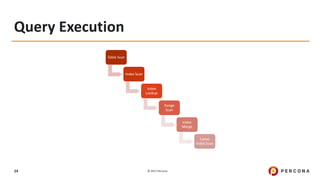
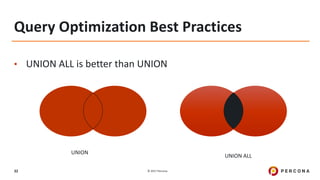
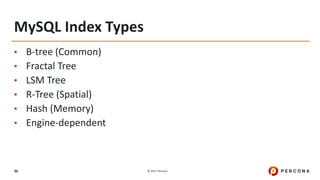
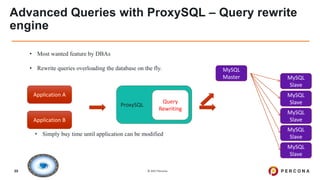
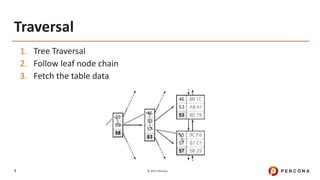
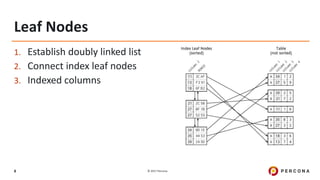
The document outlines best practices for MySQL query optimization and indexing, emphasizing the importance of indexes for efficient data access. It discusses techniques for identifying slow queries, optimizing query execution plans, and the various types of indexes available in MySQL. Additionally, it provides tips on query structure and execution strategies to enhance performance while maintaining optimal index usage.











![© 2017 Percona21
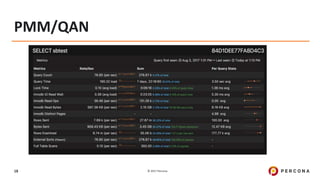
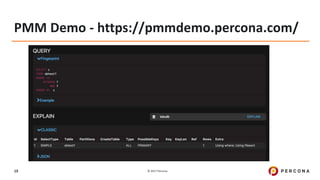
Explain Plan (JSON)
> EXPLAIN format=JSON SELECT CONCAT(customer.last_name, ', ', customer.first_name) AS customer, address.phone, film.title FROM rental INNER JOIN customer ON rental.customer_id =
customer.customer_id INNER JOIN address ON customer.address_id = address.address_id INNER JOIN inventory ON rental.inventory_id = inventory.inventory_id INNER JOIN film ON inventory.film_id =
film.film_id WHERE rental.return_date IS NULL AND rental_date + INTERVAL film.rental_duration DAY < CURRENT_DATE() LIMIT 5G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
EXPLAIN: {
"query_block": {
"select_id": 1,
"nested_loop": [
{
"table": {
"table_name": "film",
"access_type": "ALL",
"possible_keys": [
"PRIMARY"
],
"rows": 1000,
"filtered": 100
}
},
…
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlqueryoptimizationbestpracticesandindexing-180916184428/85/Mysql-query-optimization-best-practices-and-indexing-21-320.jpg)