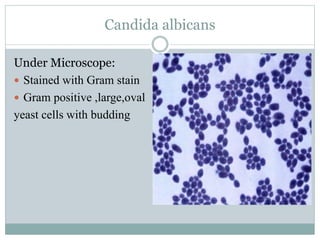
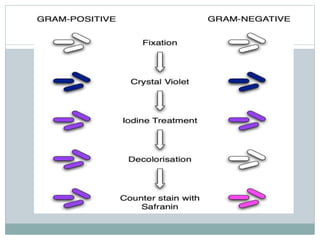
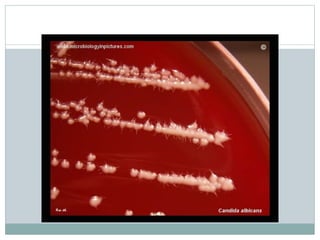
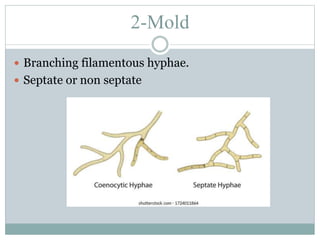
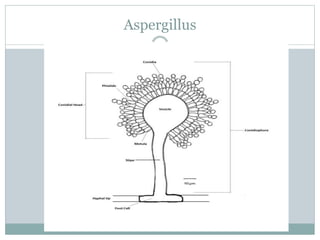
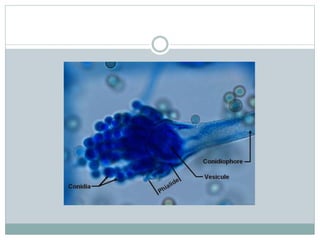
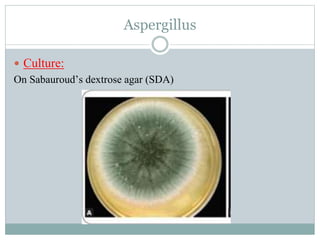
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that are divided into three main groups: yeasts, molds, and dimorphic fungi. Yeasts are unicellular, oval or rounded organisms that reproduce asexually by budding. Molds are filamentous fungi that form branching hyphae and reproduce sexually through spores. Dimorphic fungi can exist in both yeast and filamentous forms depending on temperature. Candida albicans is a common yeast pathogen of humans that appears gram-positive and oval under the microscope and forms creamy, pasty colonies on Sabouraud's dextrose agar. Aspergillus is a mold that has branching septate hyphae and conidiophores terminating