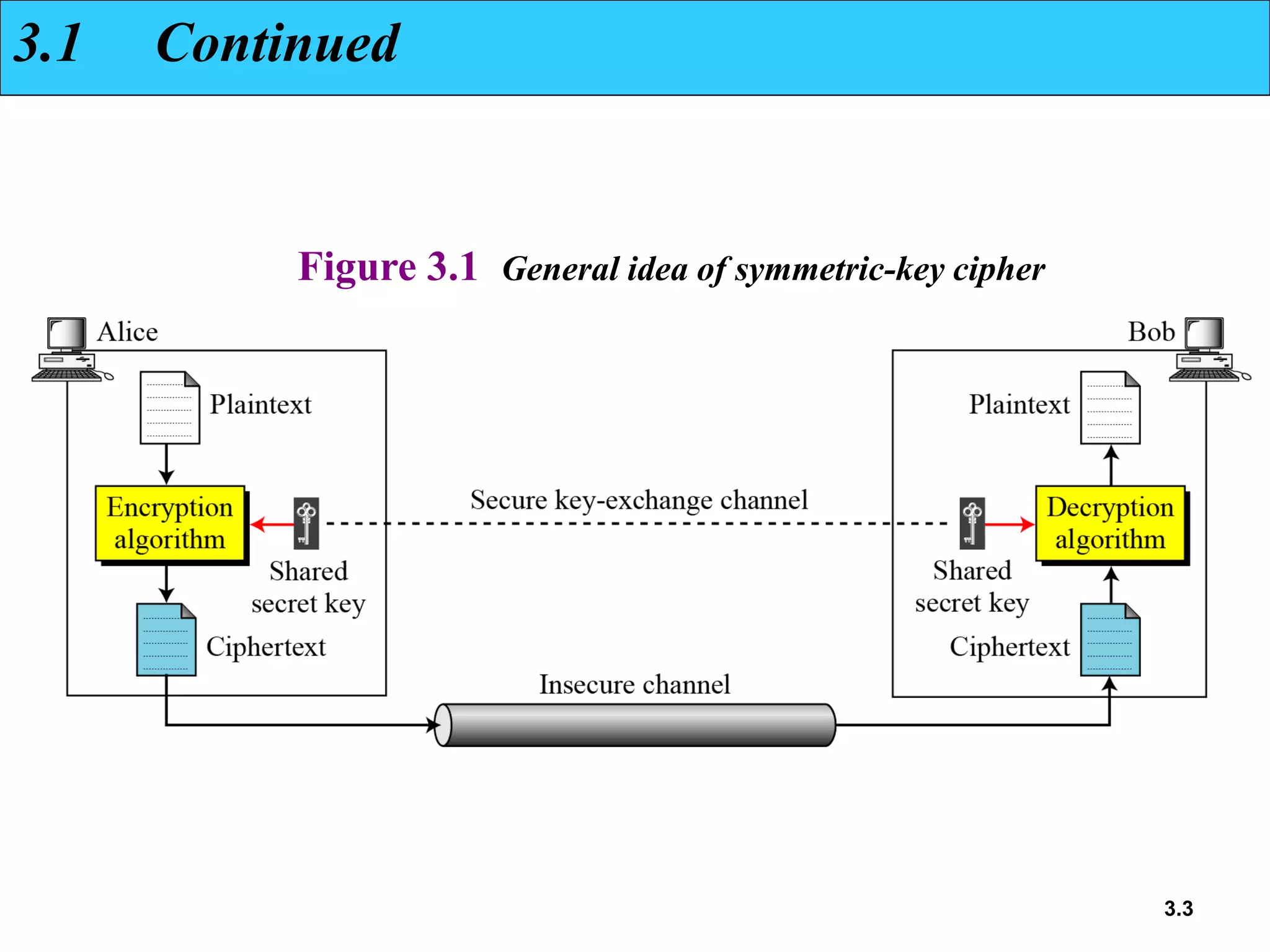
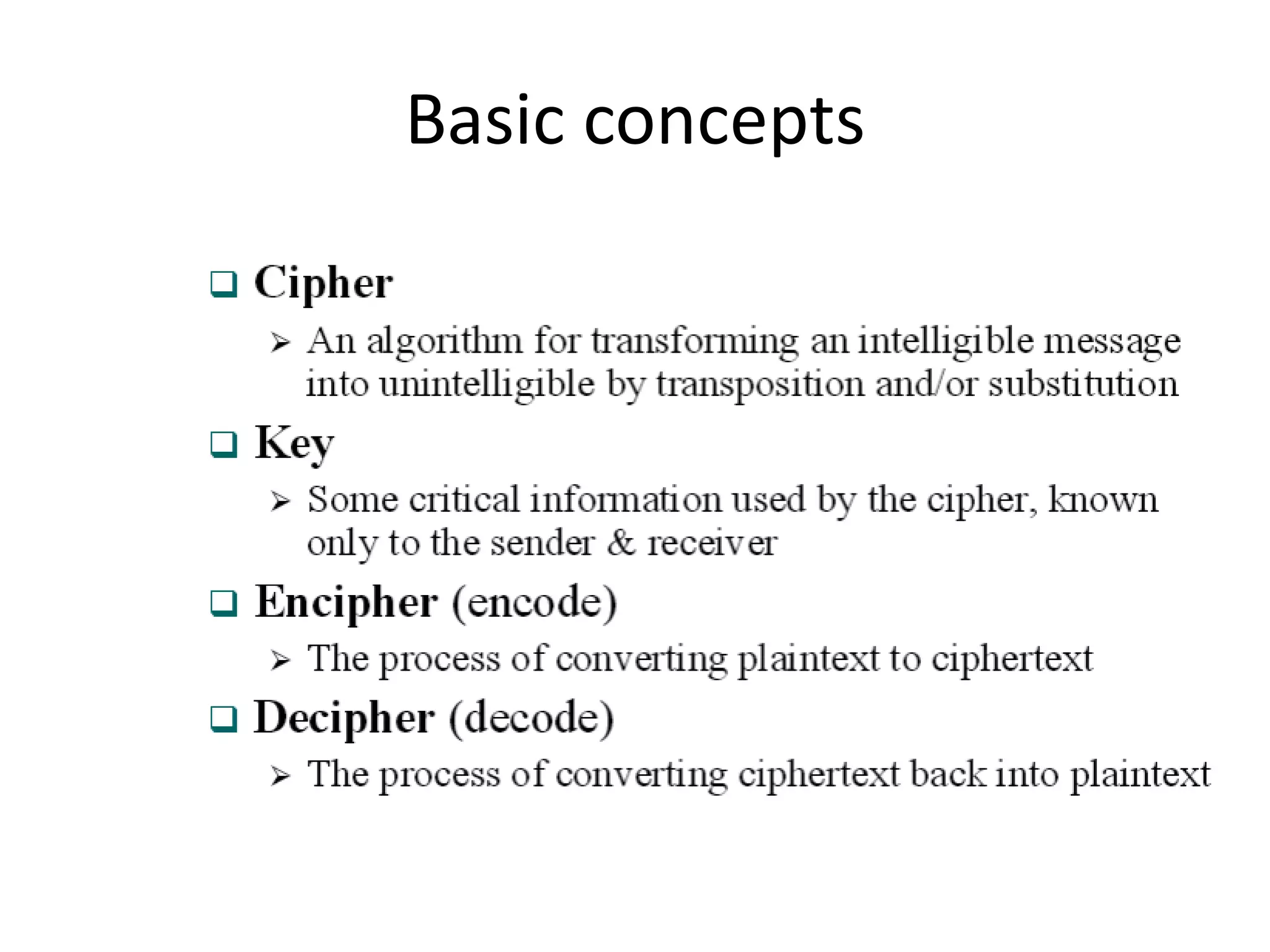
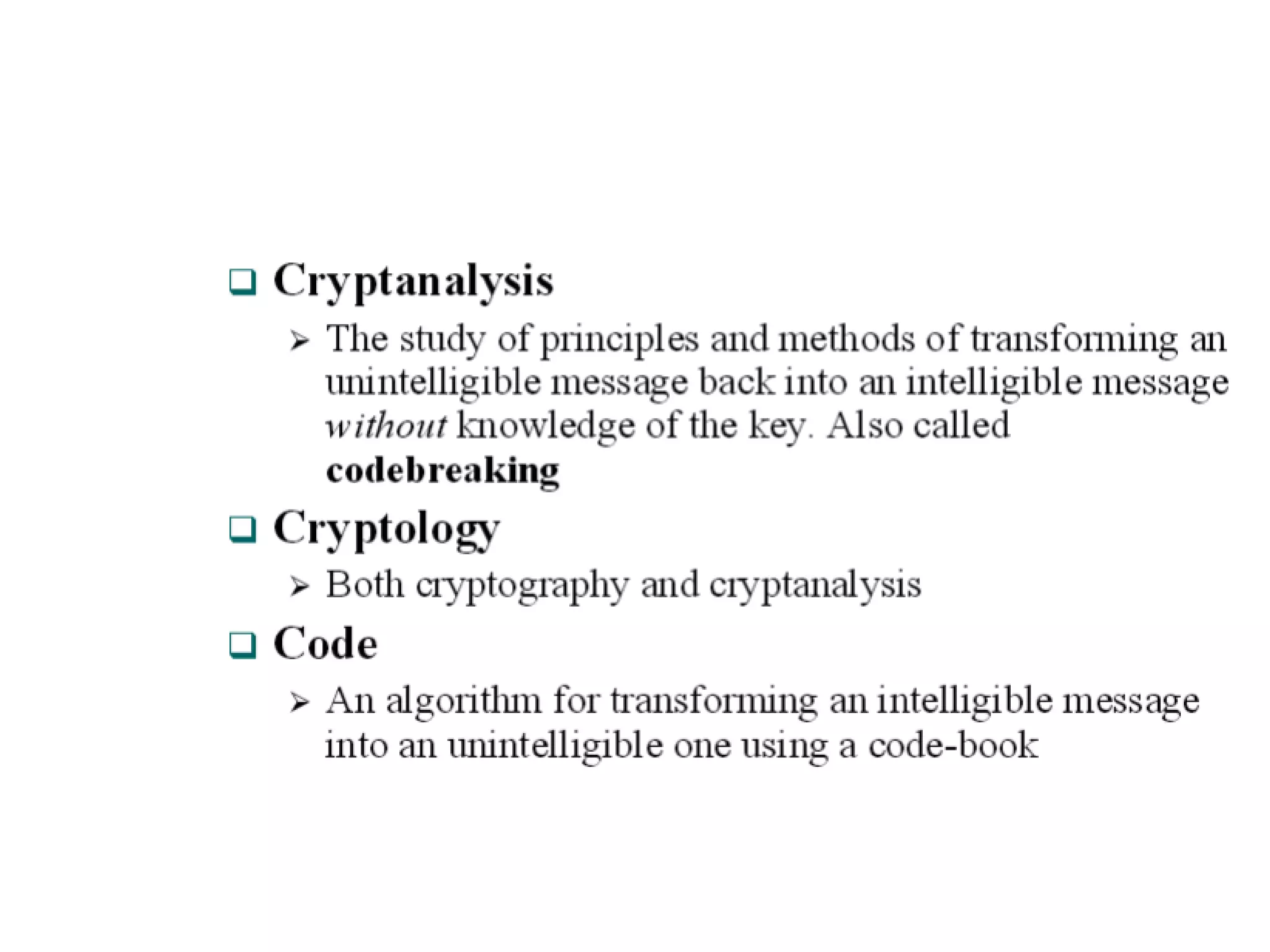
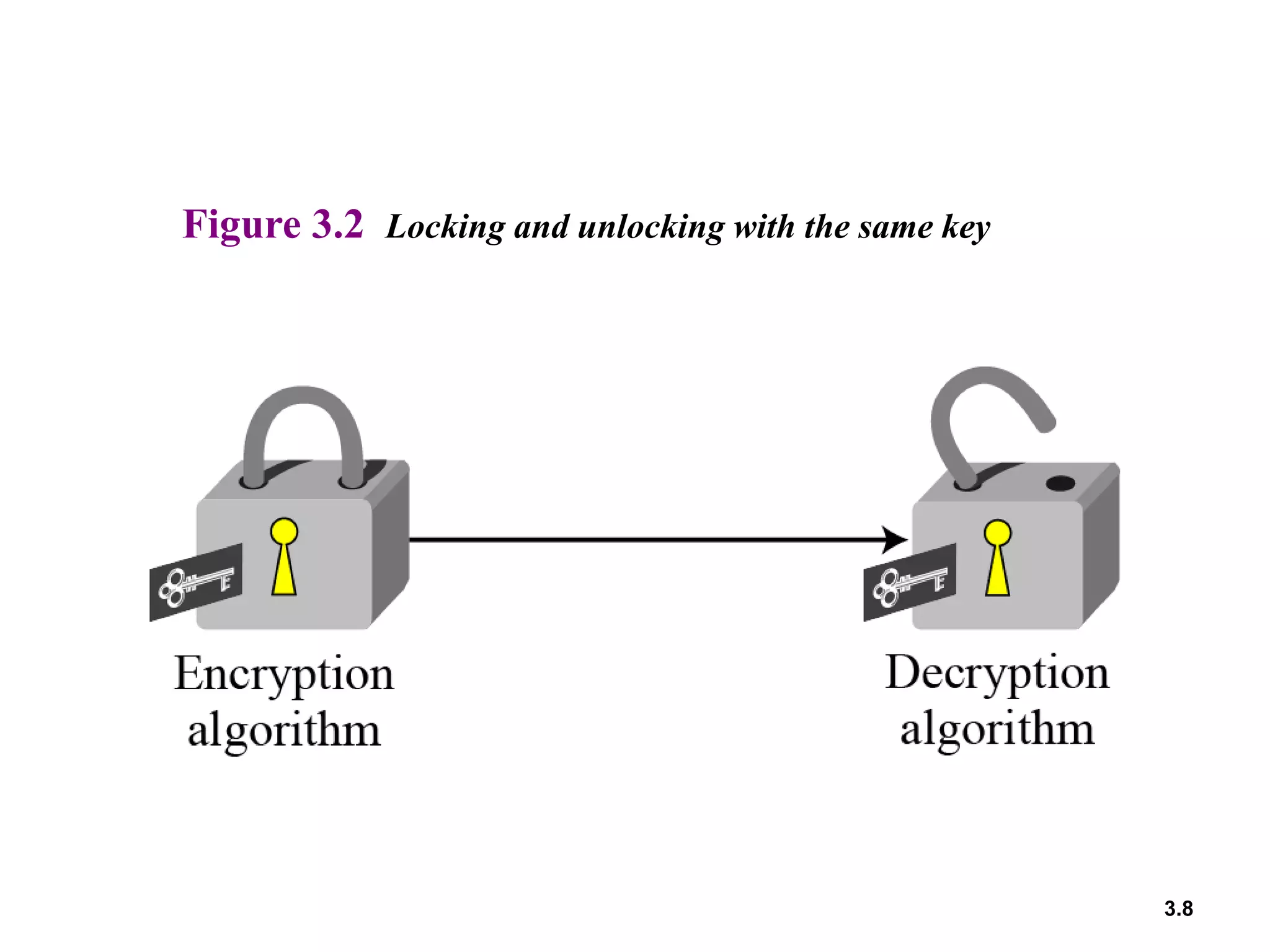
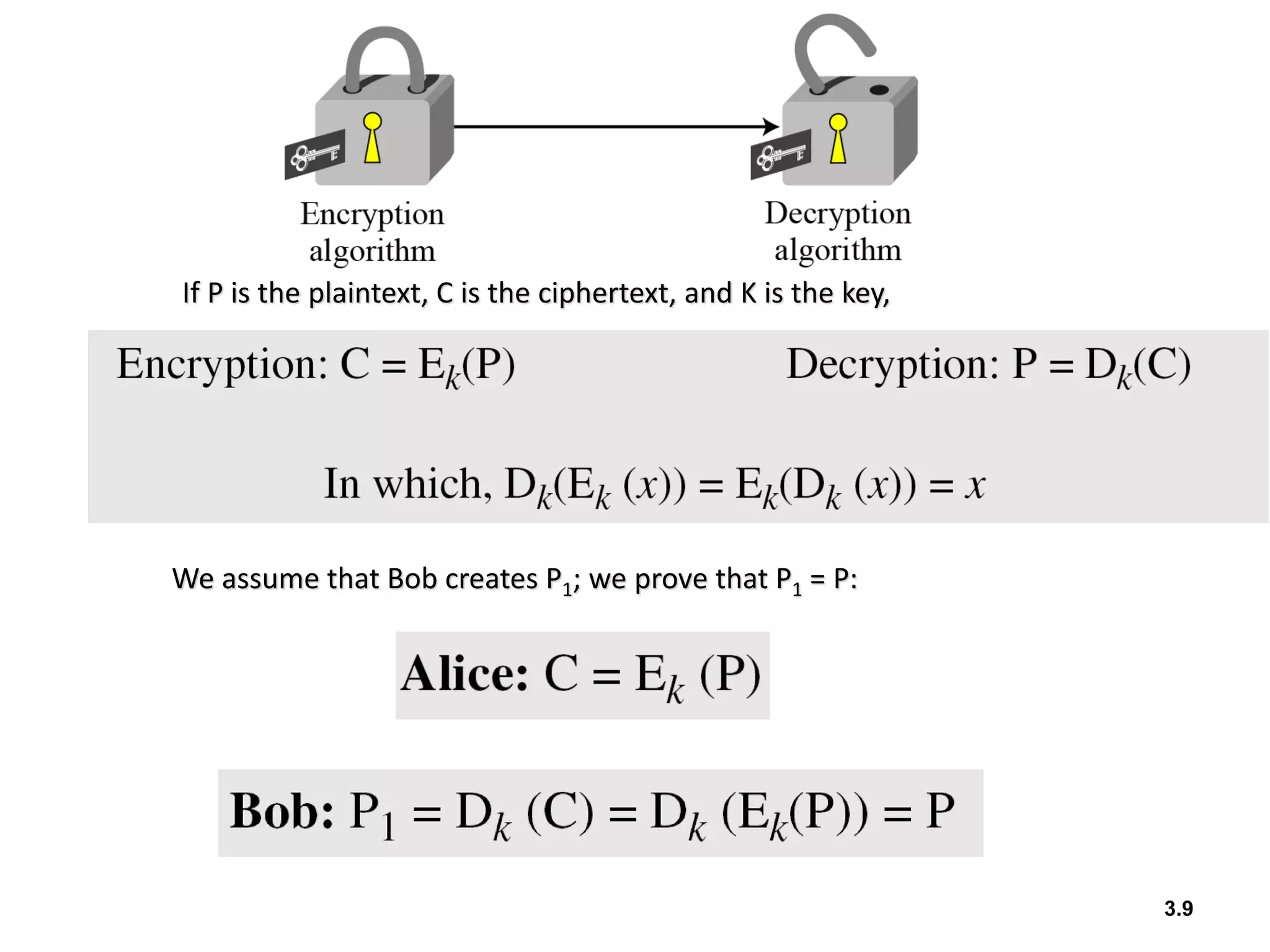
