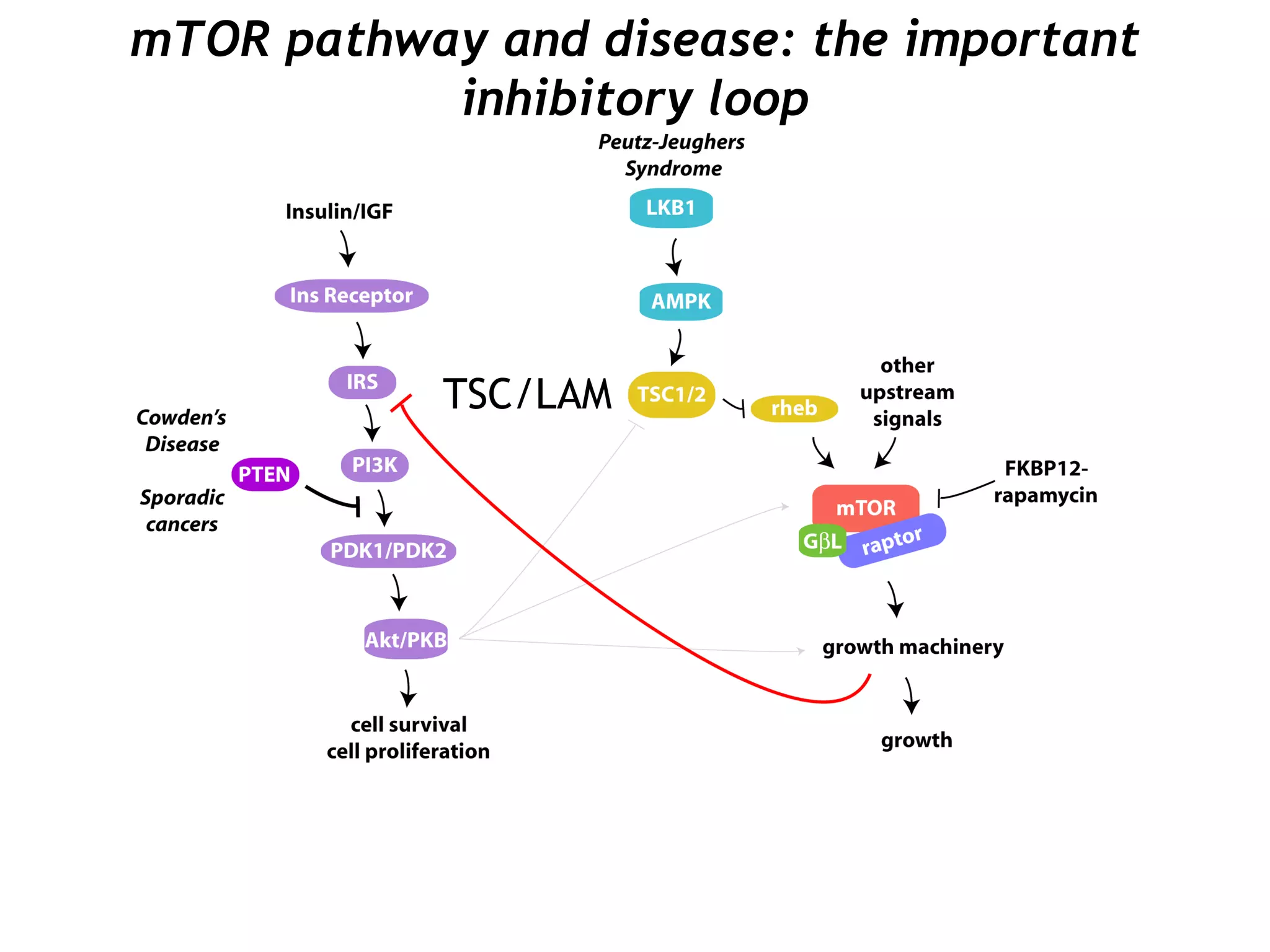
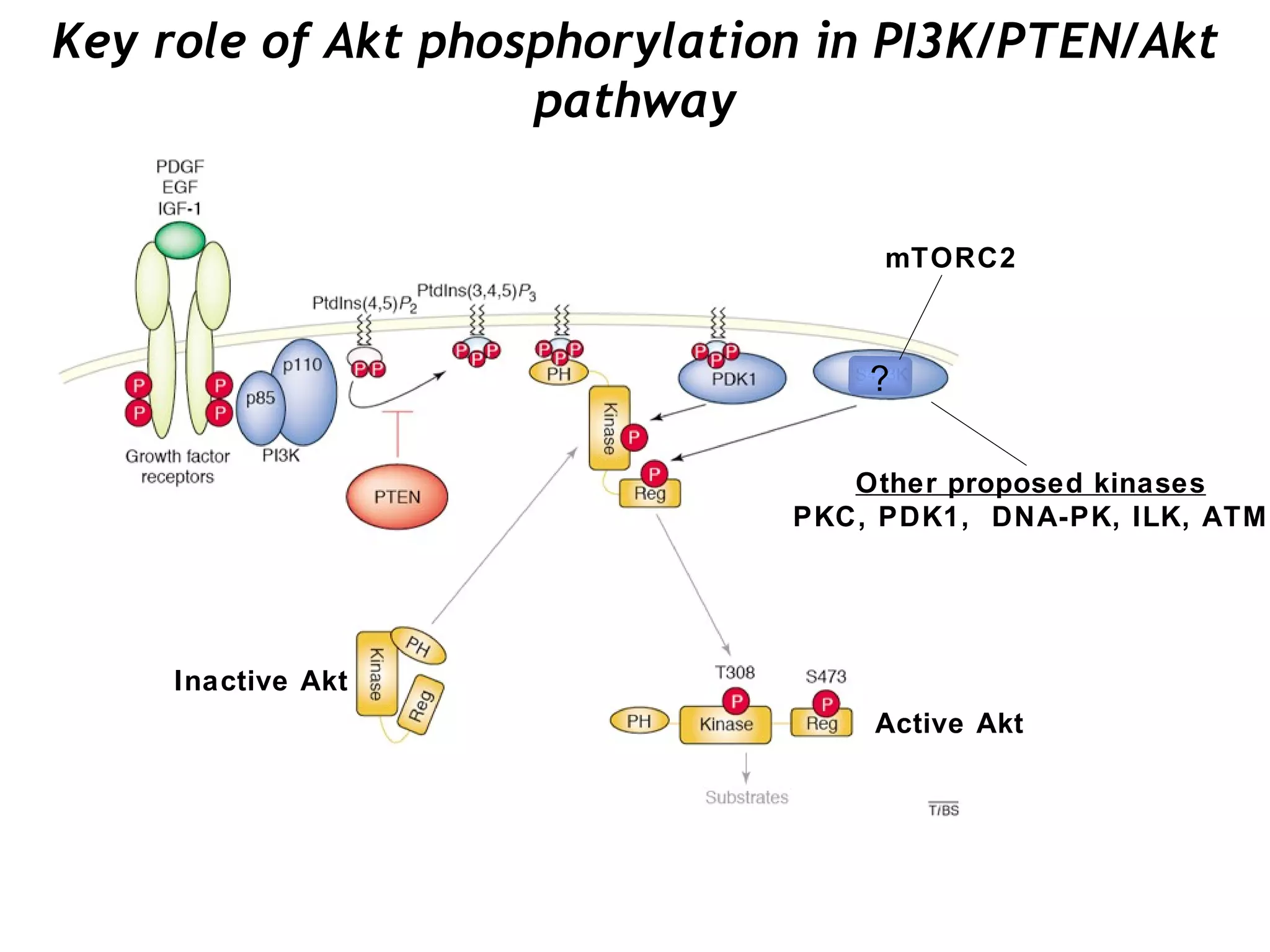
The document discusses the mTOR pathway and its role in diseases such as Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), highlighting contributions from various research labs. It explores the functions of distinct mTOR complexes (mTORC1 and mTORC2), their interactions, and possible therapeutic targets like rapamycin. Additionally, it presents open questions regarding the consequences of long-term mTOR inhibition and the relevance of downstream effectors in these diseases.