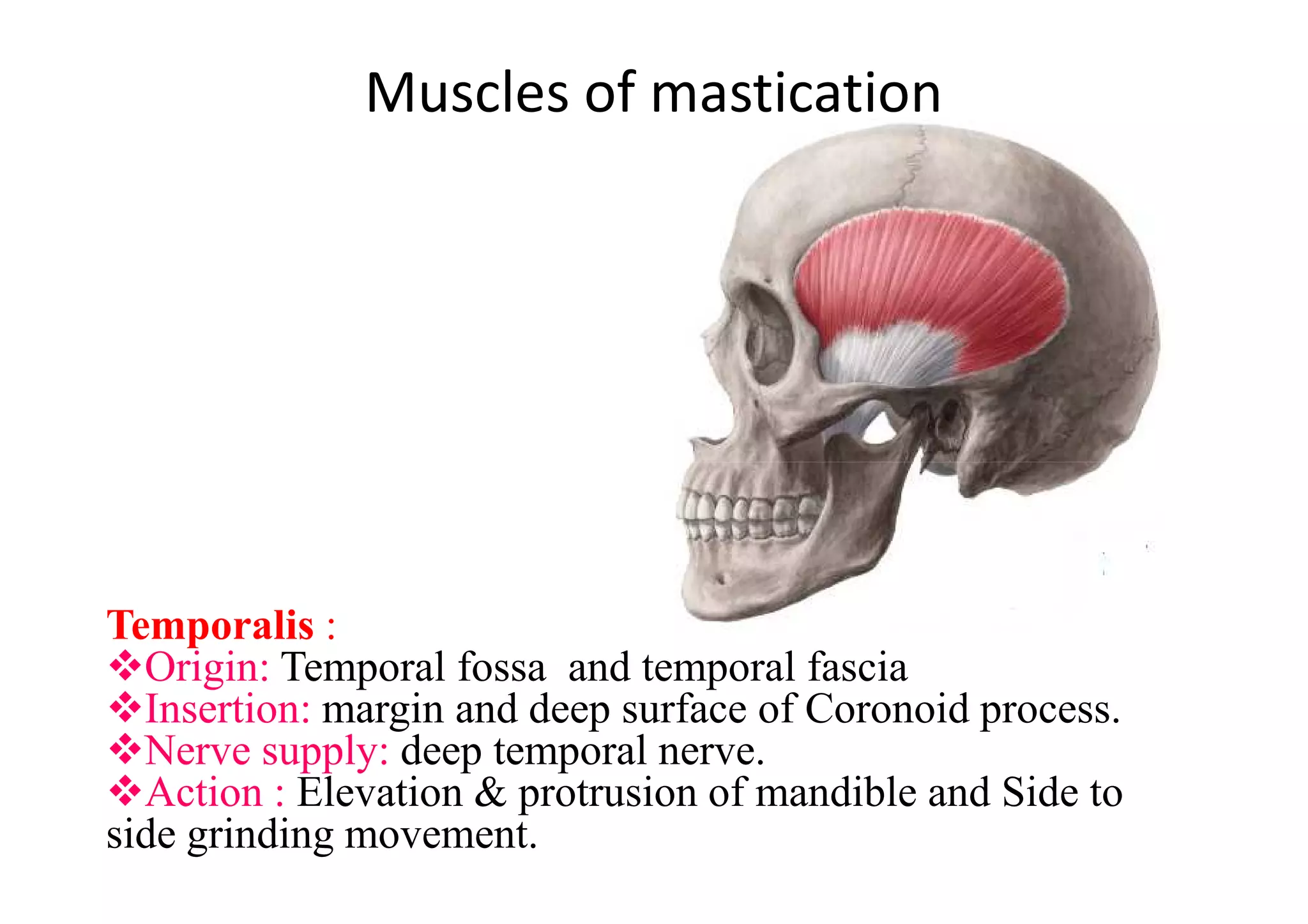
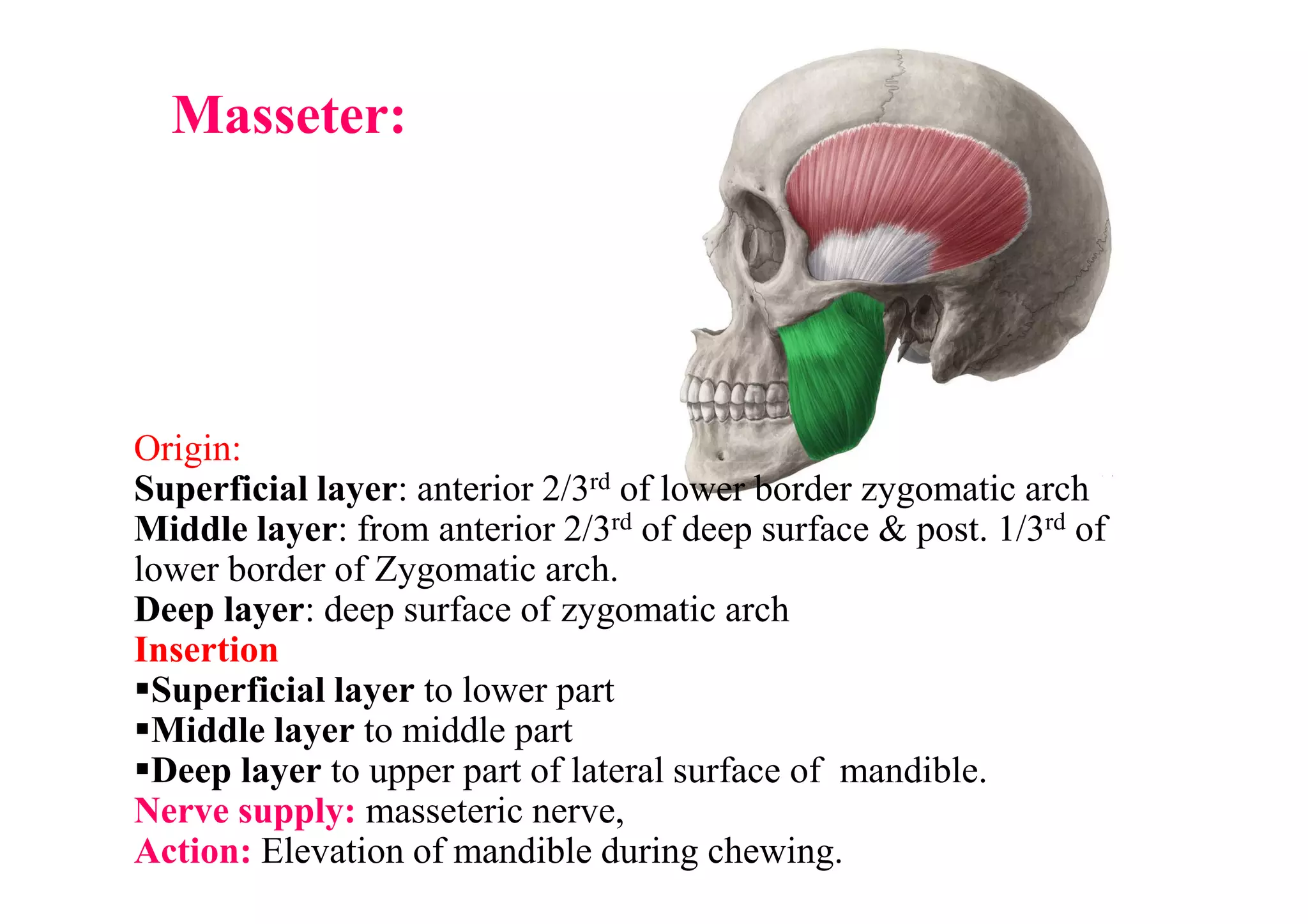
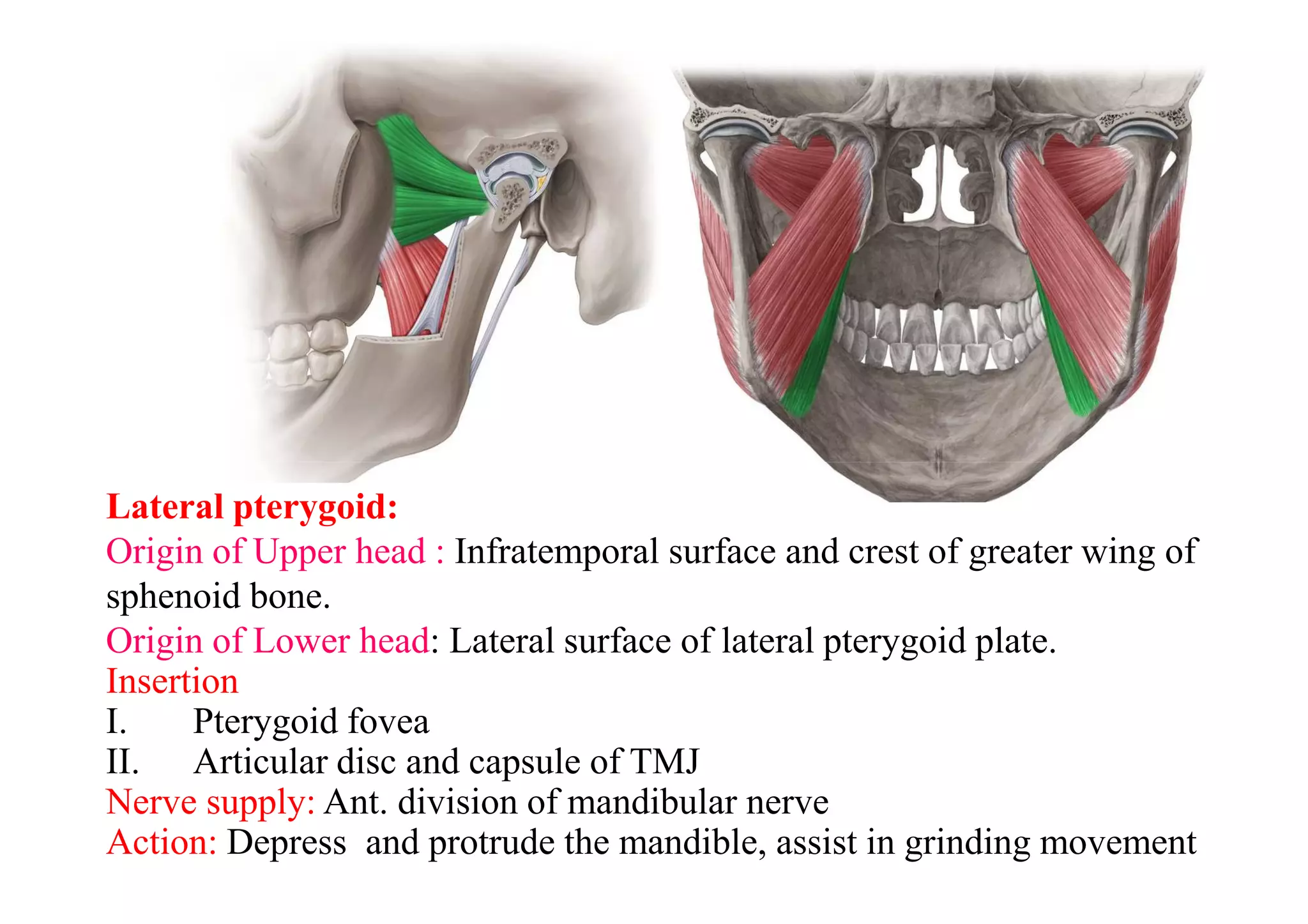
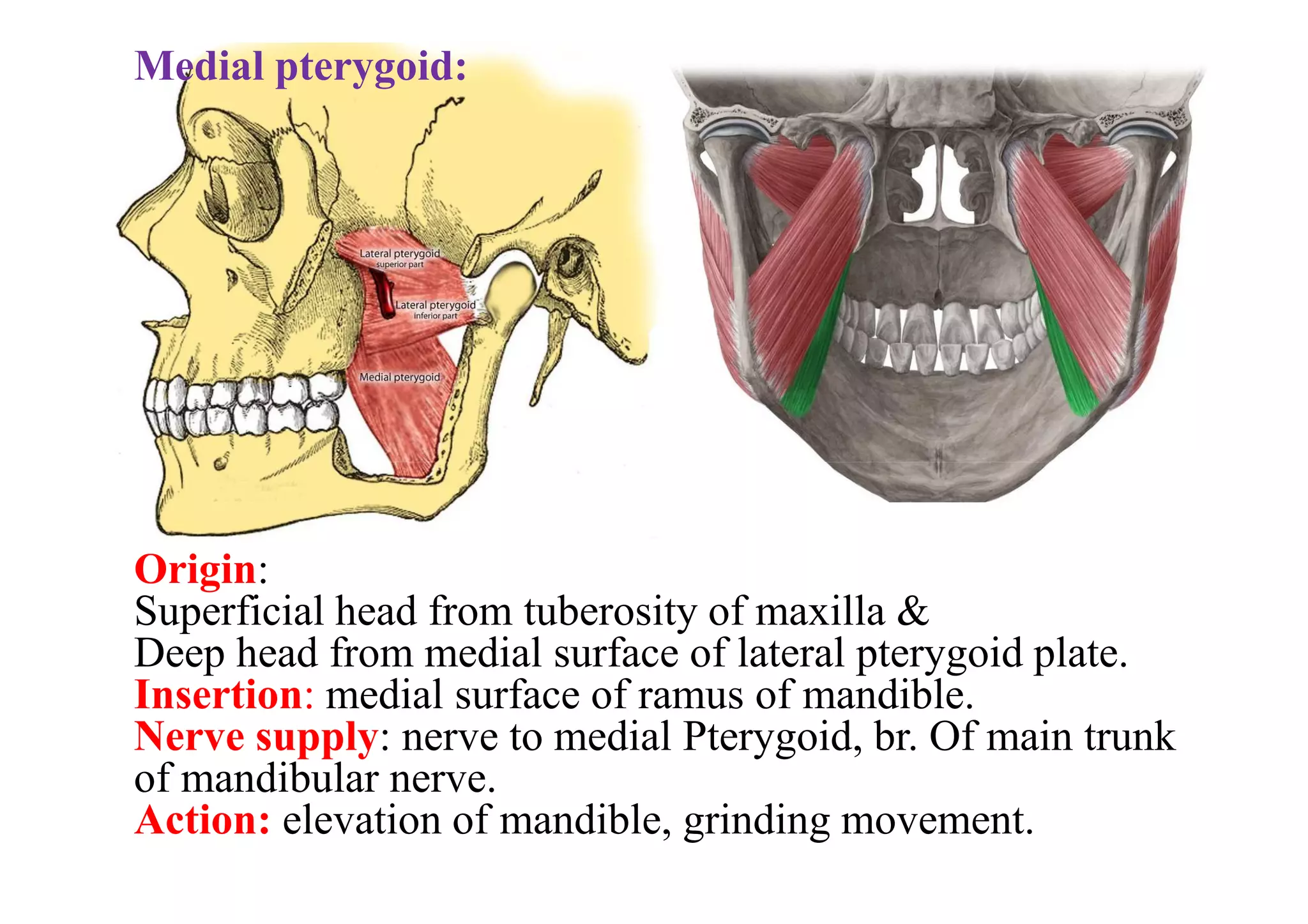
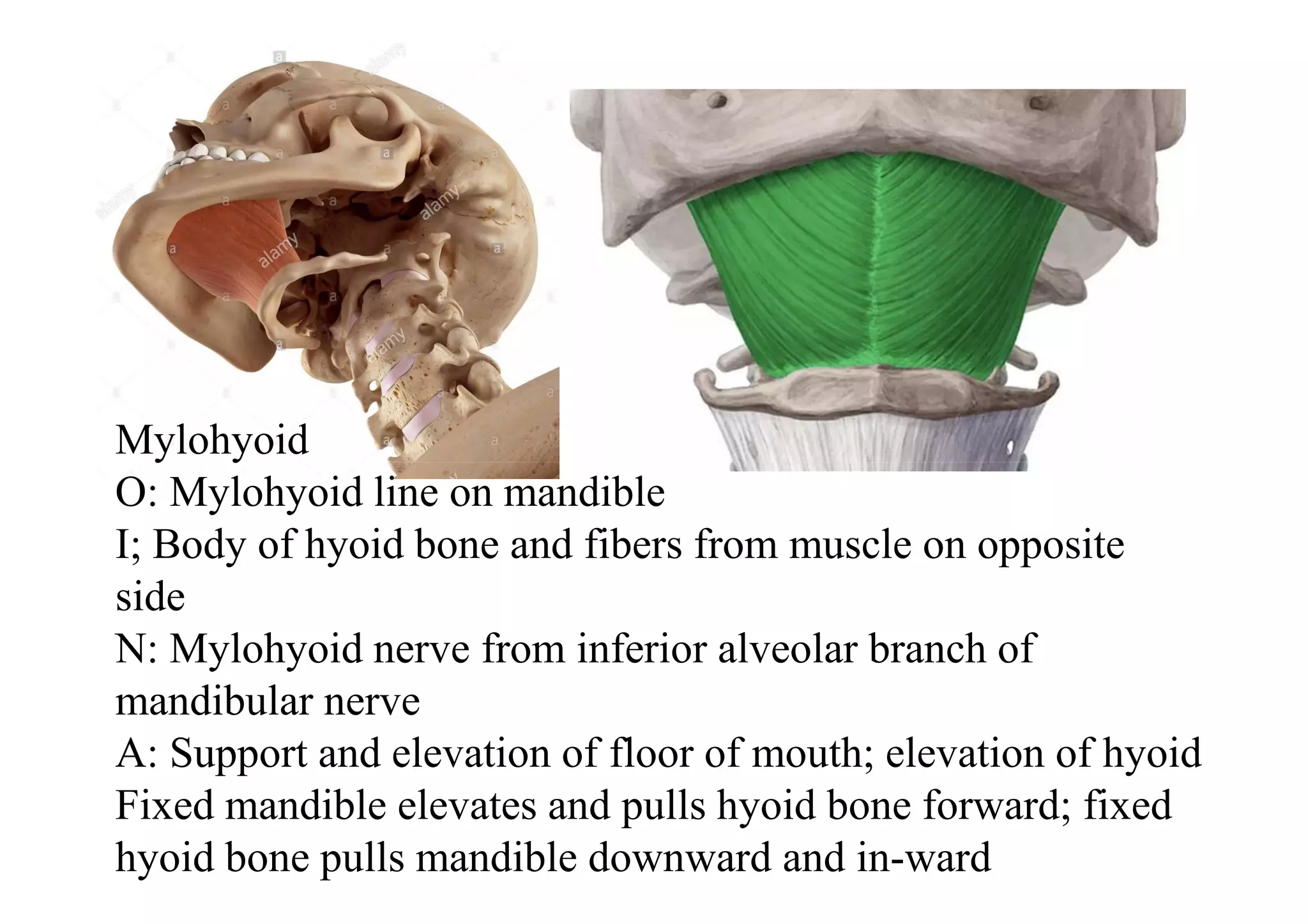
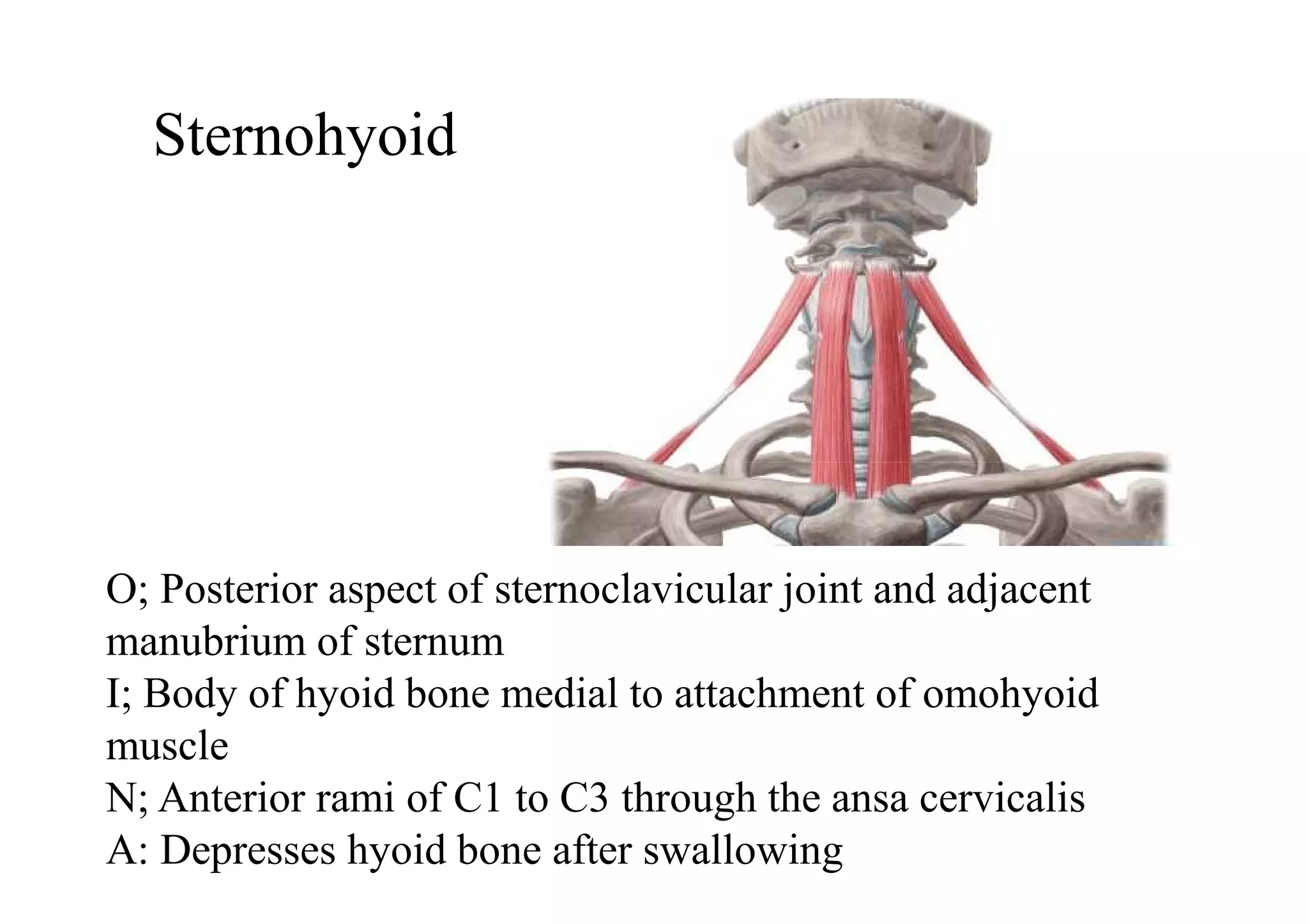
This document summarizes several muscles of the head and