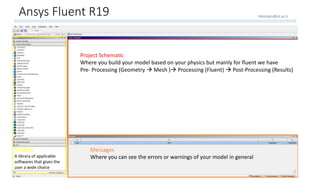
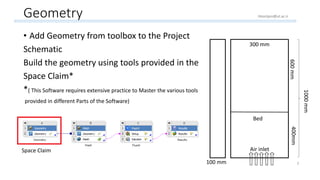
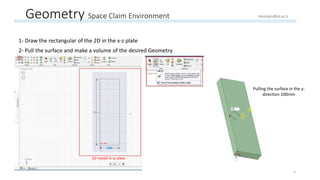
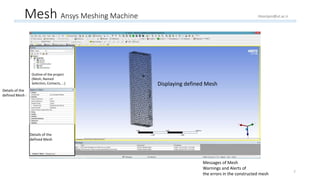
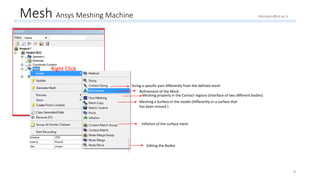
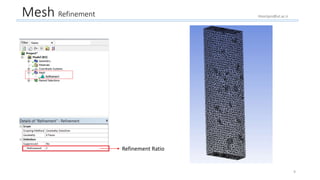
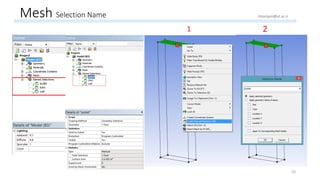
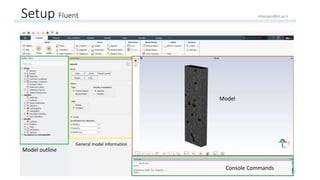
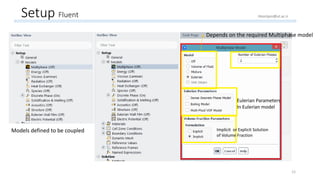
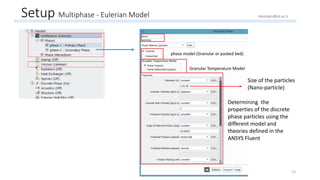
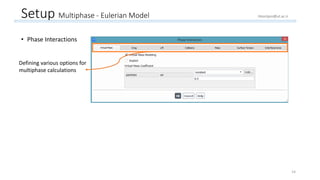
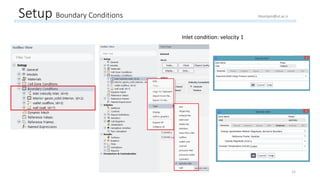
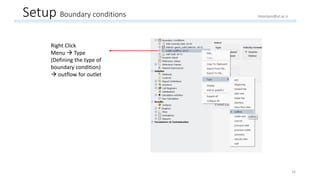
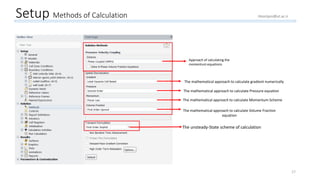
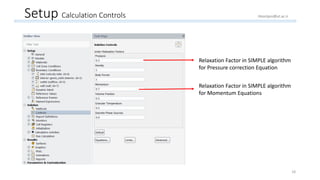
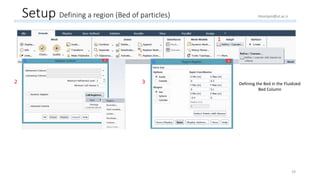
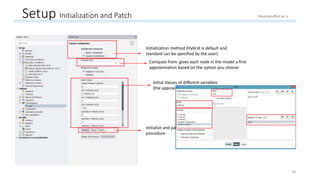
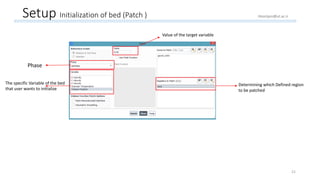
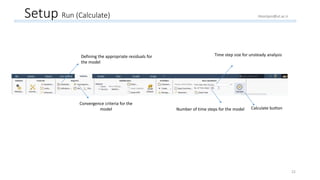
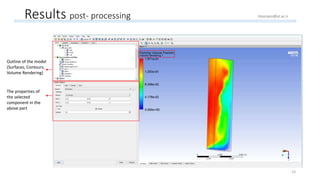
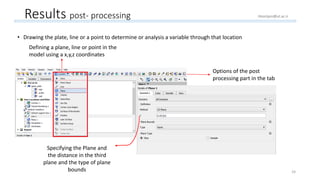
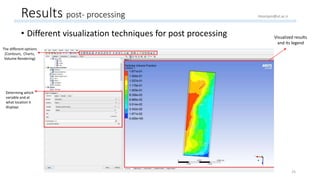
The document outlines a comprehensive guide to fluidized bed modeling using ANSYS Fluent R19, detailing the steps from geometry creation in SpaceClaim to mesh generation and setup of multiphase models. It includes instructions for defining boundary conditions, initialization, running simulations, and post-processing results. Key components such as model structure, mesh refinement, and calculation controls are also discussed to aid users in effectively conducting their simulations.