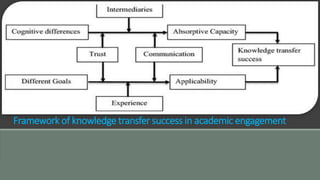
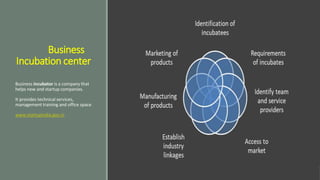
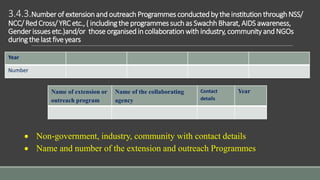
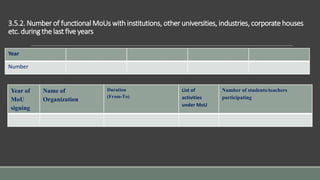
The document outlines the NAAC Criterion-III focusing on research, innovations, and extension activities in affiliated and constituent colleges. It details the key indicators for promoting research, resource mobilization, innovation ecosystems, and extension activities while addressing challenges and efforts for enhancing research culture. Additionally, it discusses funding agencies, collaborative efforts, and the community impact of various outreach initiatives conducted by the institutions over the last five years.