neck region. It describes the origin, insertion, nerve supply and action of the temporalis, masseter, lateral pterygoid, medial pterygoid, mylohyoid, geniohyoid, sternohyoid, omohyoid, thyrohyoid, sternothyroid, trapezius, and sternocleidomastoid muscles. It also provides information on torticollis, listing four types: rheumatic, reflex, congenital, and spasmodic.






![Trapezius
O ; Superior nuchal line; external occipital protuberance; ligamentum
nuchae; spinous processes of vertebrae CVII to TXII
I: Lateral one-third of clavicle; acromion; spine of scapula
N; Motor-accessory nerve [XI]; proprioception-C3 and C4
A: Assists in rotating the scapula during abduction of humerus above
horizontal; upper fibers-elevate, middle fibers-adduct, lower fibers-
depress scapula](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musclesofmasticationcompatibilitymode-200609102134/75/Muscles-of-mastication-13-2048.jpg)
![Sternocleidomastoid muscle
O; Upper part of anterior surface of manubrium of sternum
I; Lateral one-half of superior nuchal line
O; Superior surface of medial one-third of clavicle
I : Lateral surface of mastoid process
N : Accessory nerve [XI] and branches from anterior rami of C2 to C3 (C4)
A: Individually-will tilt head to-wards shoulder on same side rotating head to turn face
to opposite side; acting to-gether, draw head forwards](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musclesofmasticationcompatibilitymode-200609102134/75/Muscles-of-mastication-14-2048.jpg)


