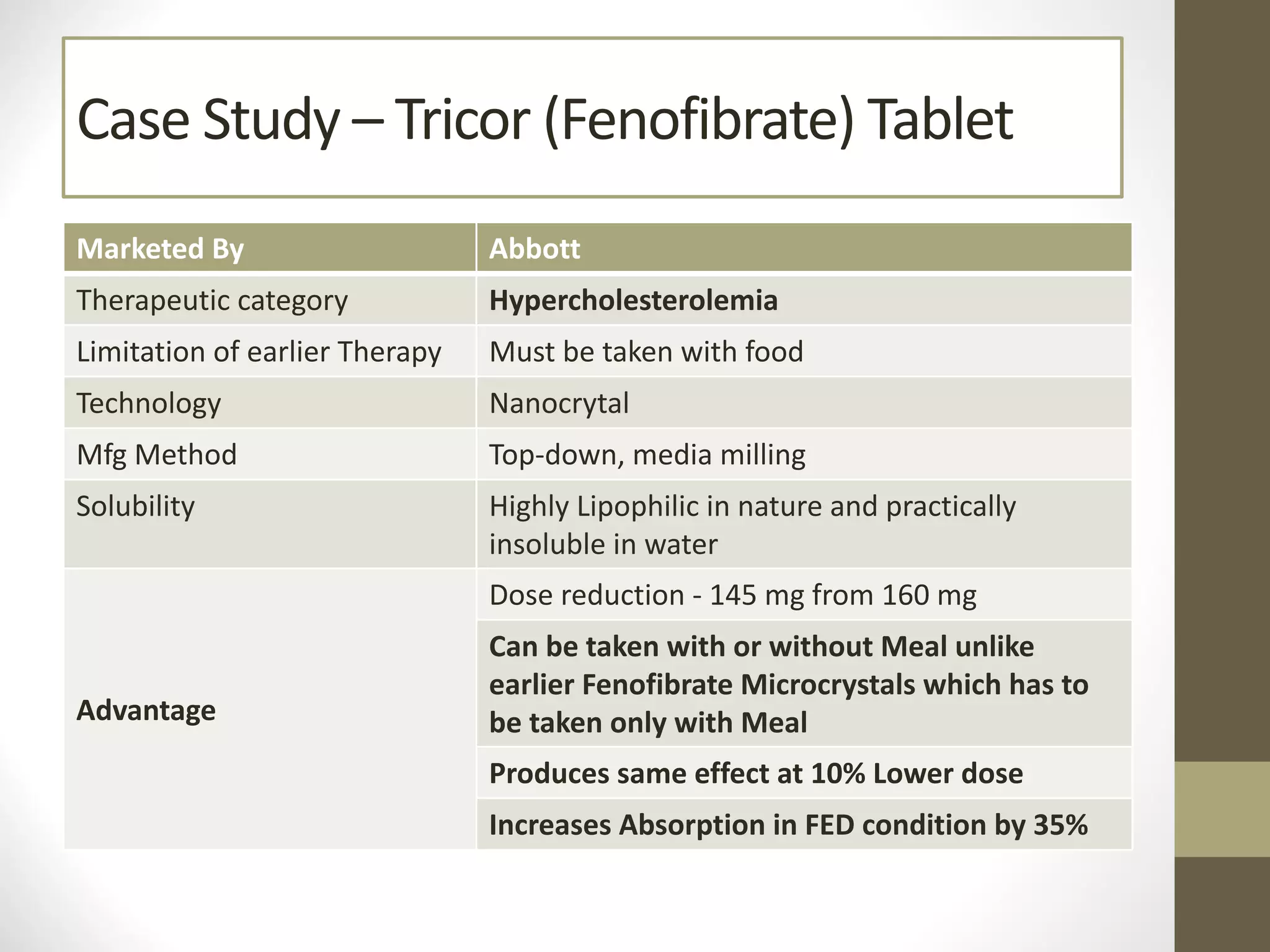
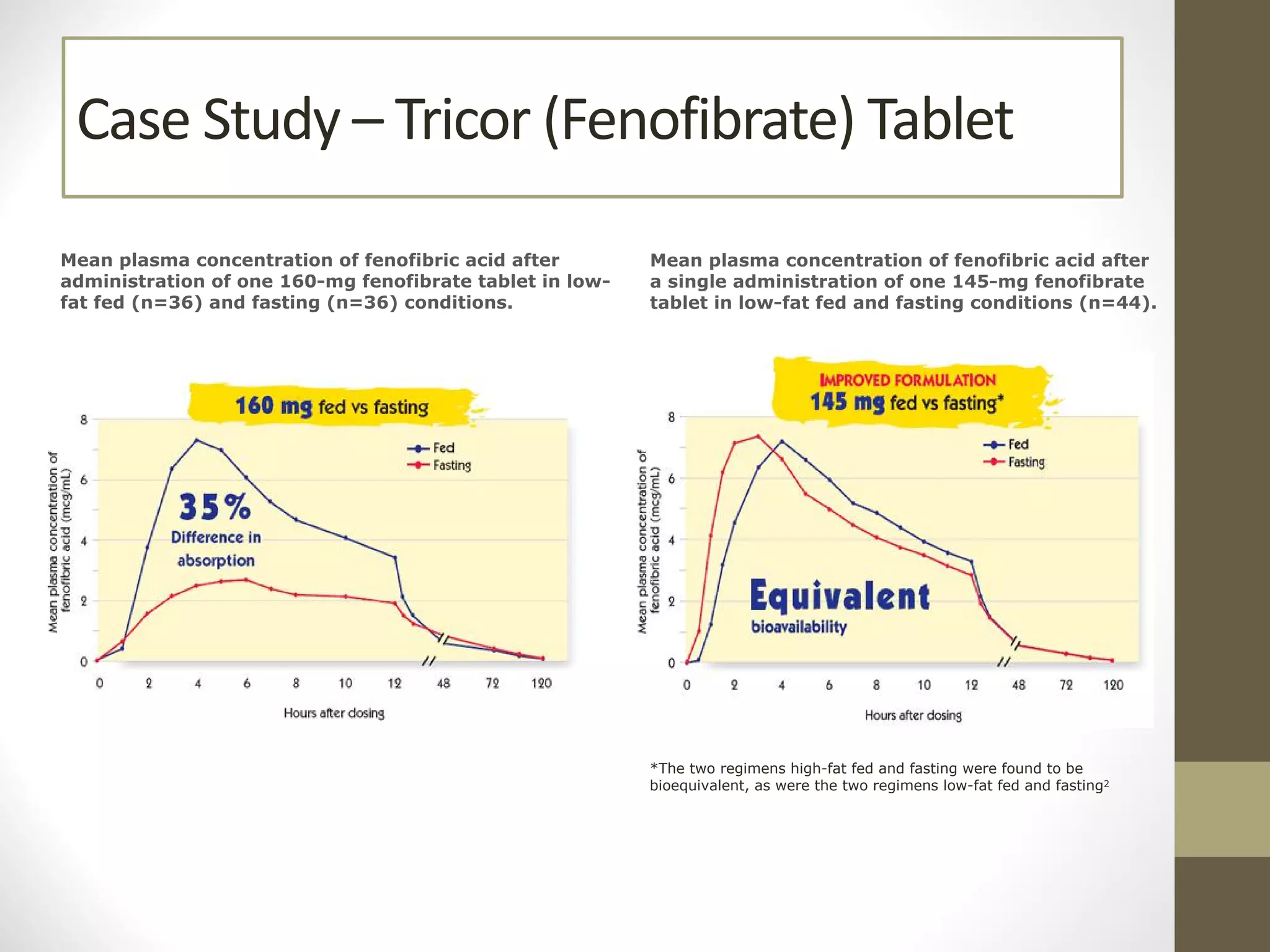
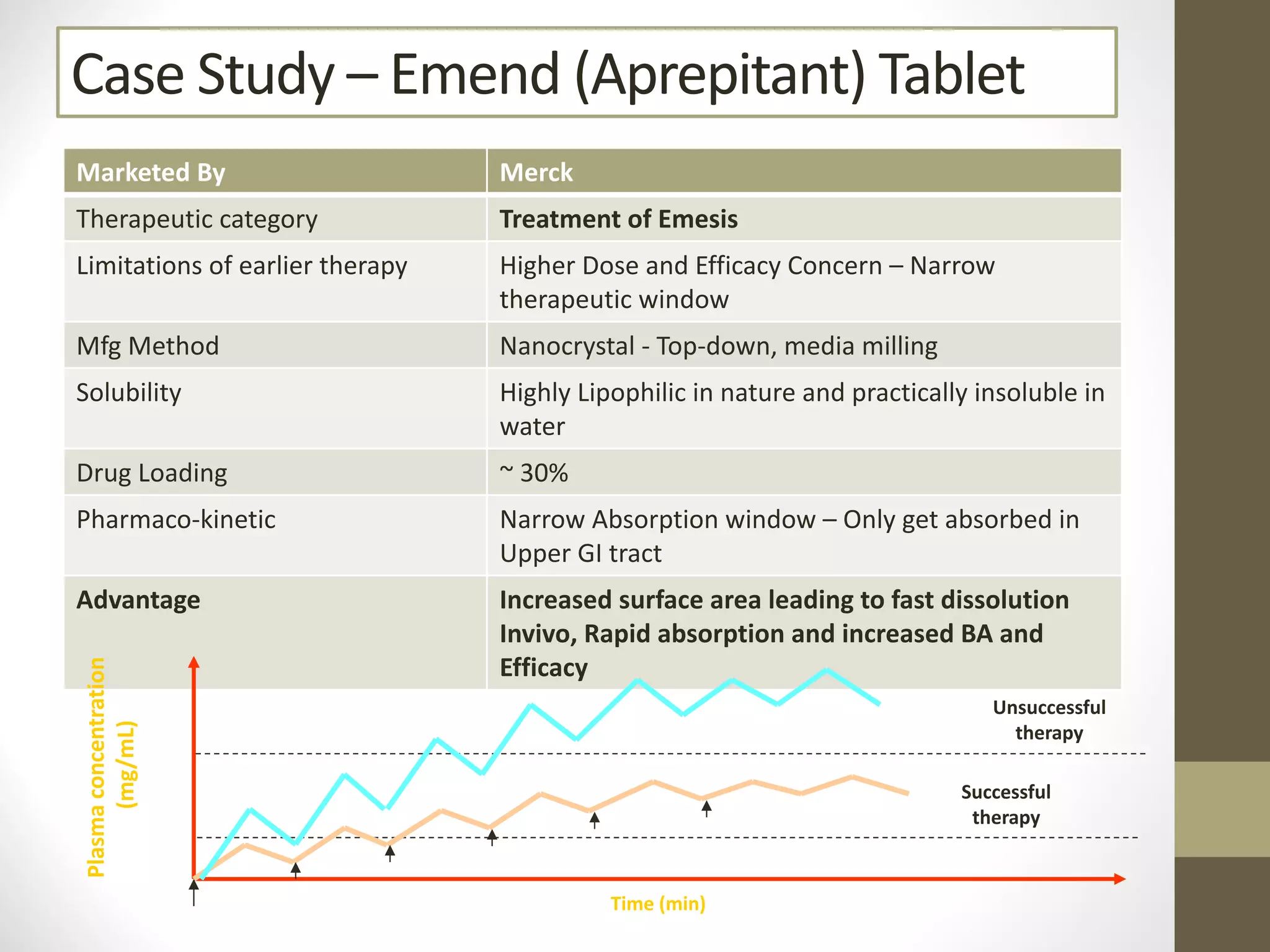