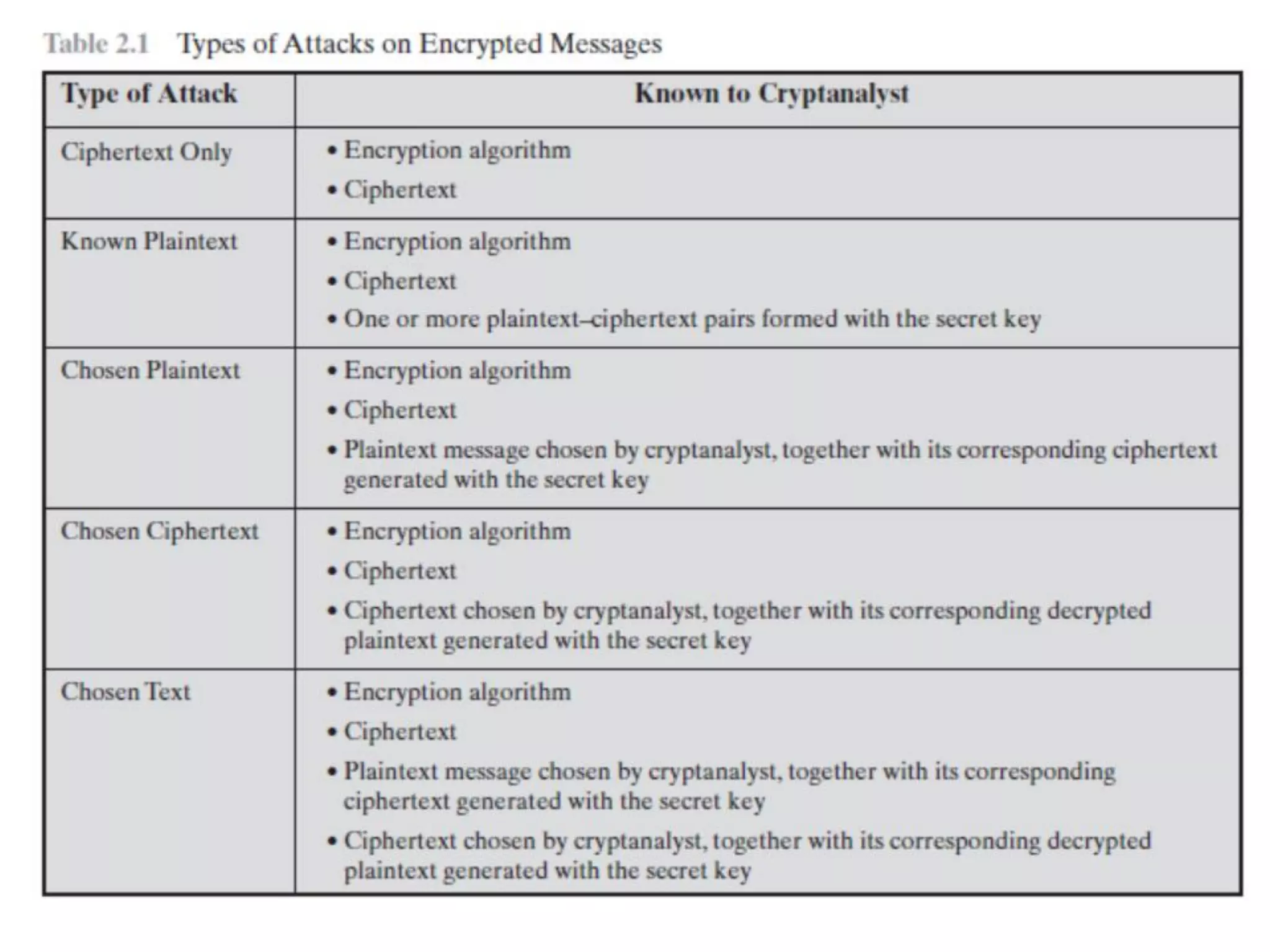
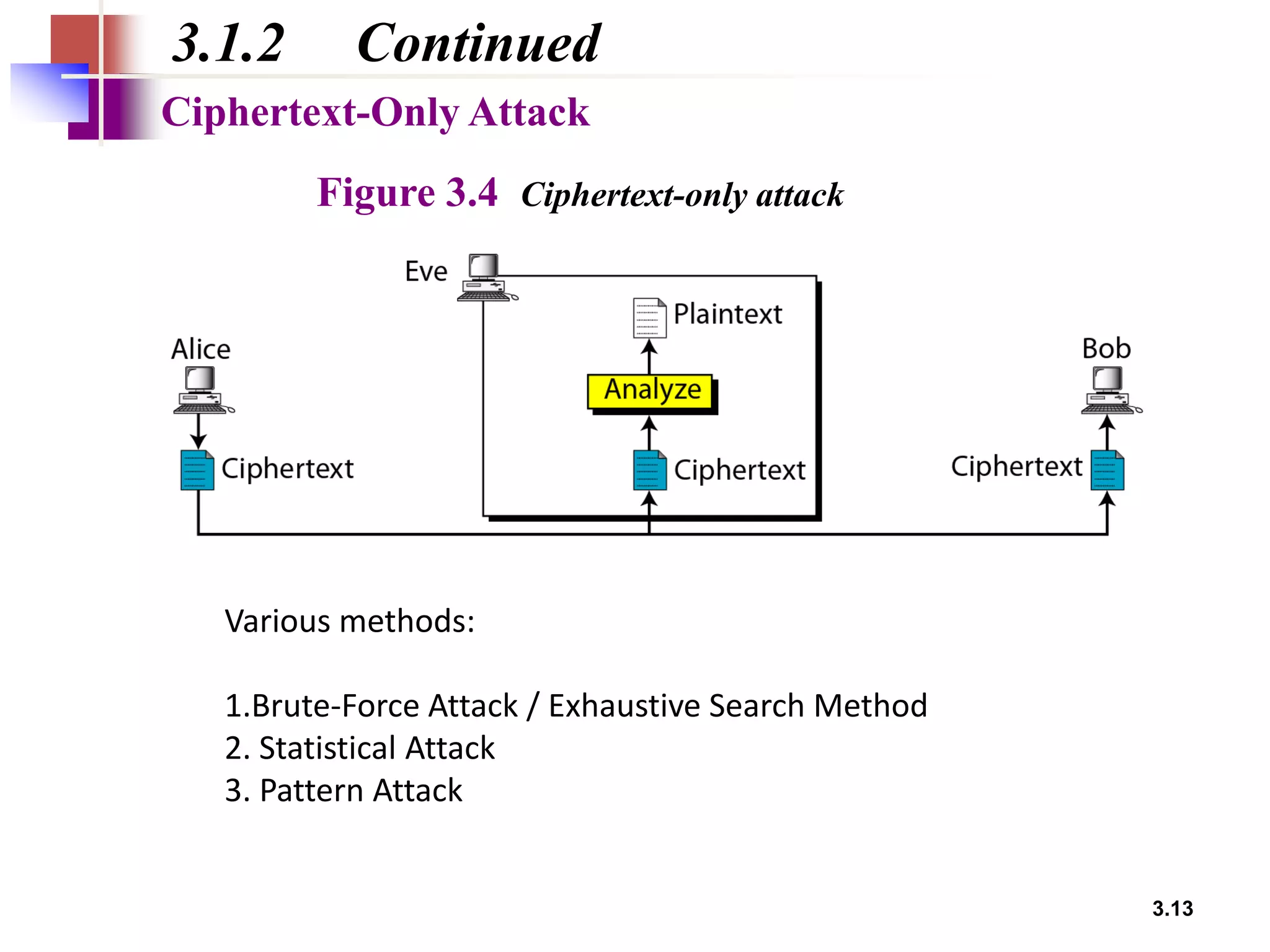
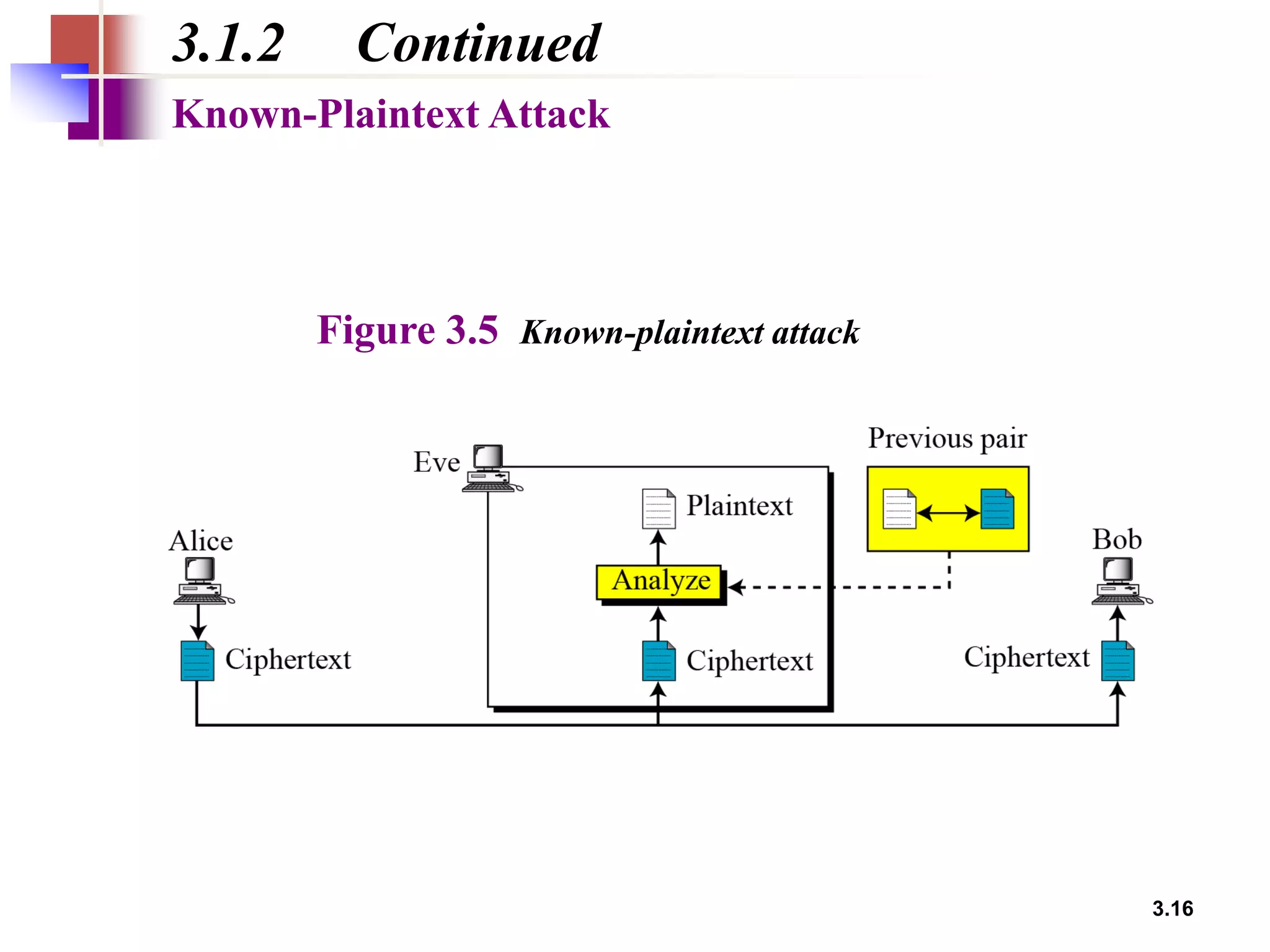
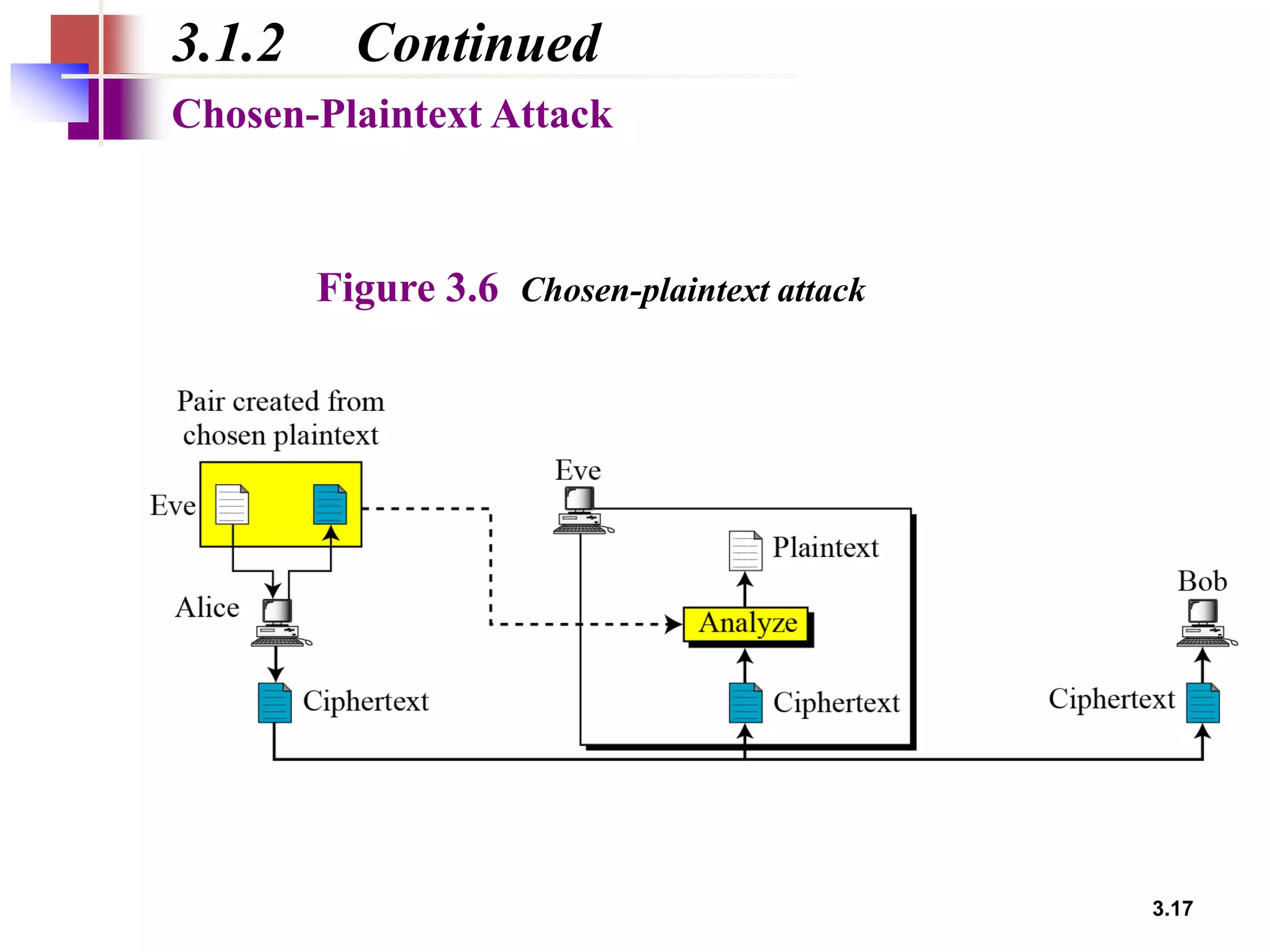
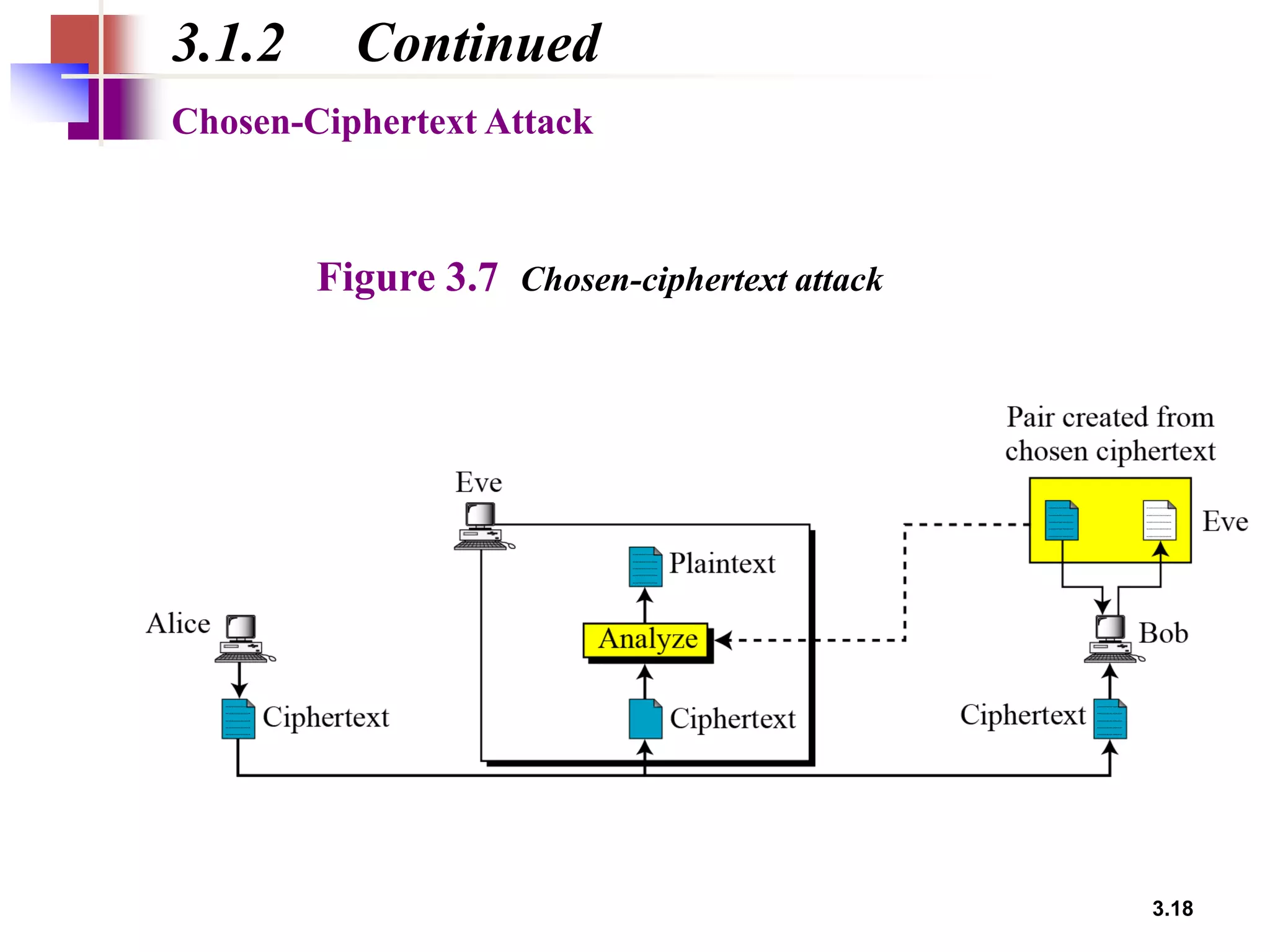
