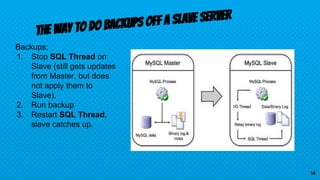
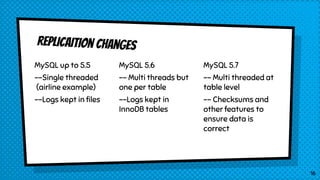
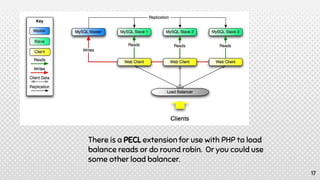
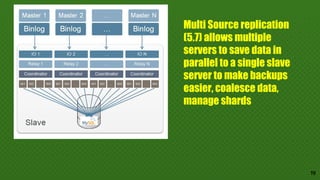
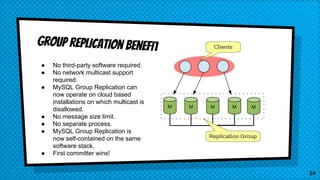
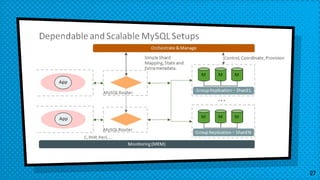
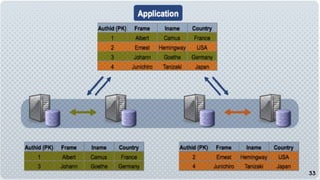
This document discusses various approaches for scaling MySQL databases. It begins with an overview of using replication between a master and slave server to offload reads. Additional approaches covered include load balancing reads across multiple slaves, sharding data across multiple database instances, using MySQL Fabric or Galera Cluster for high availability, and deploying a MySQL Cluster for high performance and redundancy. The document cautions that scaling databases comes with costs and challenges, and emphasizes starting with normalized data and monitoring growth.