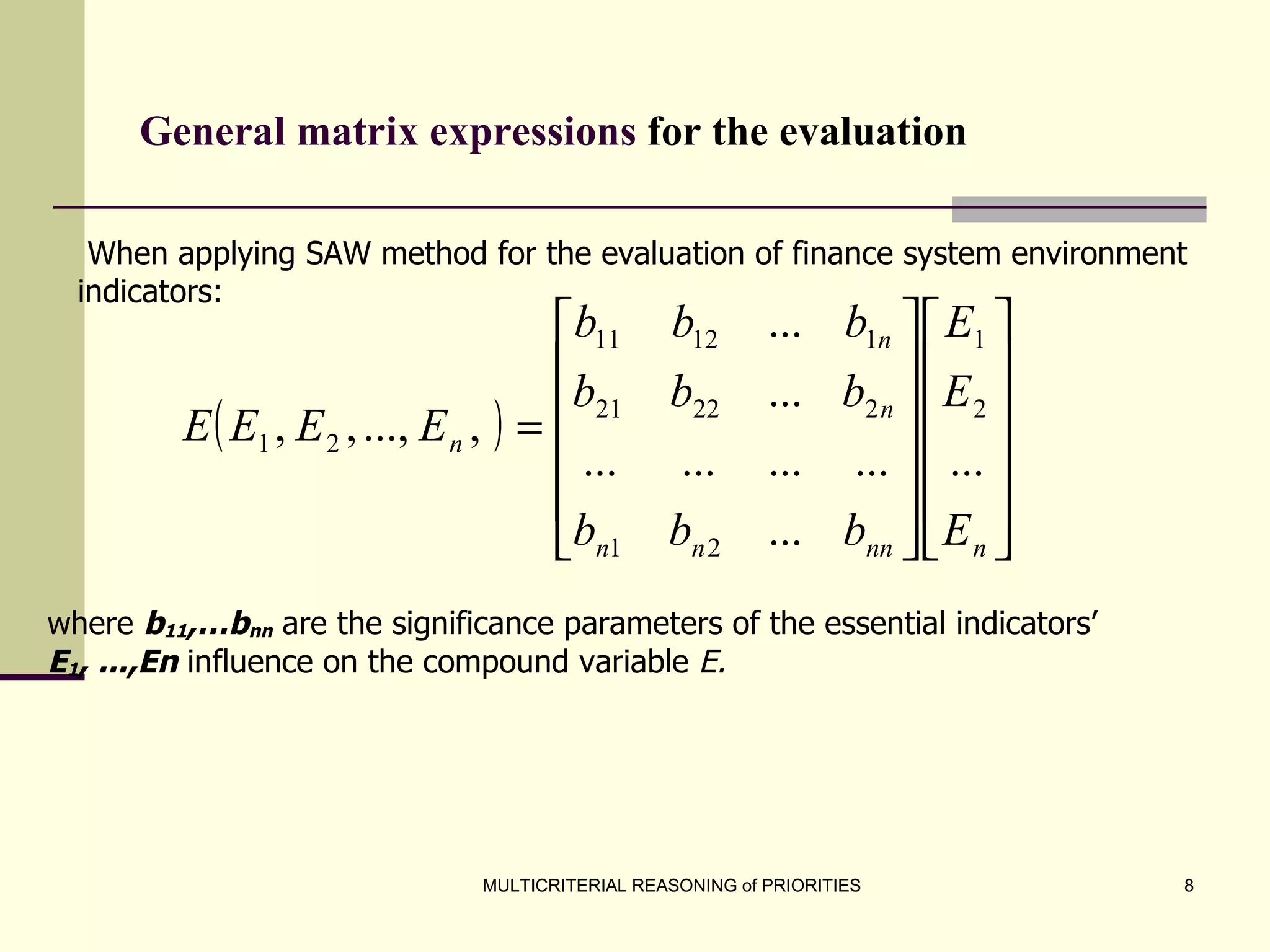
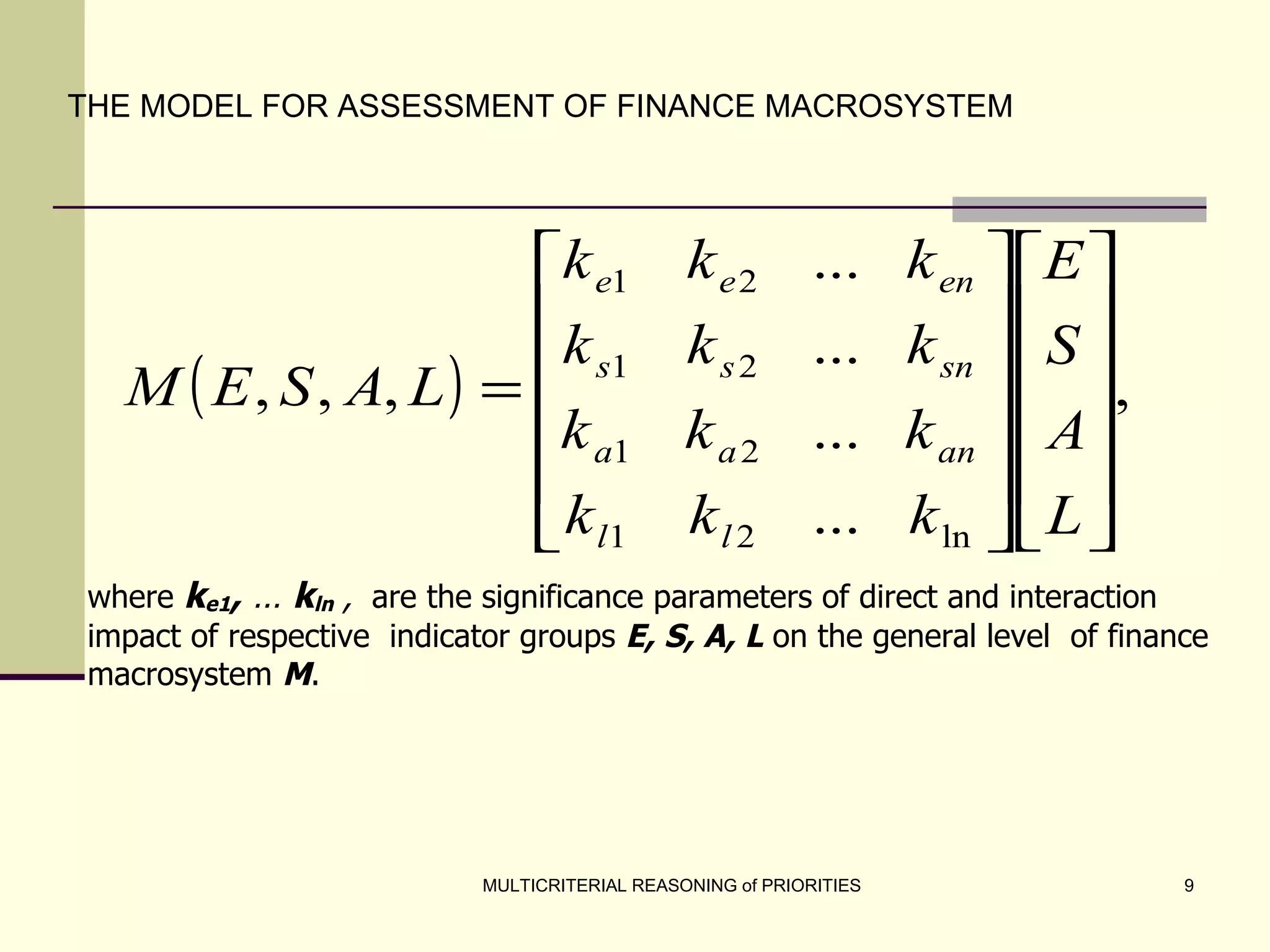
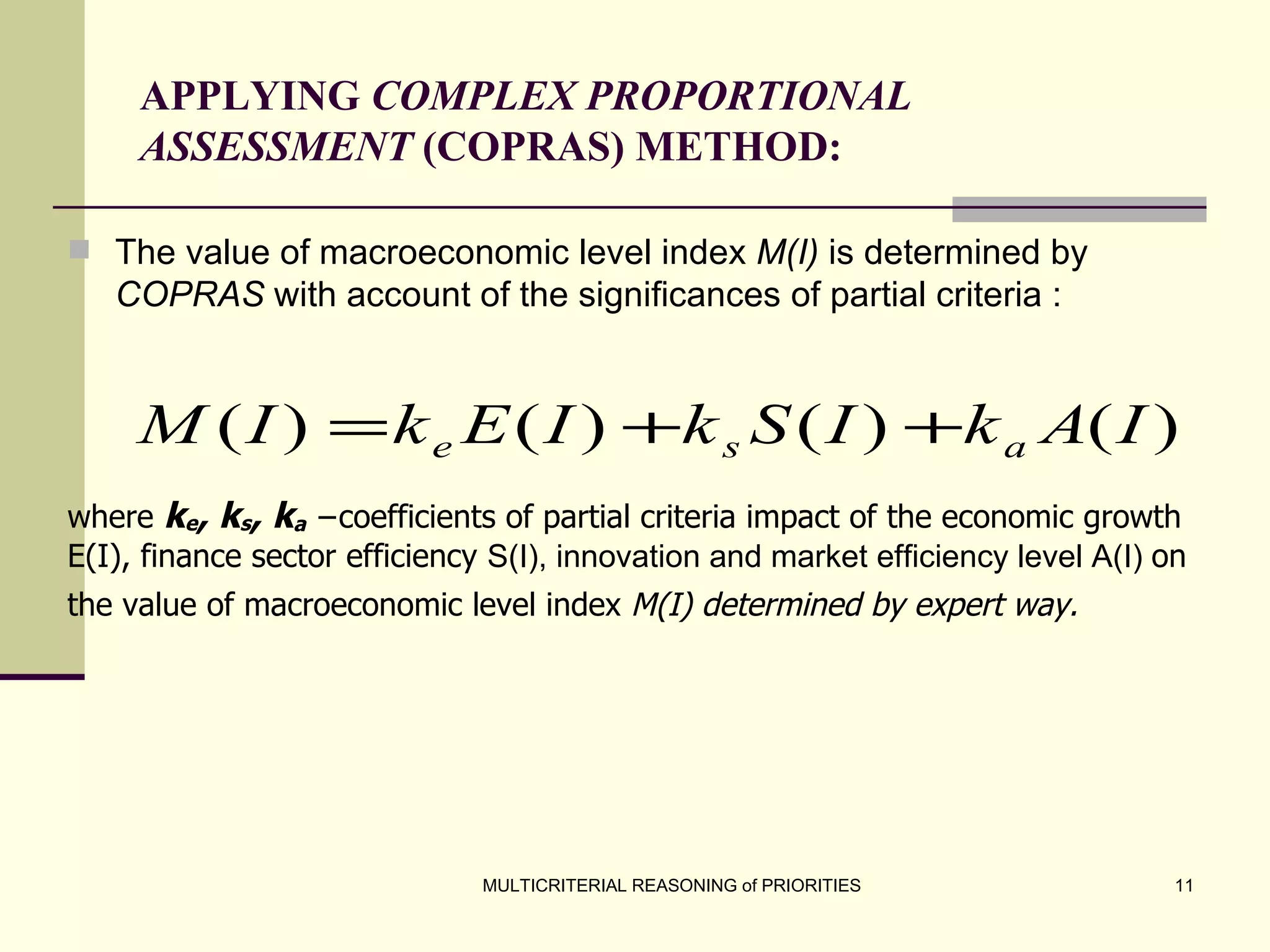
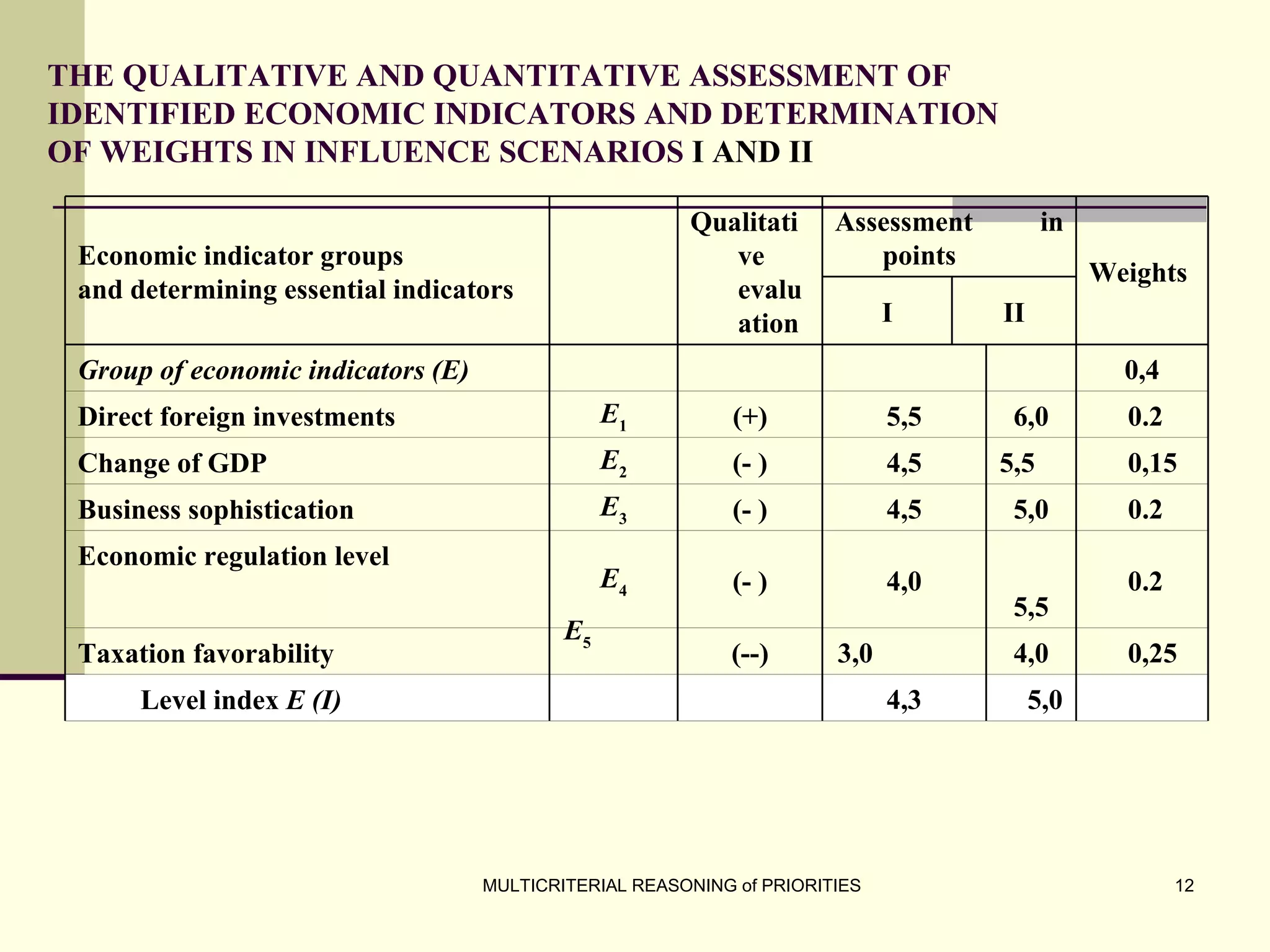
The document discusses the principles of multicriterial reasoning for developing national economic strategies, emphasizing the importance of systematic evaluation, ranking, and optimizing priorities. It outlines key stages in forming economic strategies, including SWOT analysis and the application of various evaluation methods such as AHP, SAW, and TOPSIS. Ultimately, it highlights the potential of multicriterial evaluation to enhance strategic development programs and supports the integration of these principles into management systems for more effective planning.
![THE PRINCIPLES OF MULTICRITERIAL REASONING OF THE DEVELOPMENT PRIORITIES Buracas & Zvirblis [email_address] PROF. HAB. DR. ALGIS ŽVIRBLIS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multicriterialpriorities-090919031925-phpapp01/75/Multicriterial-Priorities-1-2048.jpg)