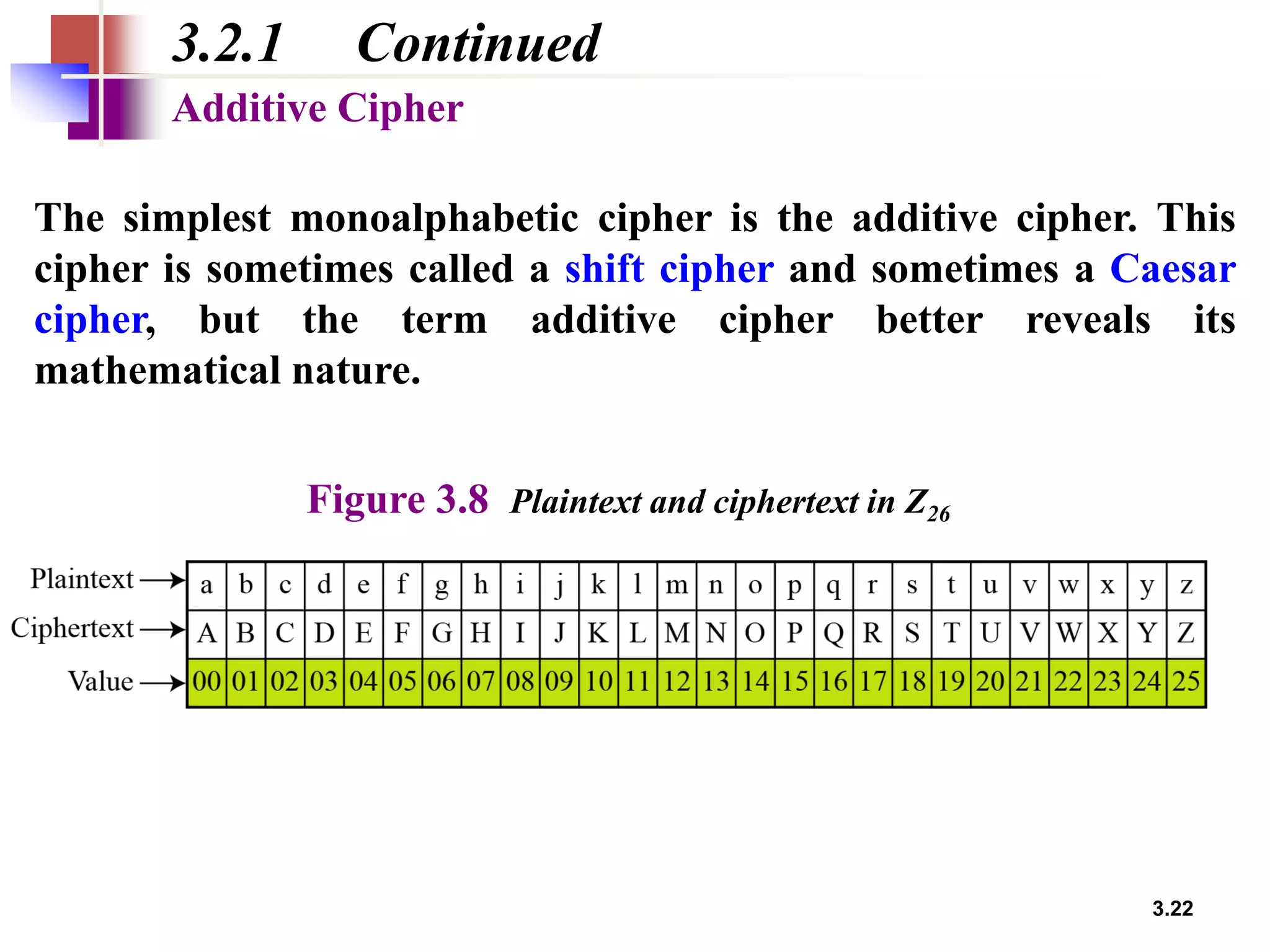
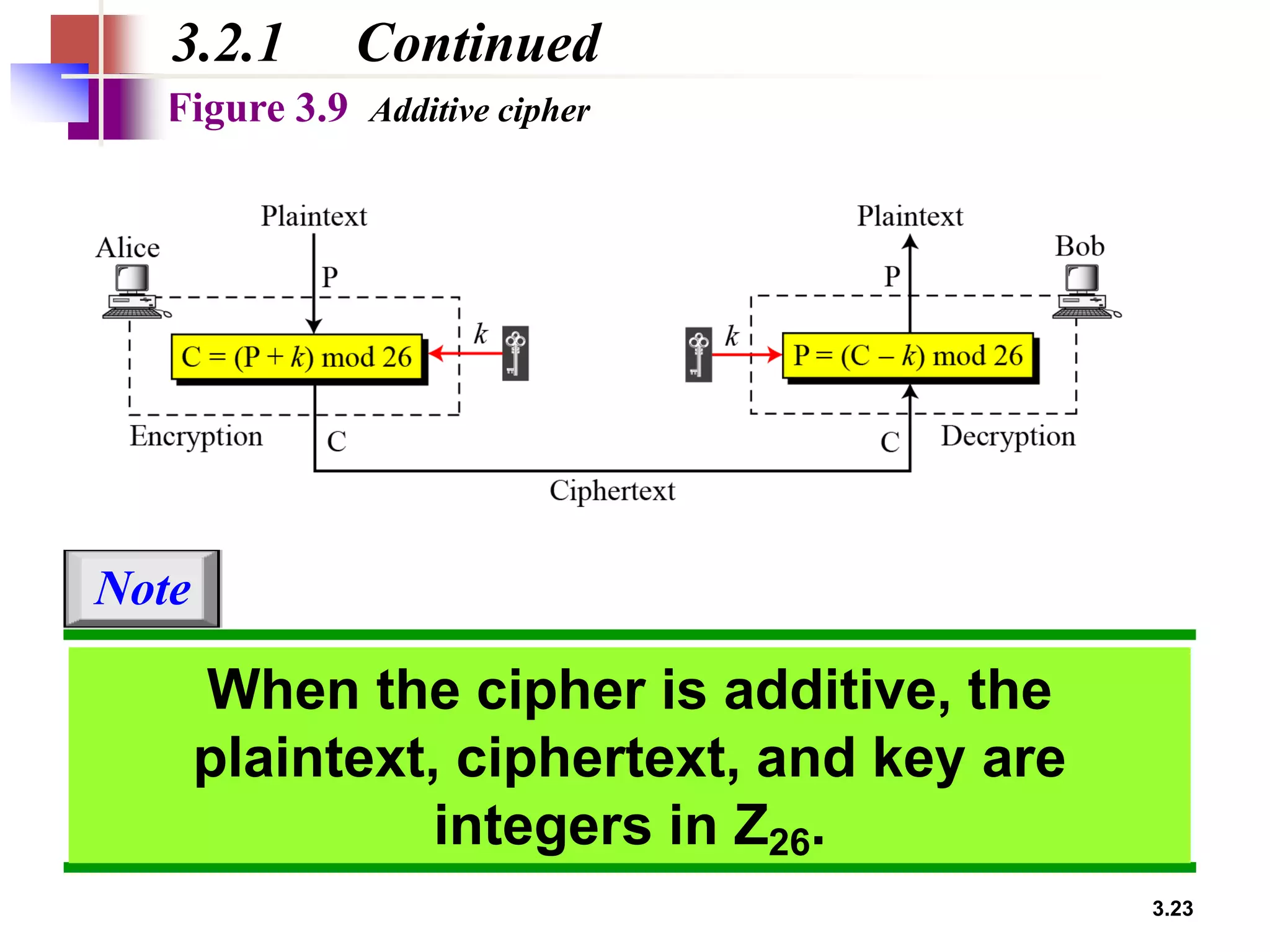
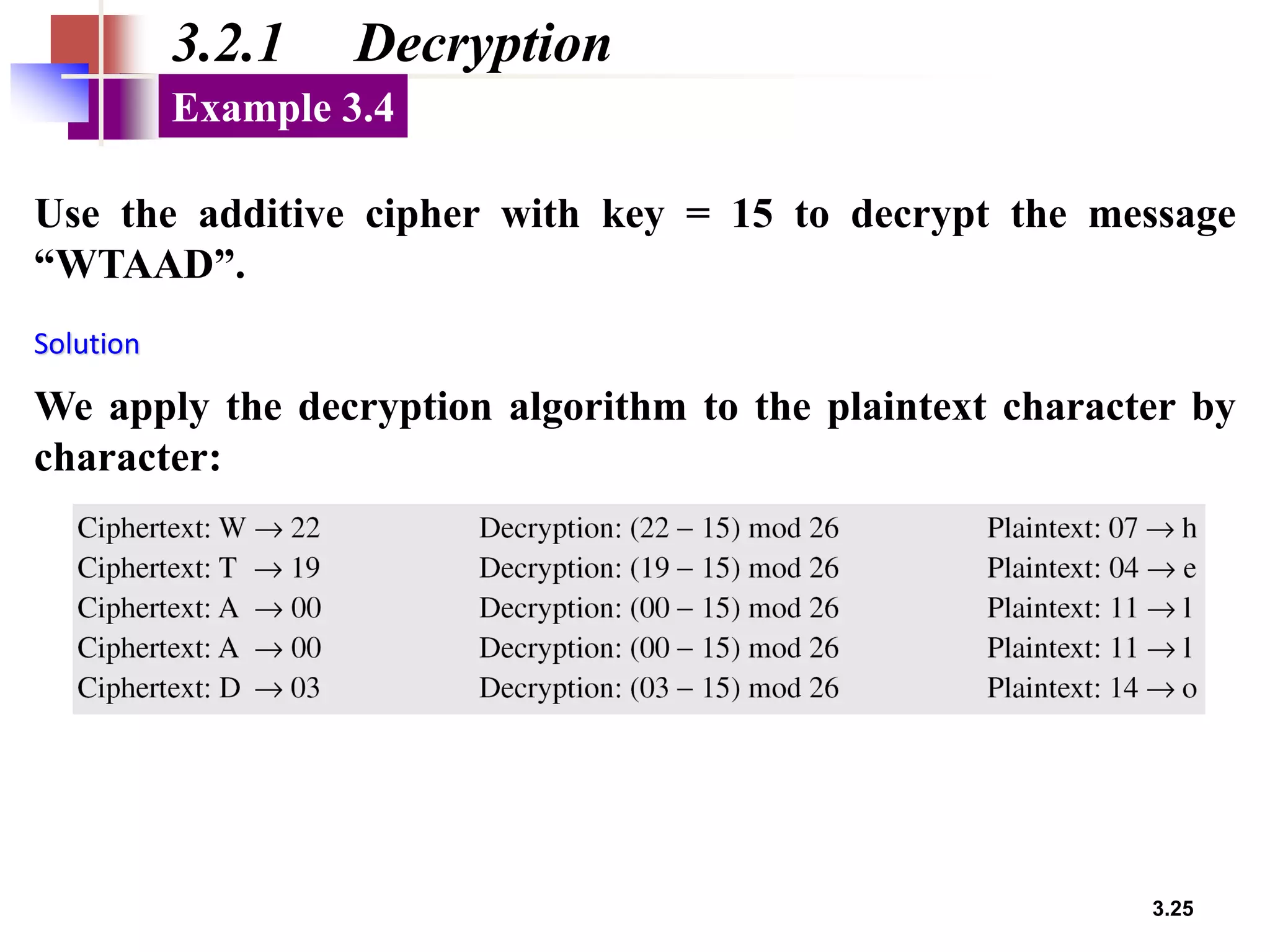
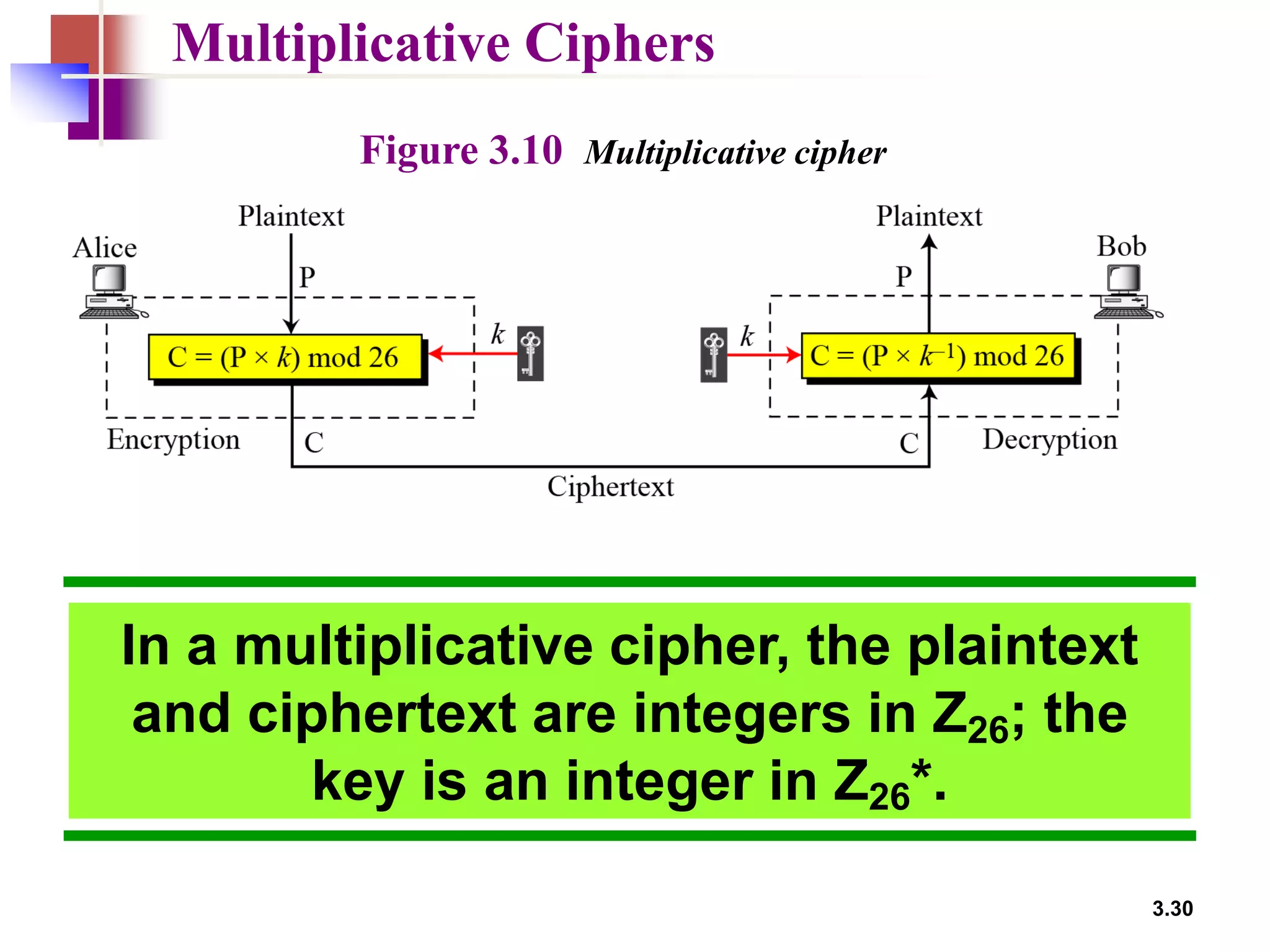
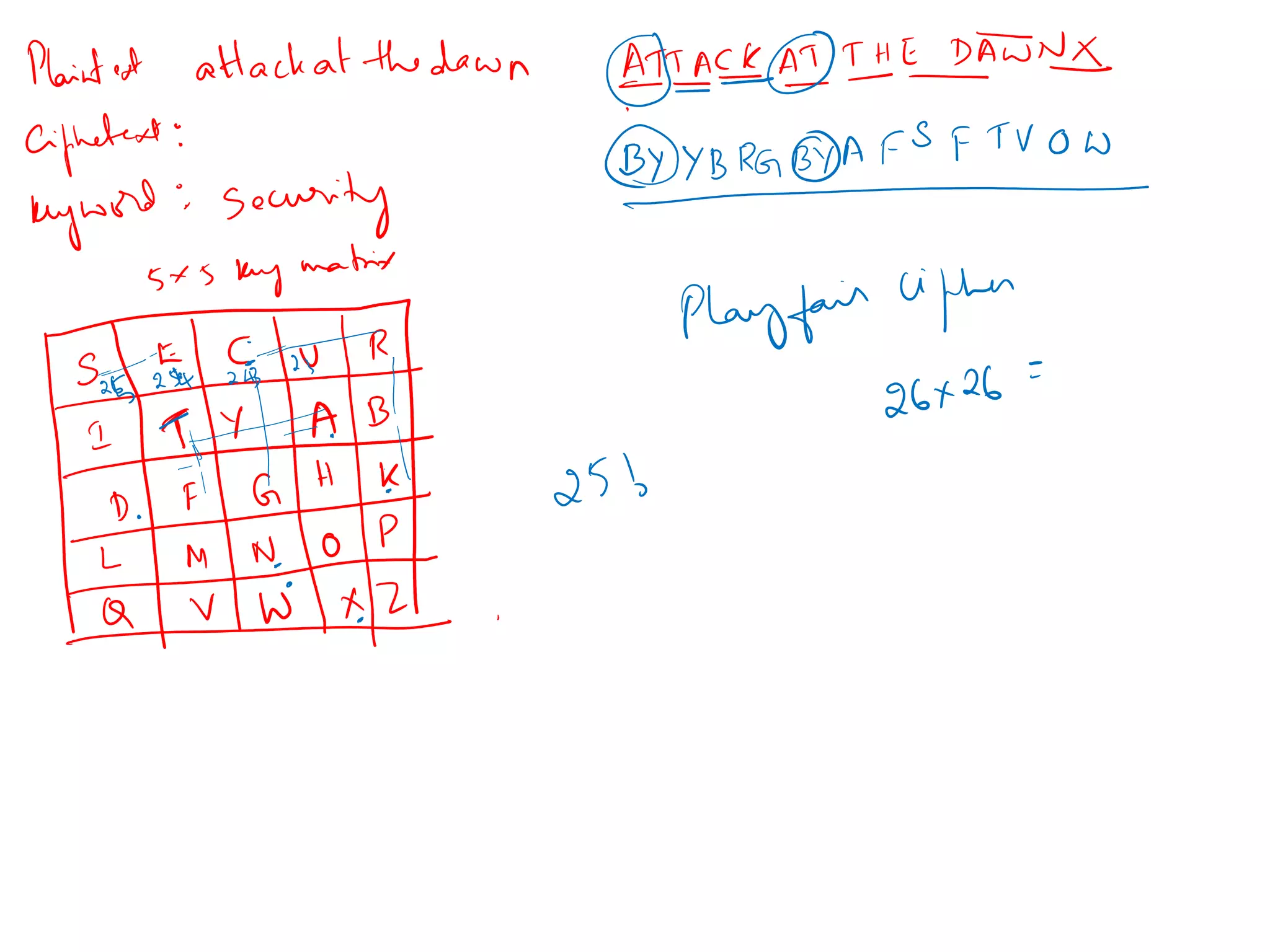