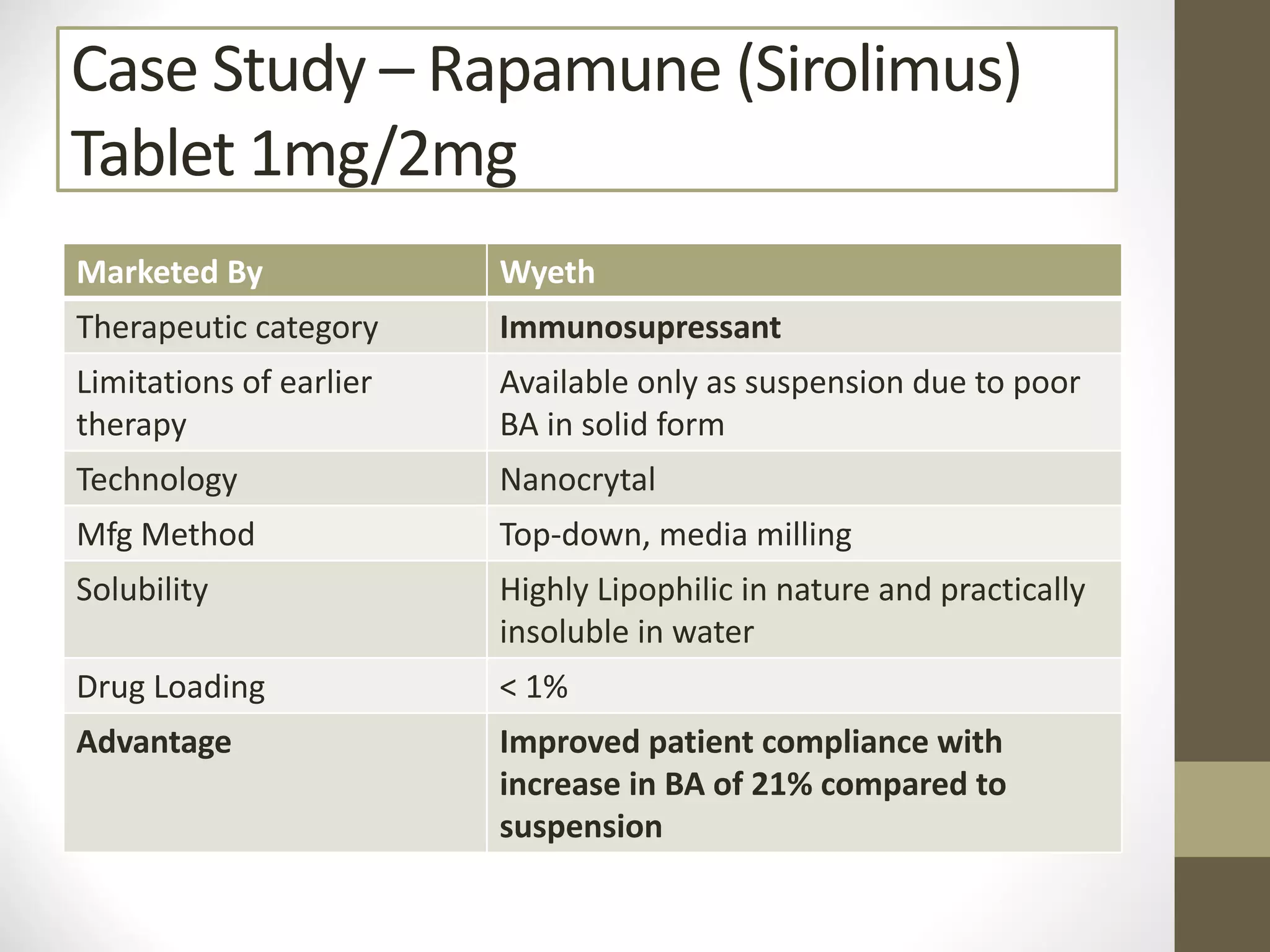
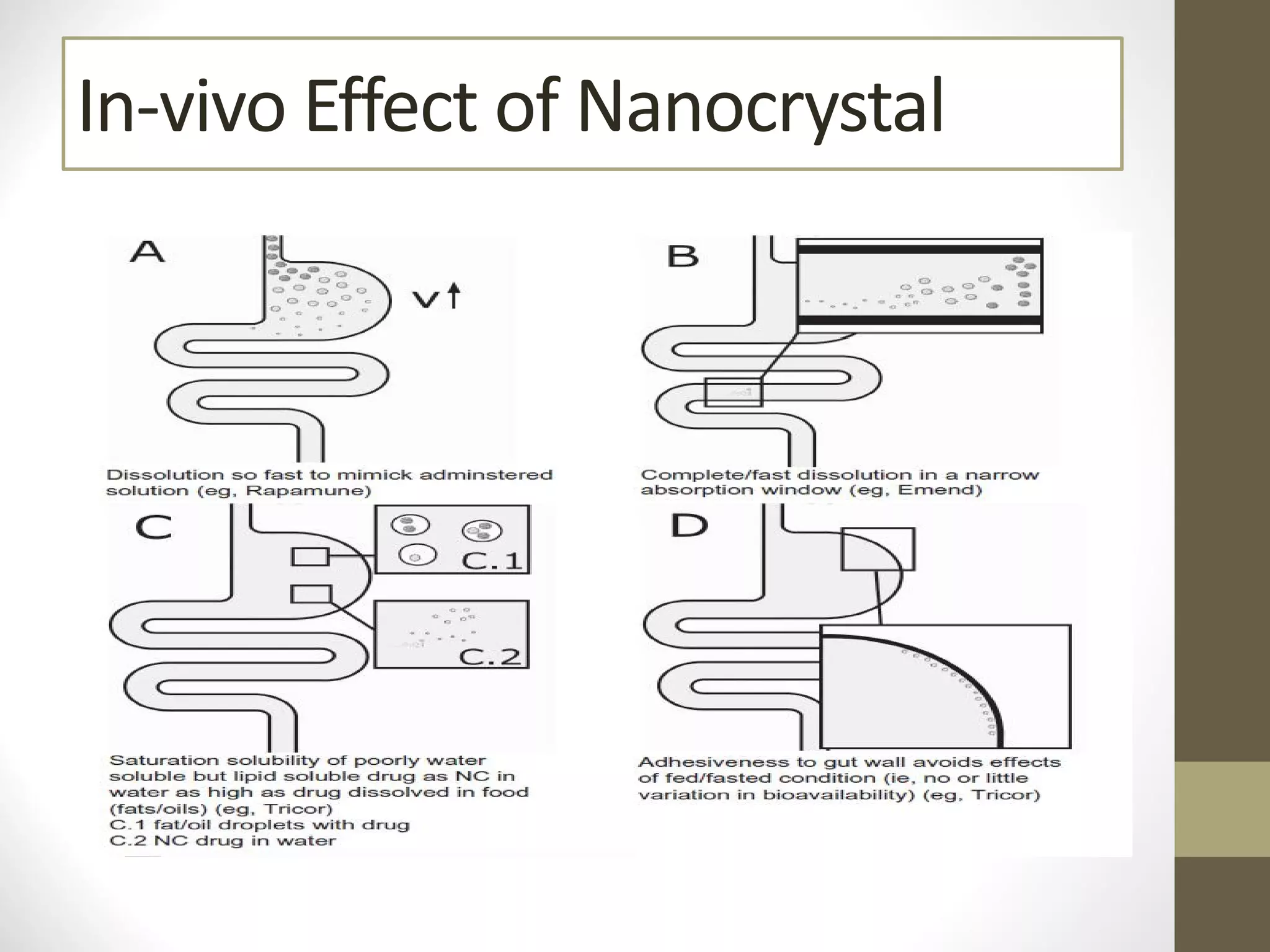
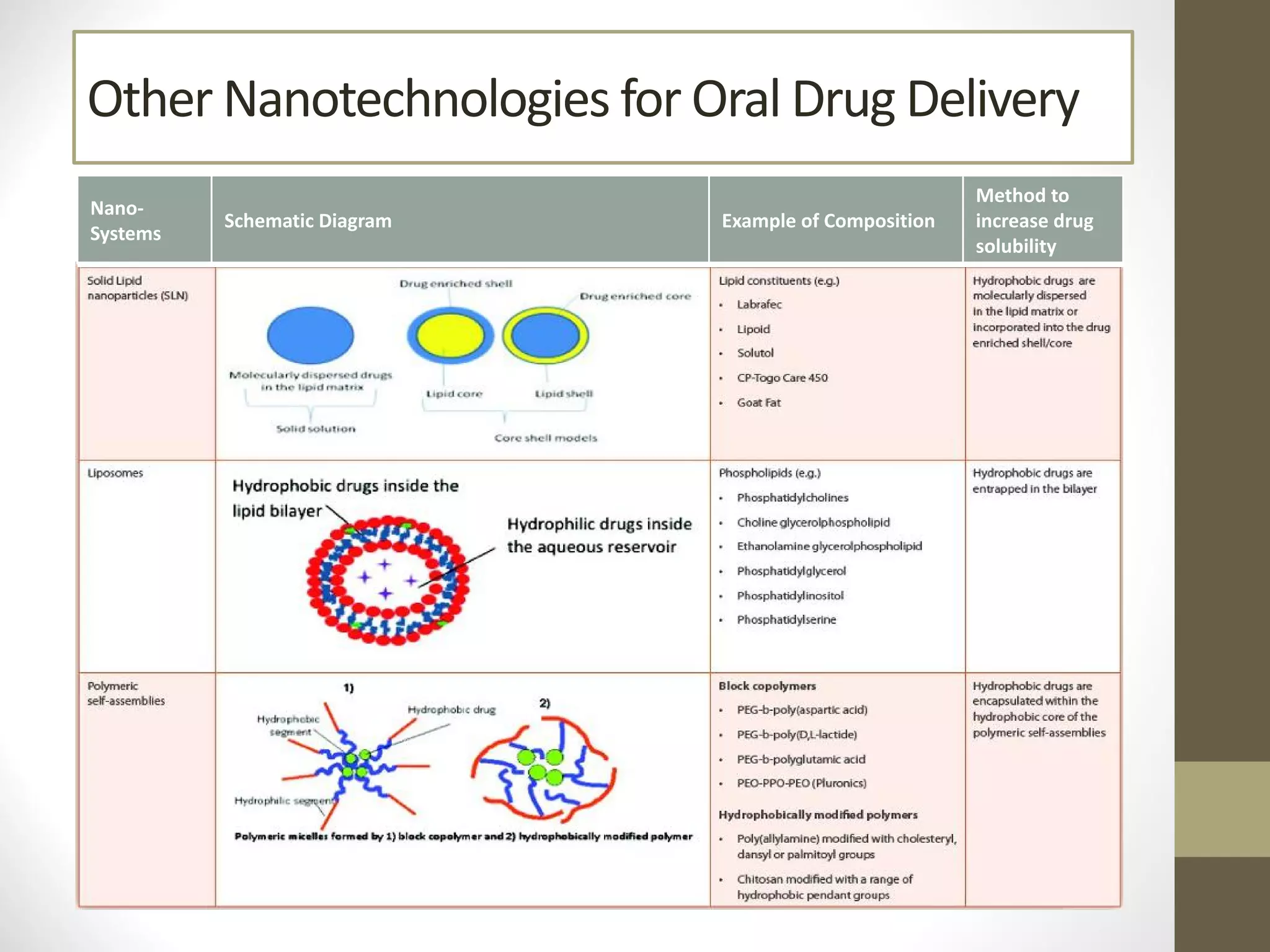
