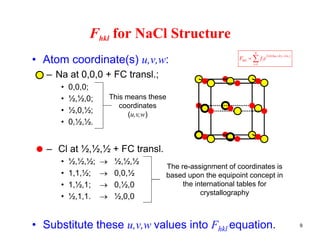
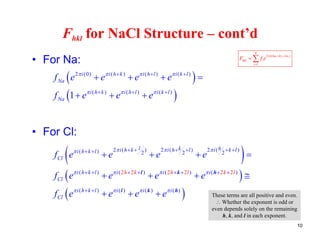
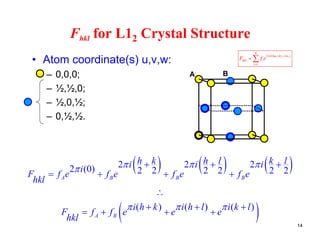
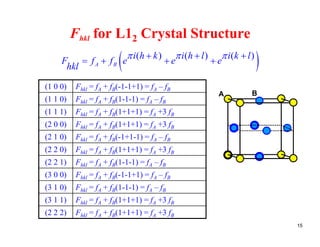
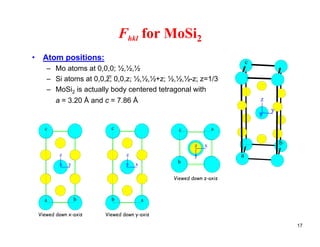
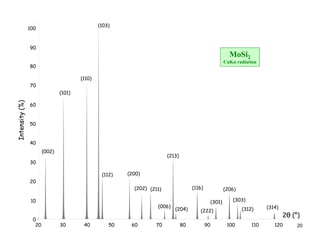
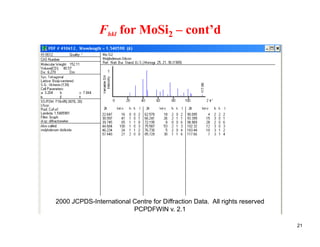
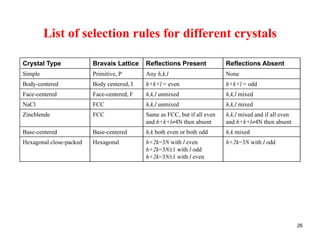
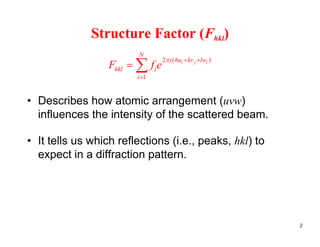
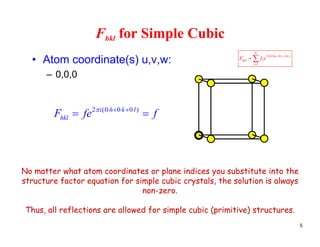
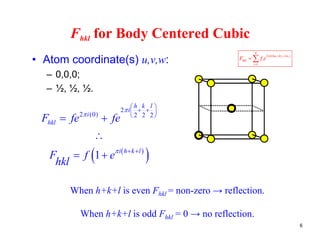
The structure factor (Fhkl) describes how the atomic arrangement influences the intensity of scattered x-rays in diffraction patterns. It is calculated as the sum of all atomic scattering factors multiplied by their positions. Fhkl tells us which diffraction peaks (hkl reflections) will be present. Different crystal structures have characteristic Fhkl equations and diffraction patterns depending on their atomic positions. Examples include simple cubic, body centered cubic, face centered cubic, NaCl, L12, and MoSi2 structures.



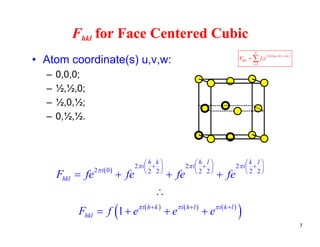
![Fhkl for Face Centered Cubic
1 i h k i h l i k l
hklF f e e e
• Substitute in a few values of hkl and you will find
the following:the following:
– When h,k,l are unmixed (i.e. all even or all odd), then
Fhkl = 4f. [NOTE: zero is considered even]
F 0 f i d i di (i bi ti f dd– Fhkl = 0 for mixed indices (i.e., a combination of odd
and even).
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mte583class18b-130630065556-phpapp01/85/Mte-583-class-18b-8-320.jpg)