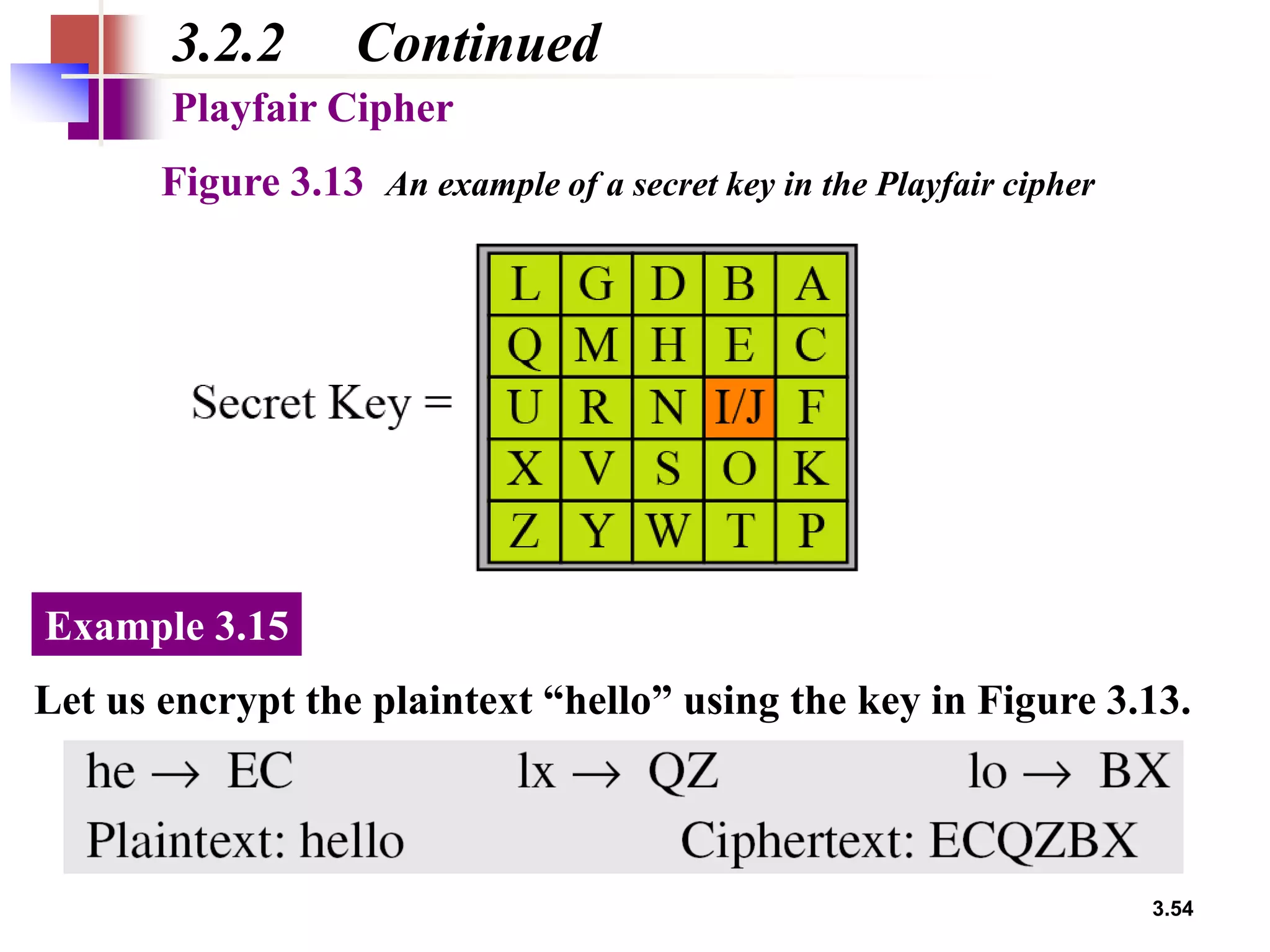
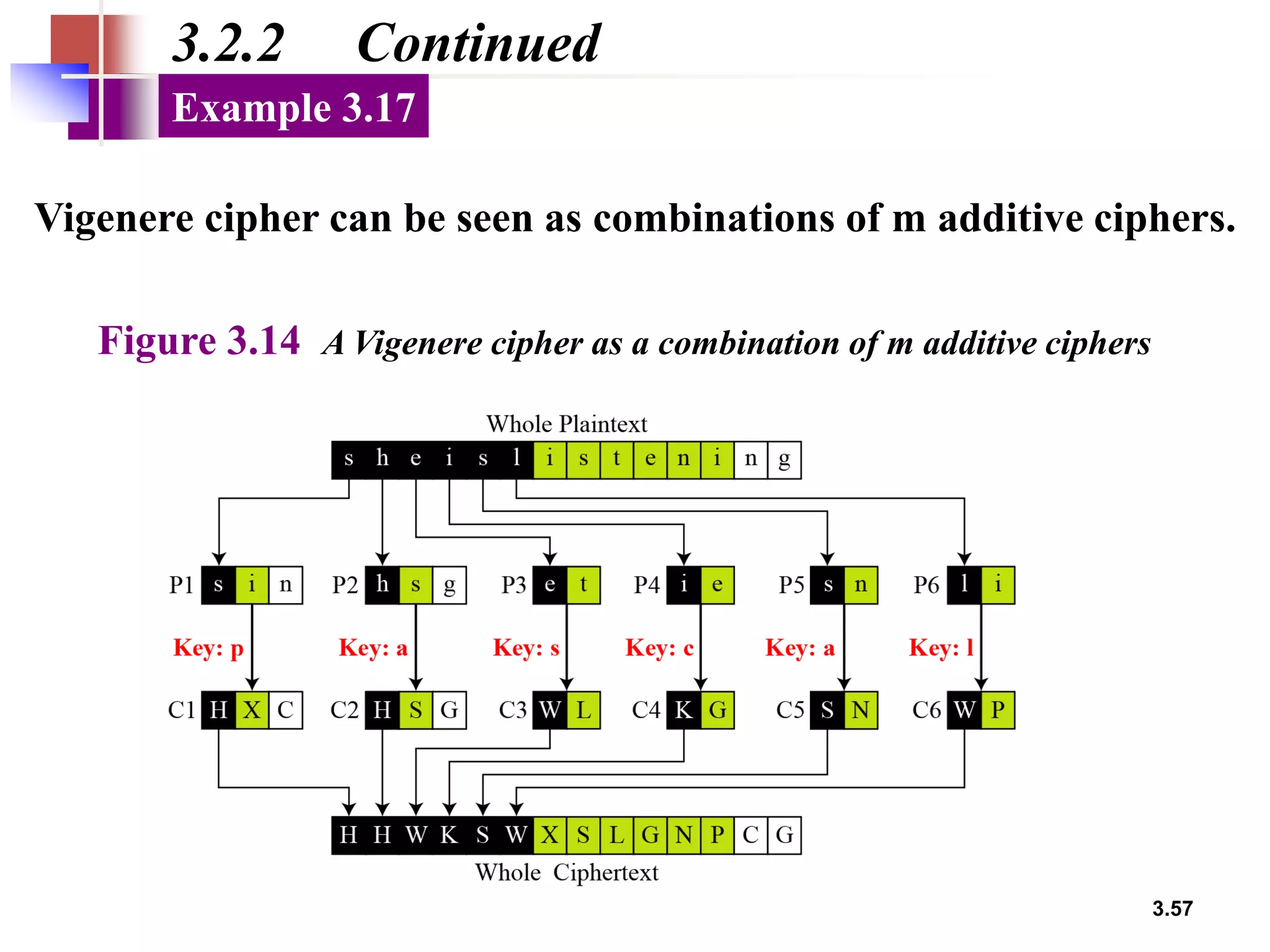
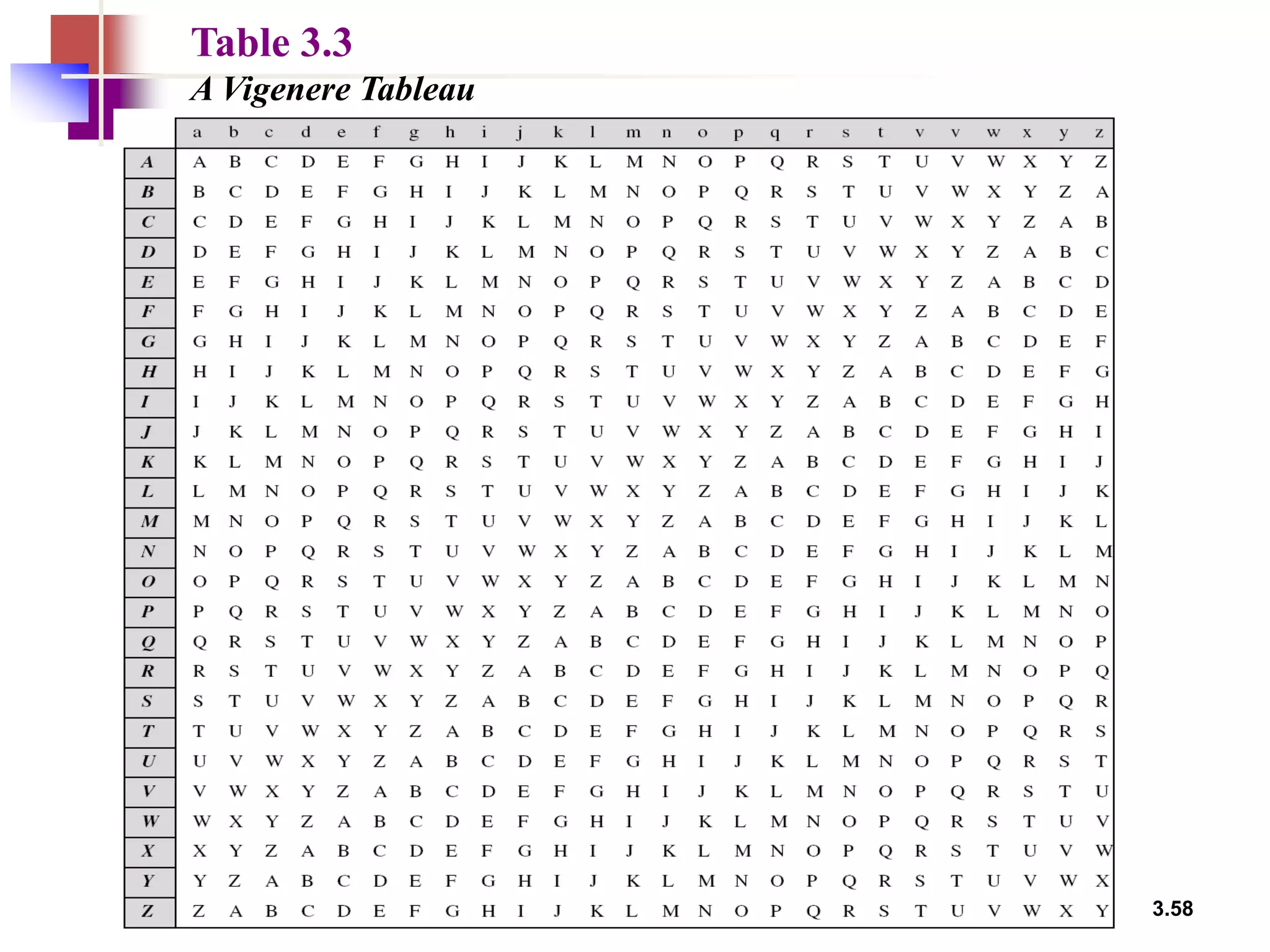
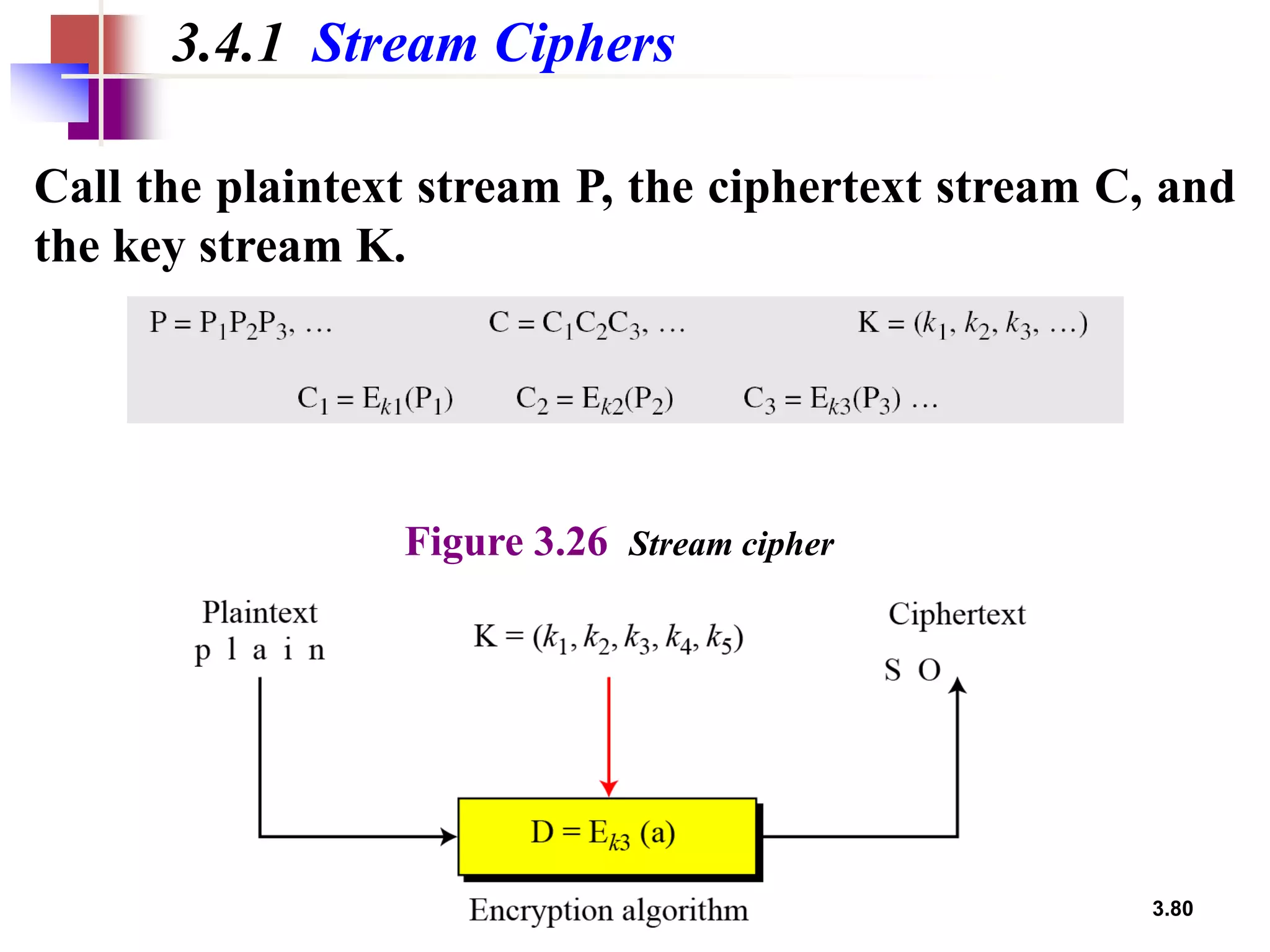