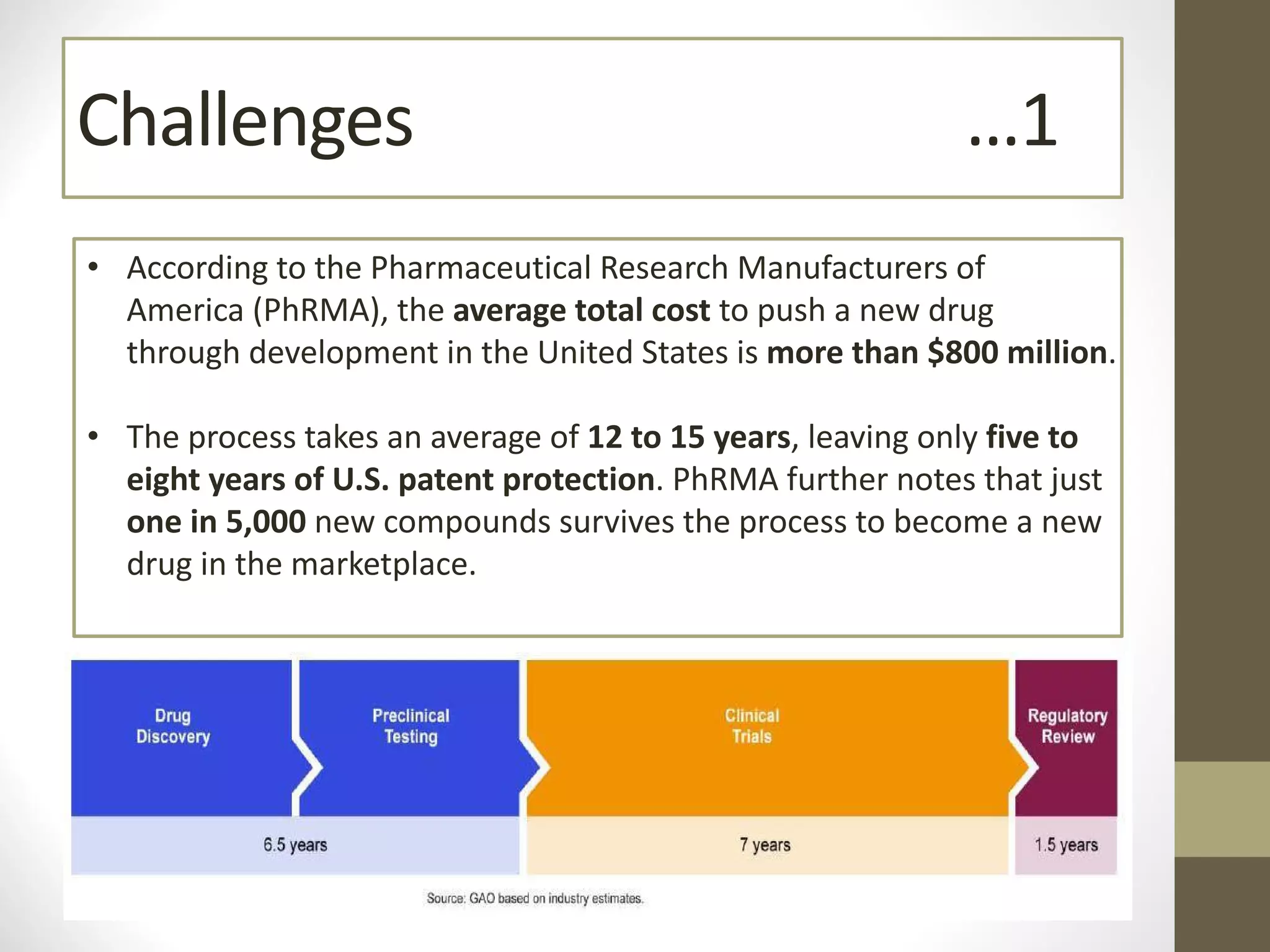
Nanotechnology shows promise for improving oral drug delivery by increasing solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. Nanocrystal formulations have been commercialized, such as Tricor and Emend tablets, that demonstrate higher absorption and lower dosing compared to earlier forms. However, challenges remain around fully characterizing nanoparticles, understanding their safety, ADME profiles, and environmental impacts which will require further research to fully realize the potential of this technology.