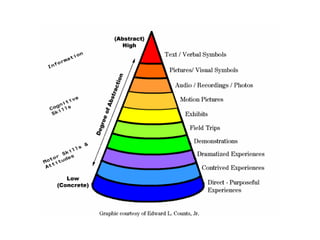
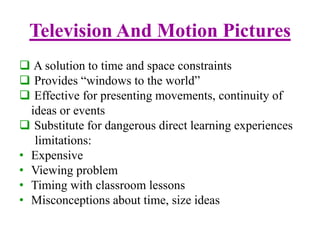
This document discusses multi-sensory approaches to teaching and learning. It defines multi-sensory as involving more than one sense and describes how Margaret Taylor Smith developed the Multi-Sensory Teaching Approach. It outlines the VAKT model involving visual, auditory, kinesthetic and tactile learning. It also discusses different types of learners - visual, auditory, tactile and kinesthetic - and how they learn best. Finally, it explains Dale's Cone of Experience which shows the relationship between different types of instructional resources and their effectiveness.