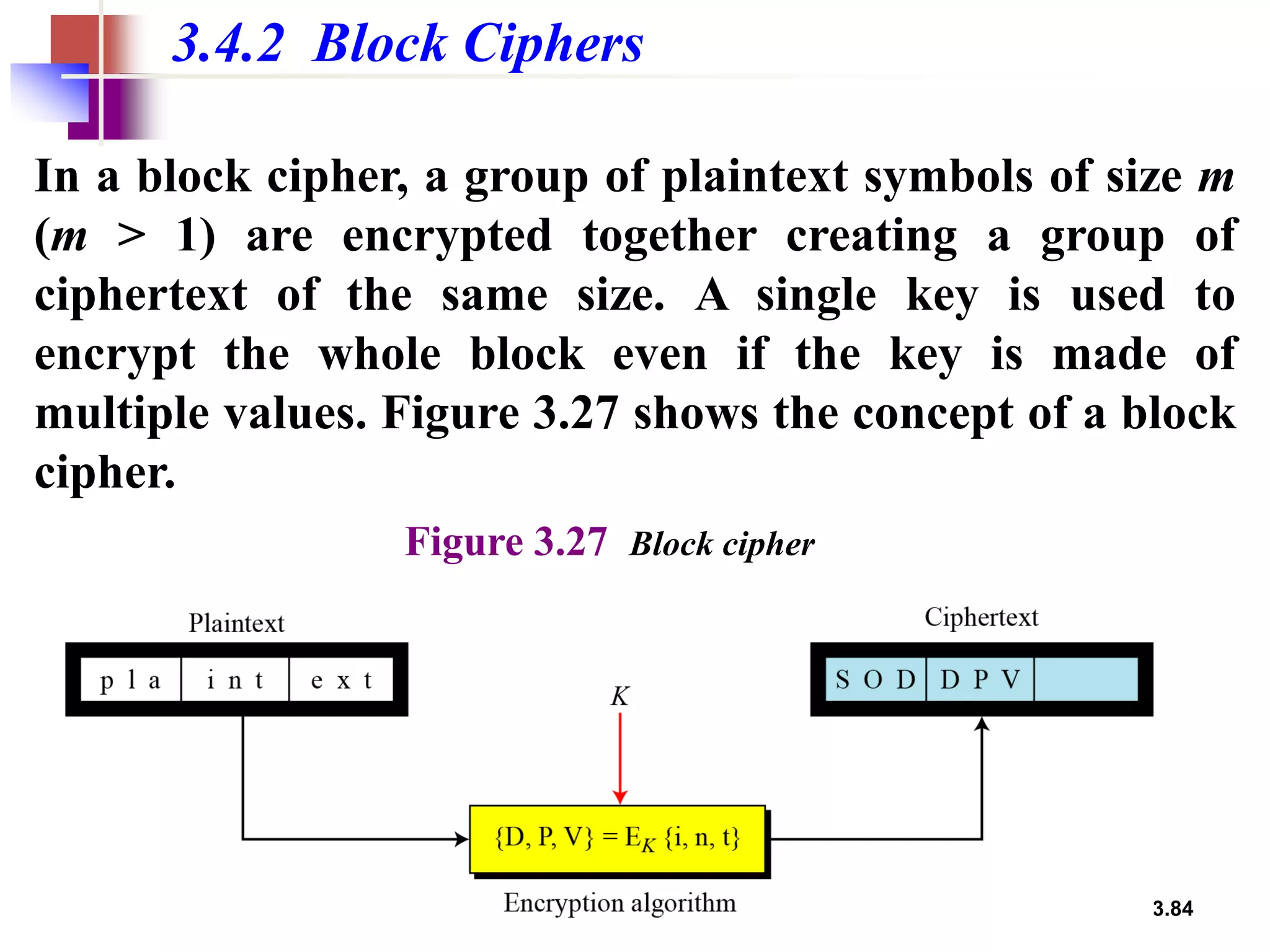
- Traditional symmetric key ciphers can be categorized as either substitution ciphers, which replace symbols, or transposition ciphers, which change the location of symbols.
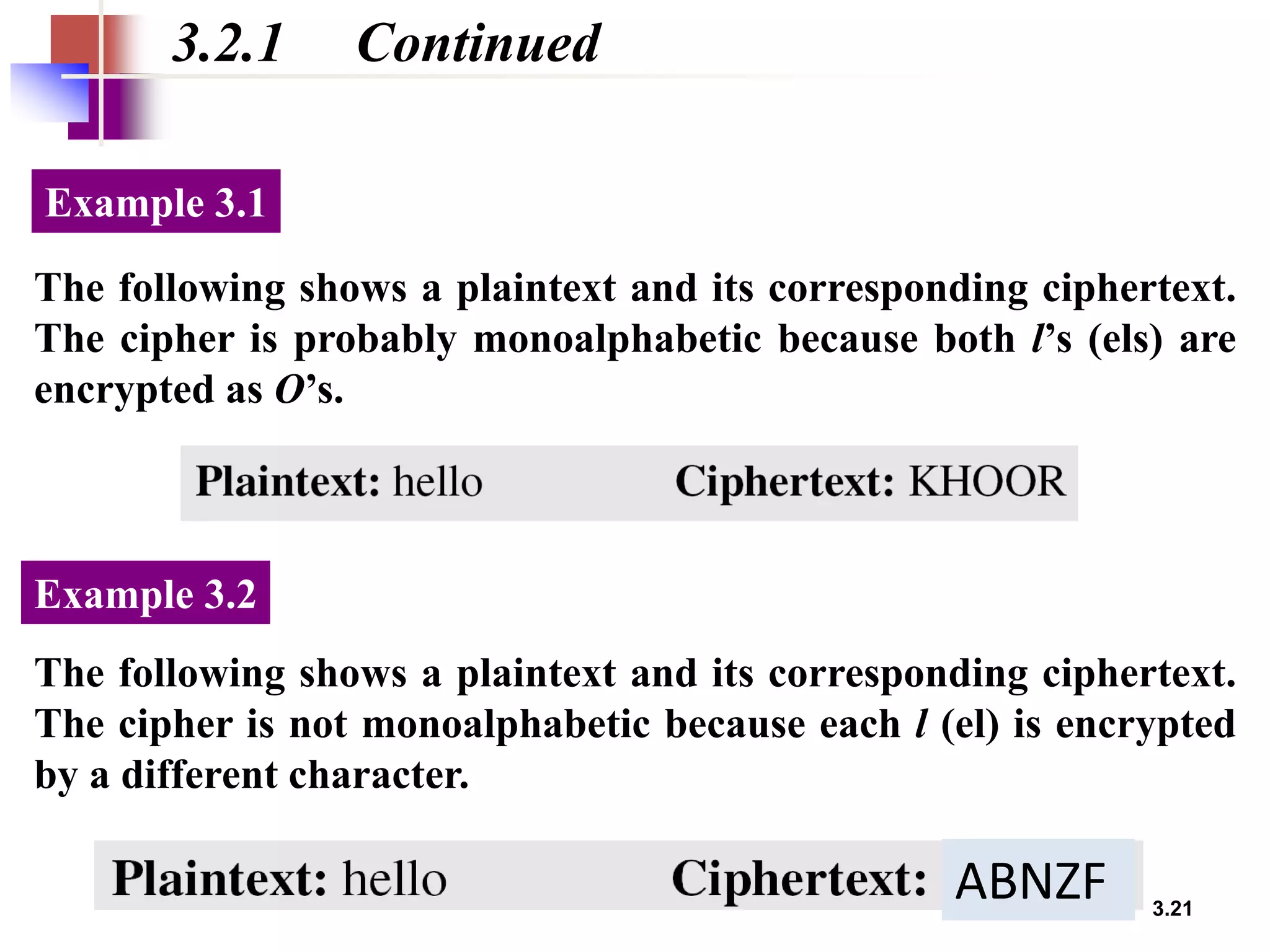
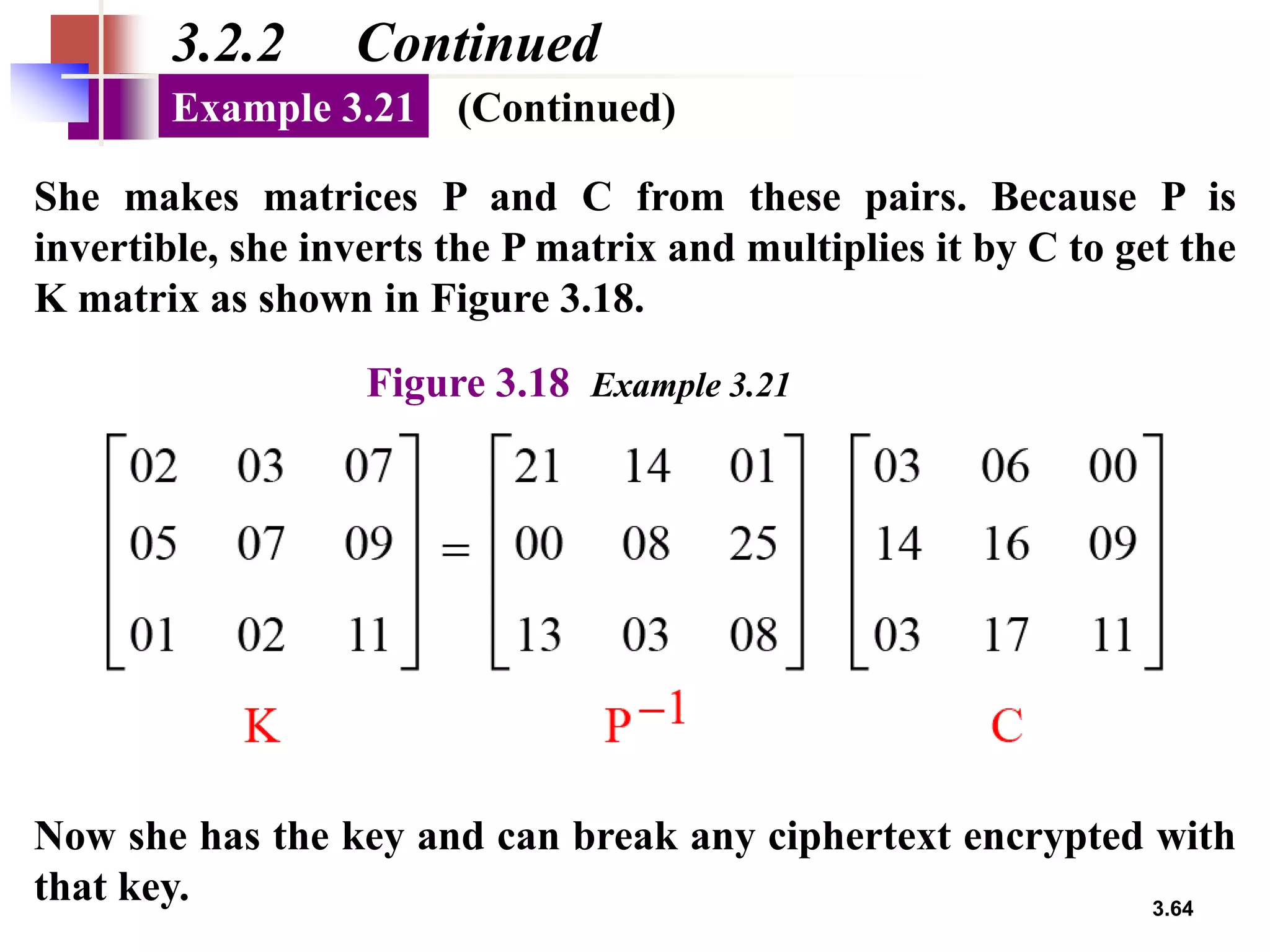
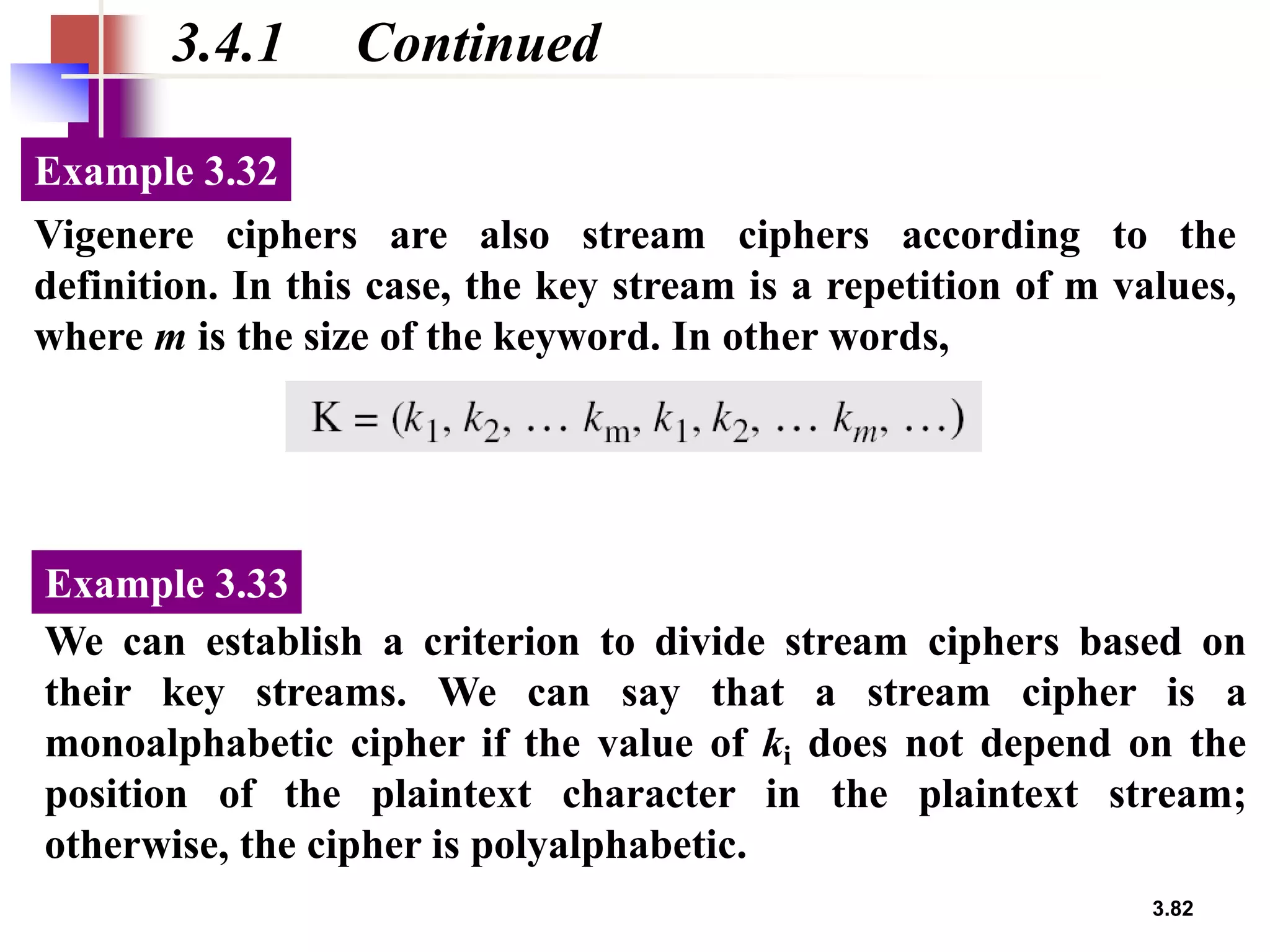
- For substitution ciphers, the document describes various monoalphabetic ciphers (such as the Caesar cipher) and polyalphabetic ciphers (such as the Vigenere cipher and Hill cipher).
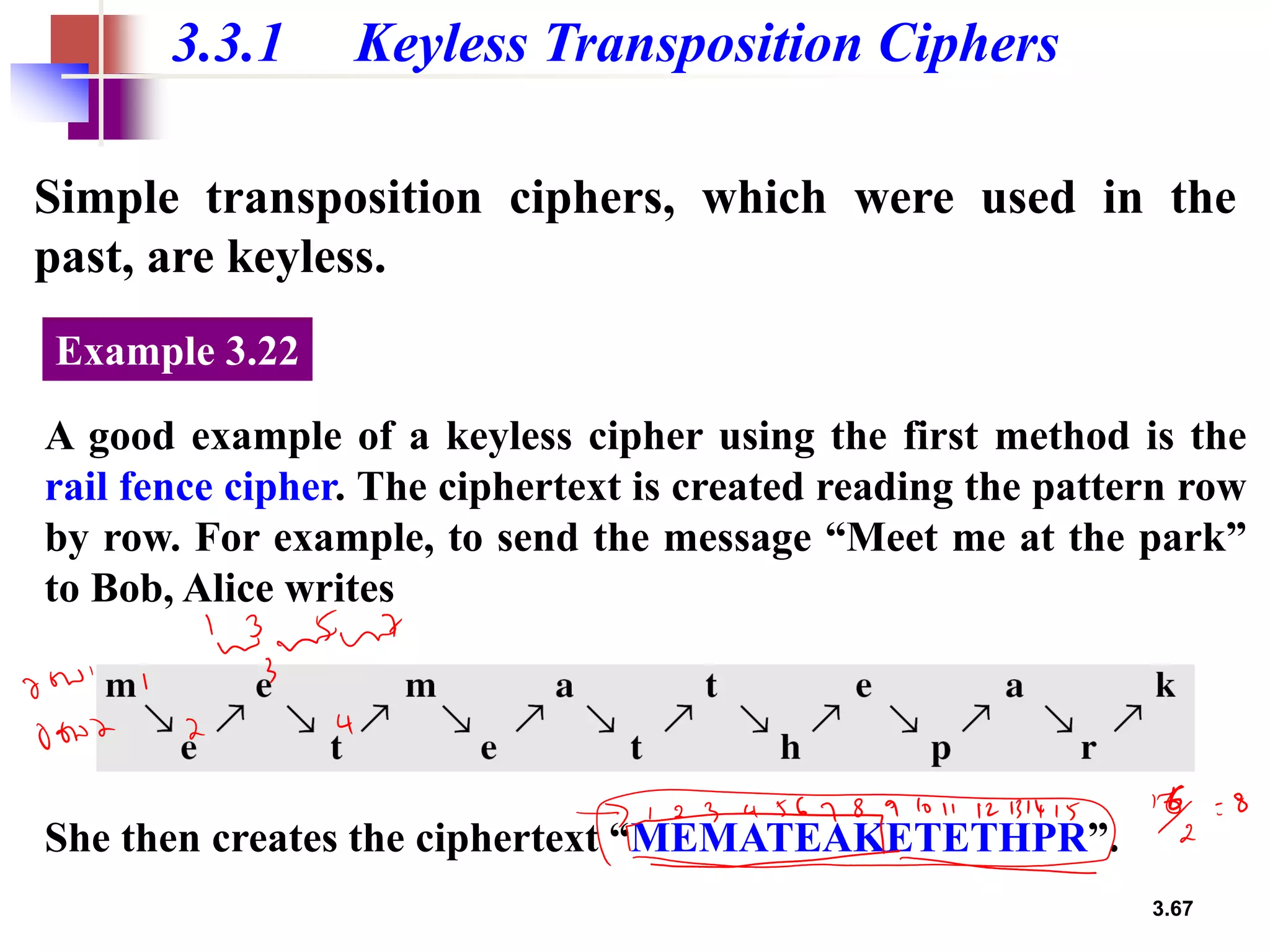
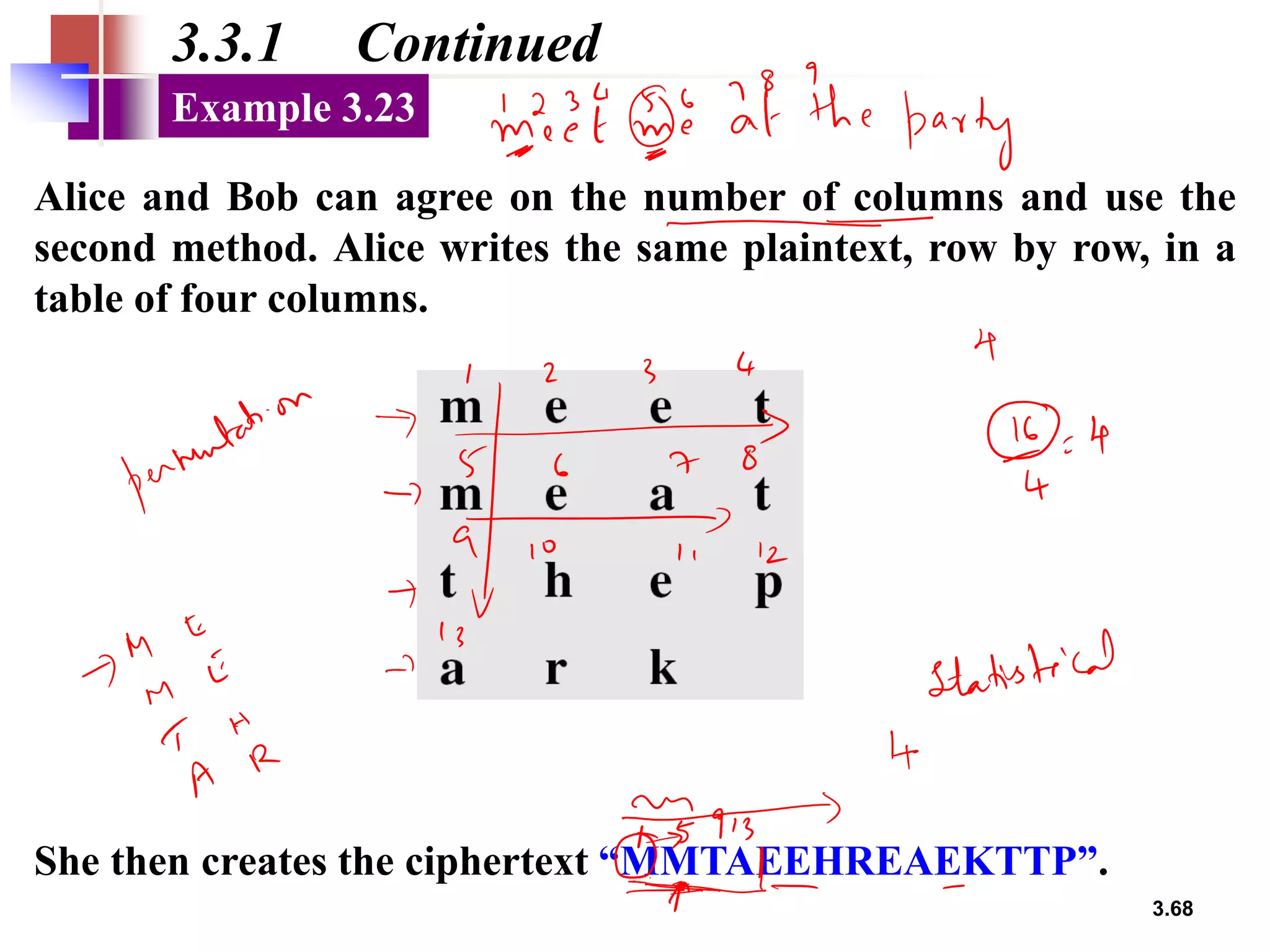
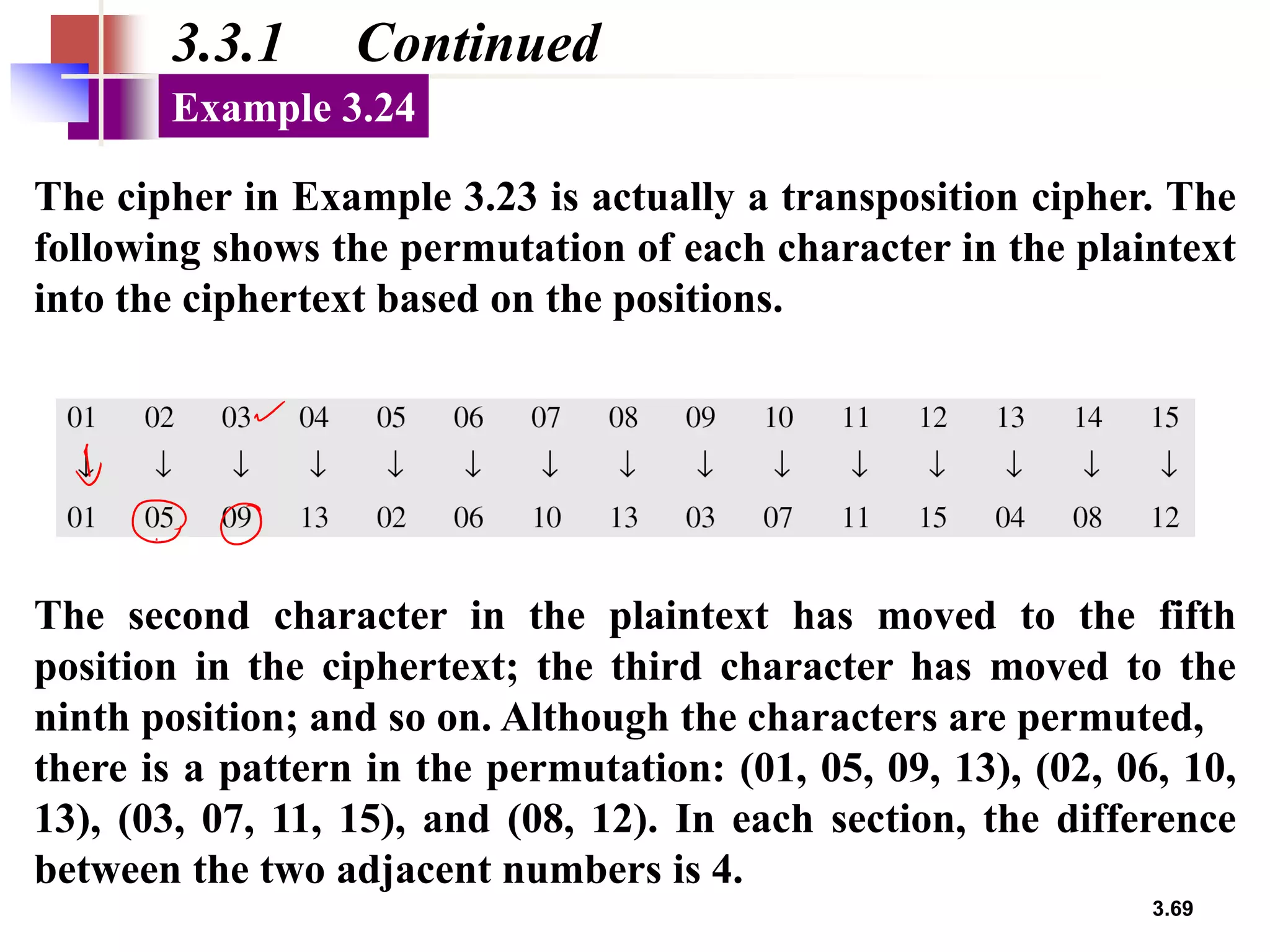
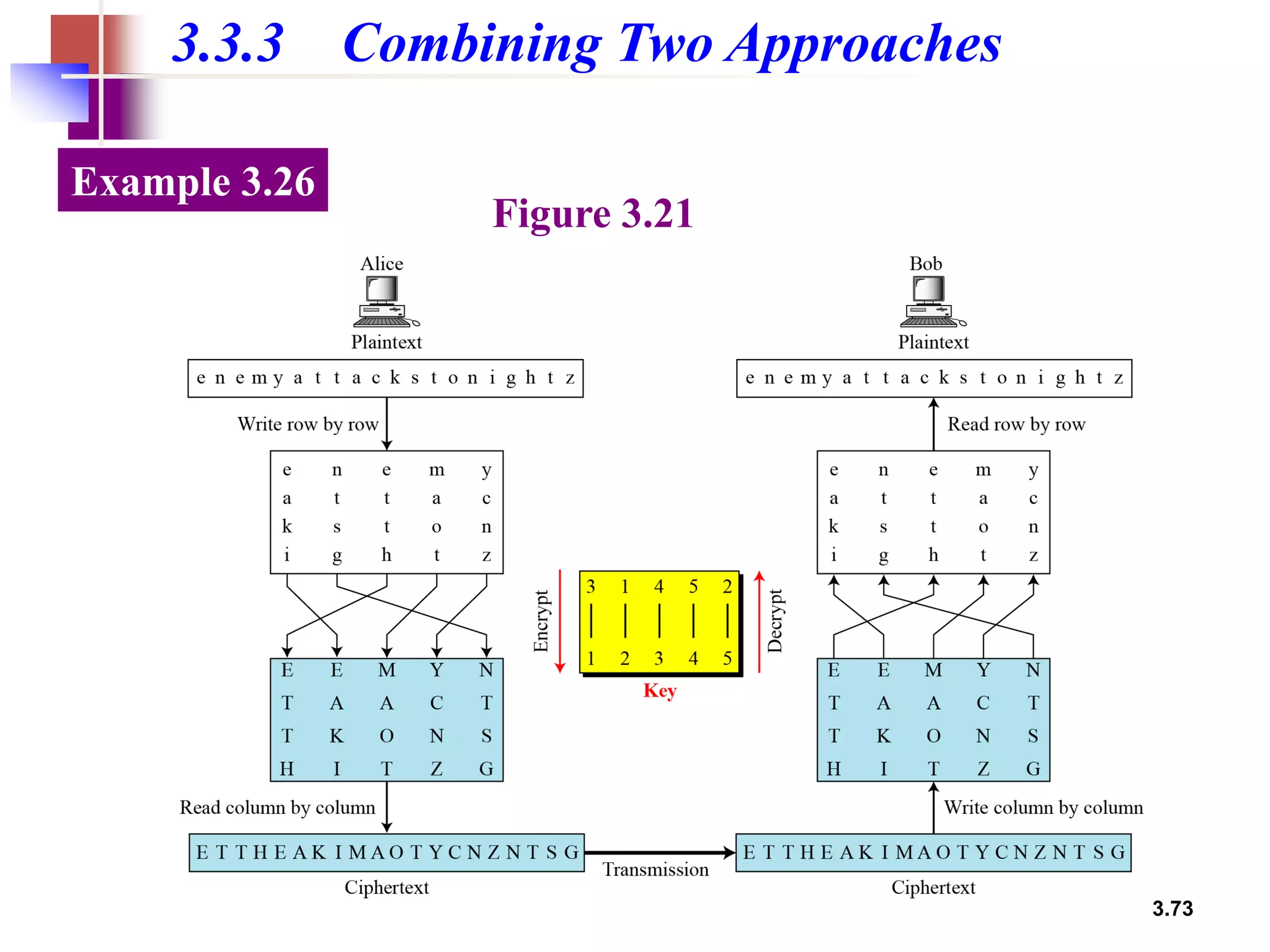
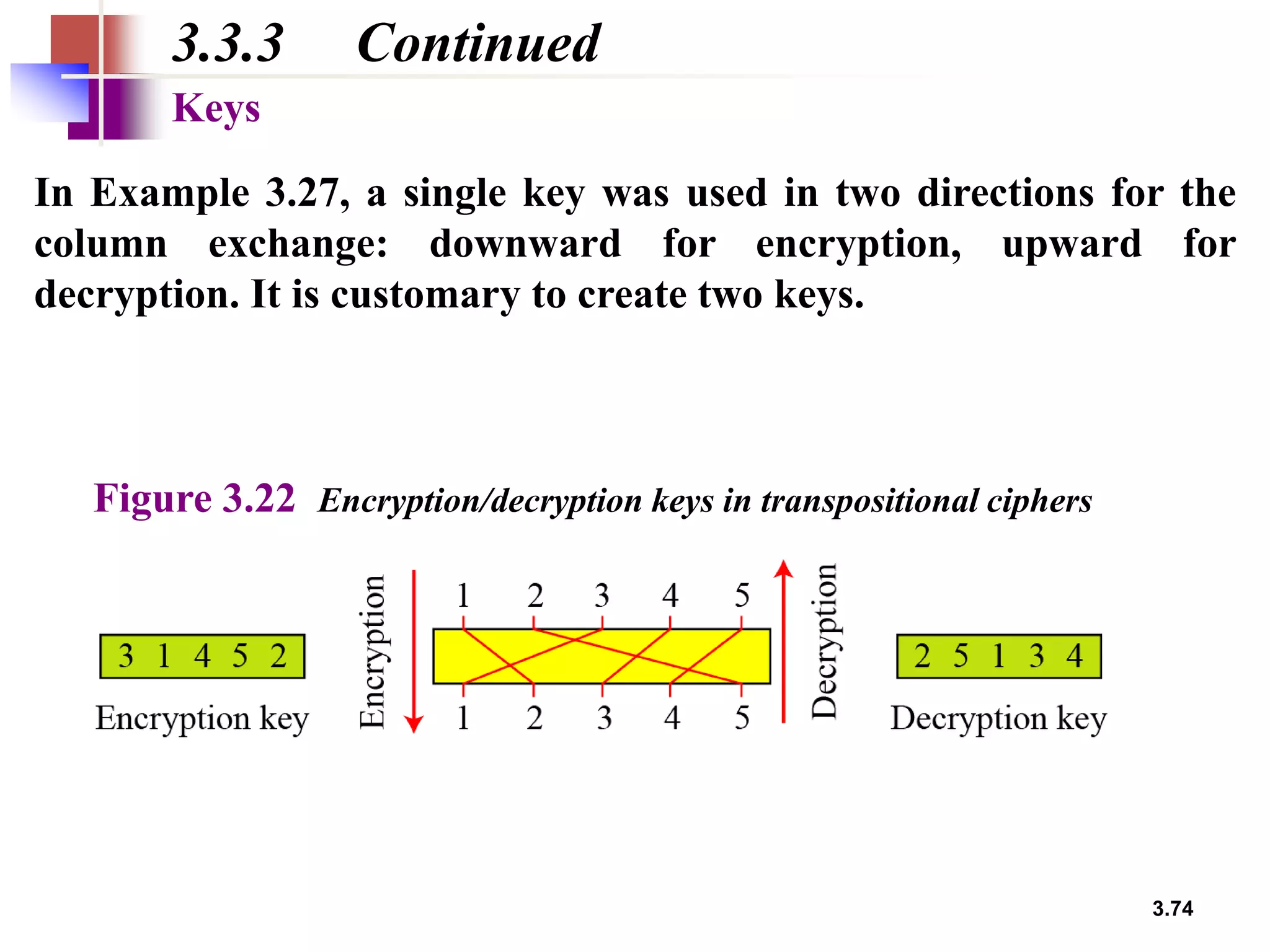
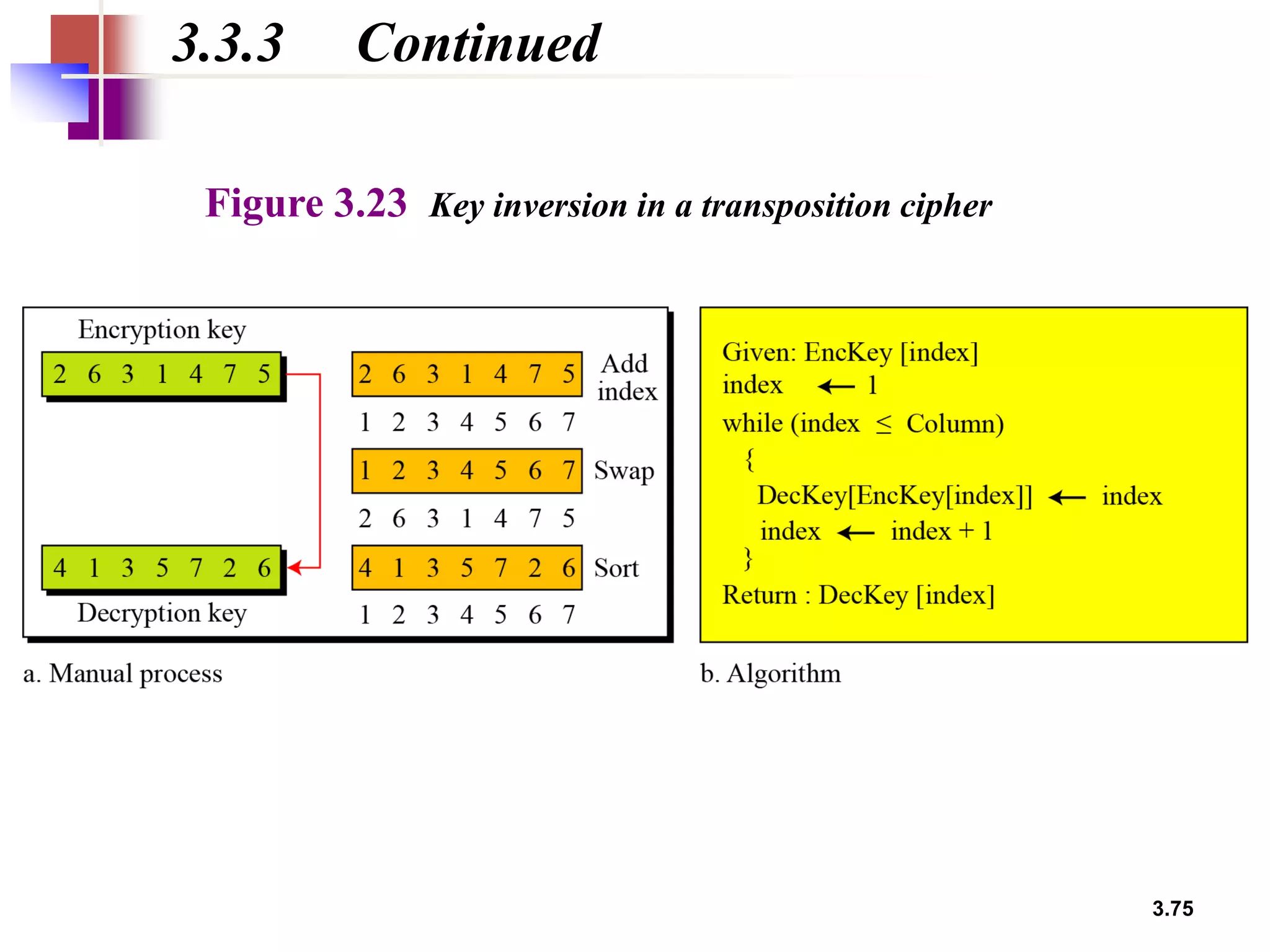
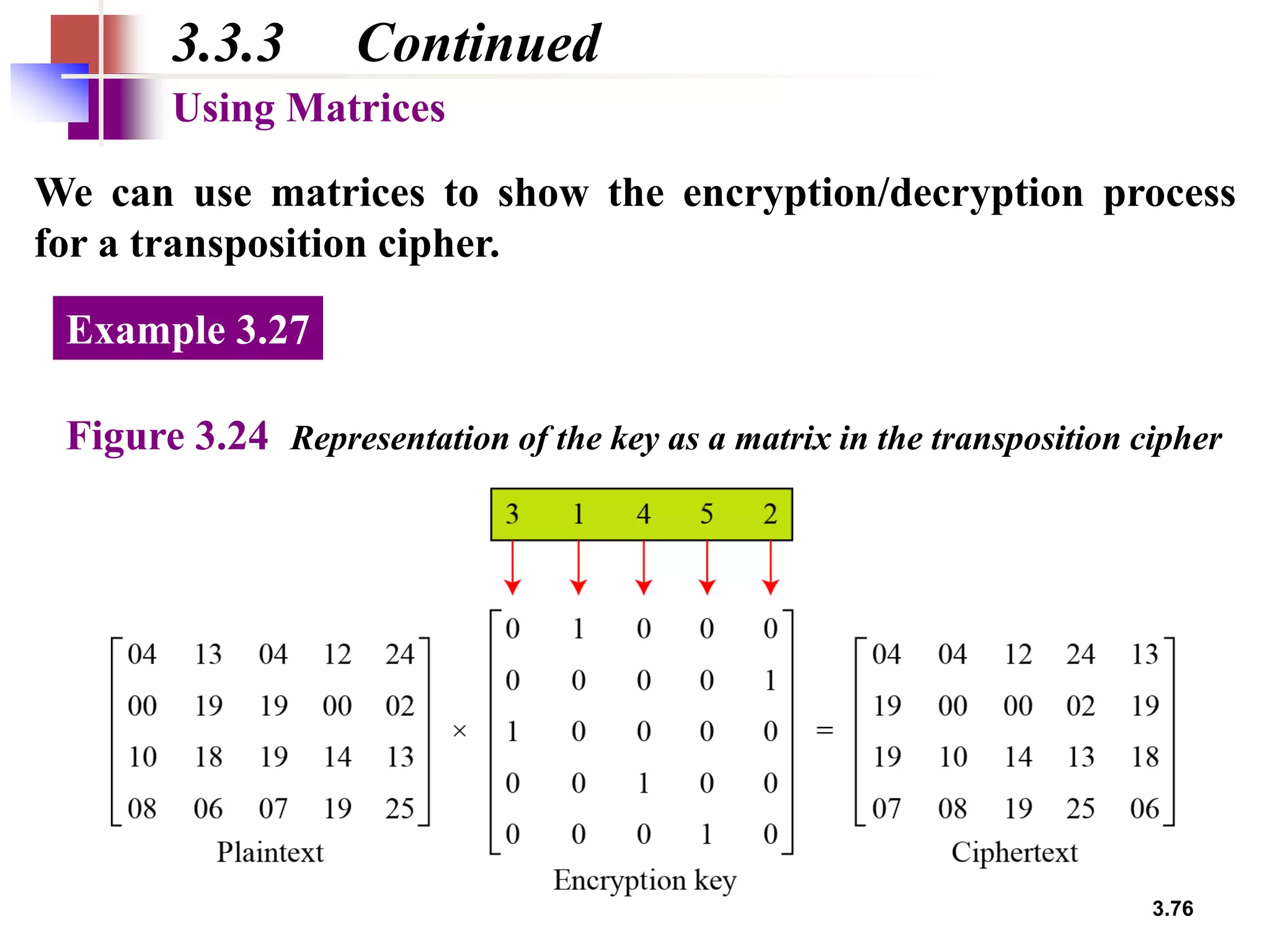
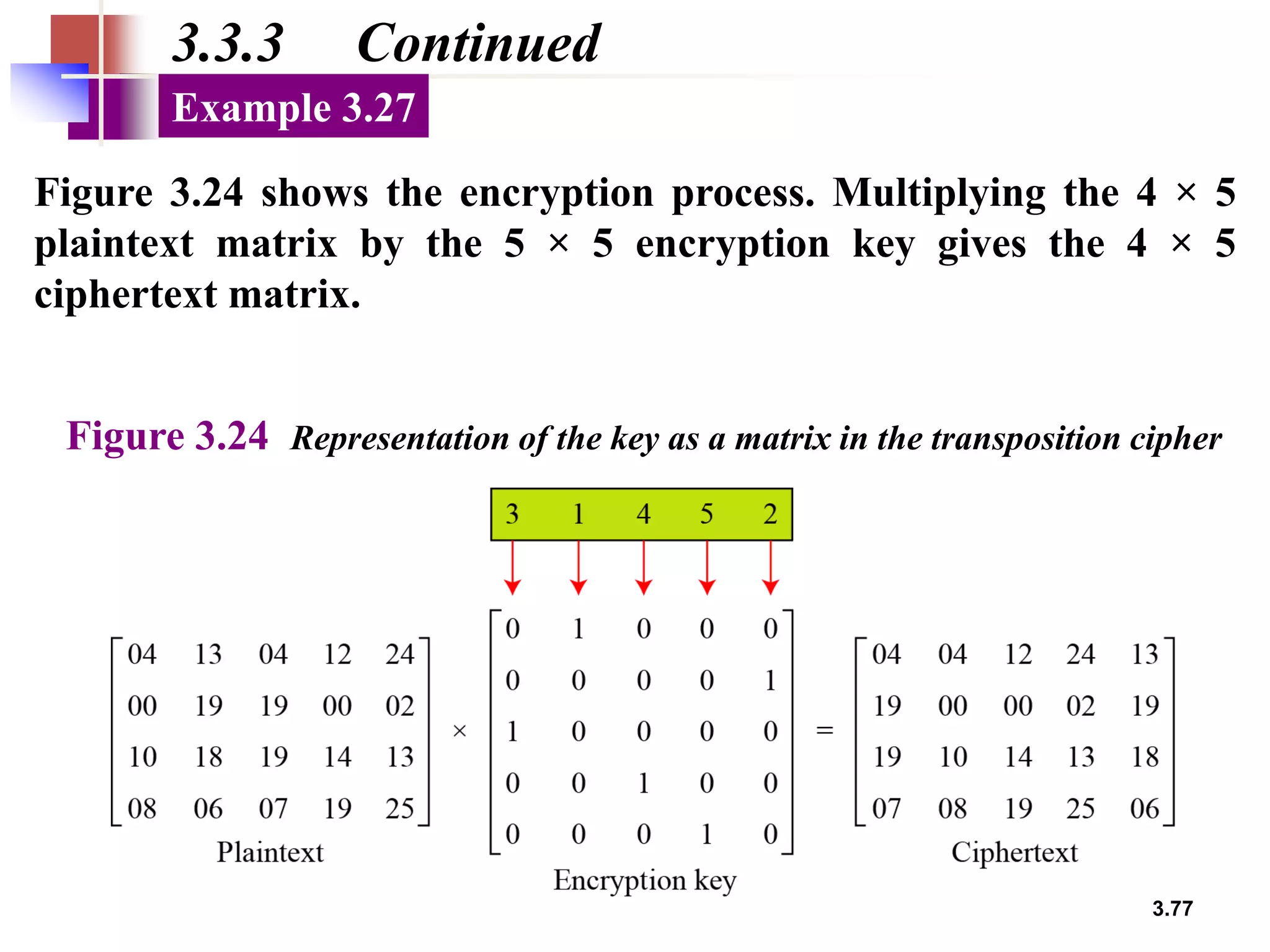
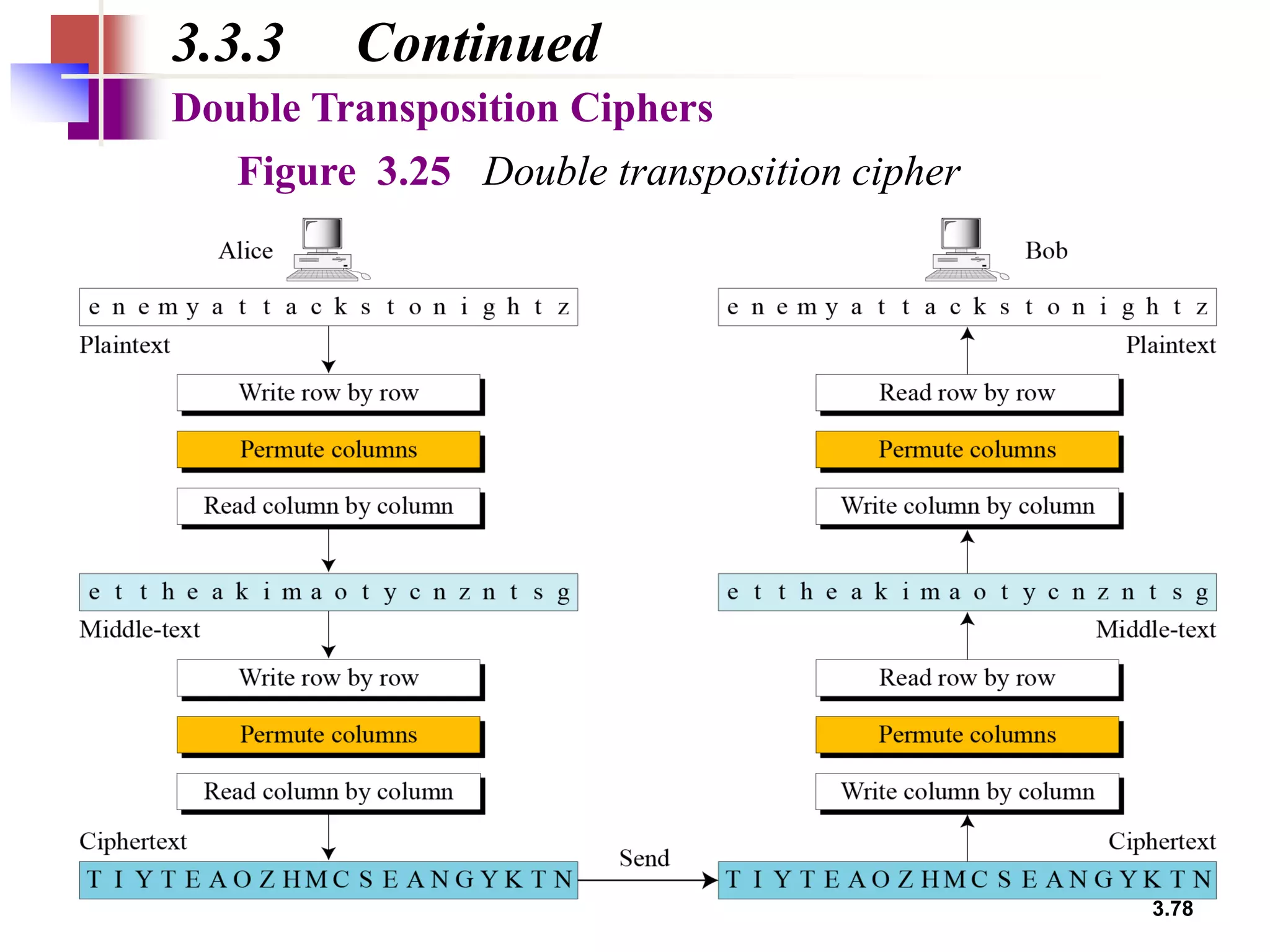
- For transposition ciphers, it discusses both keyless transposition techniques like the rail fence cipher as well as keyed transposition ciphers that permute symbols within blocks defined by a key.