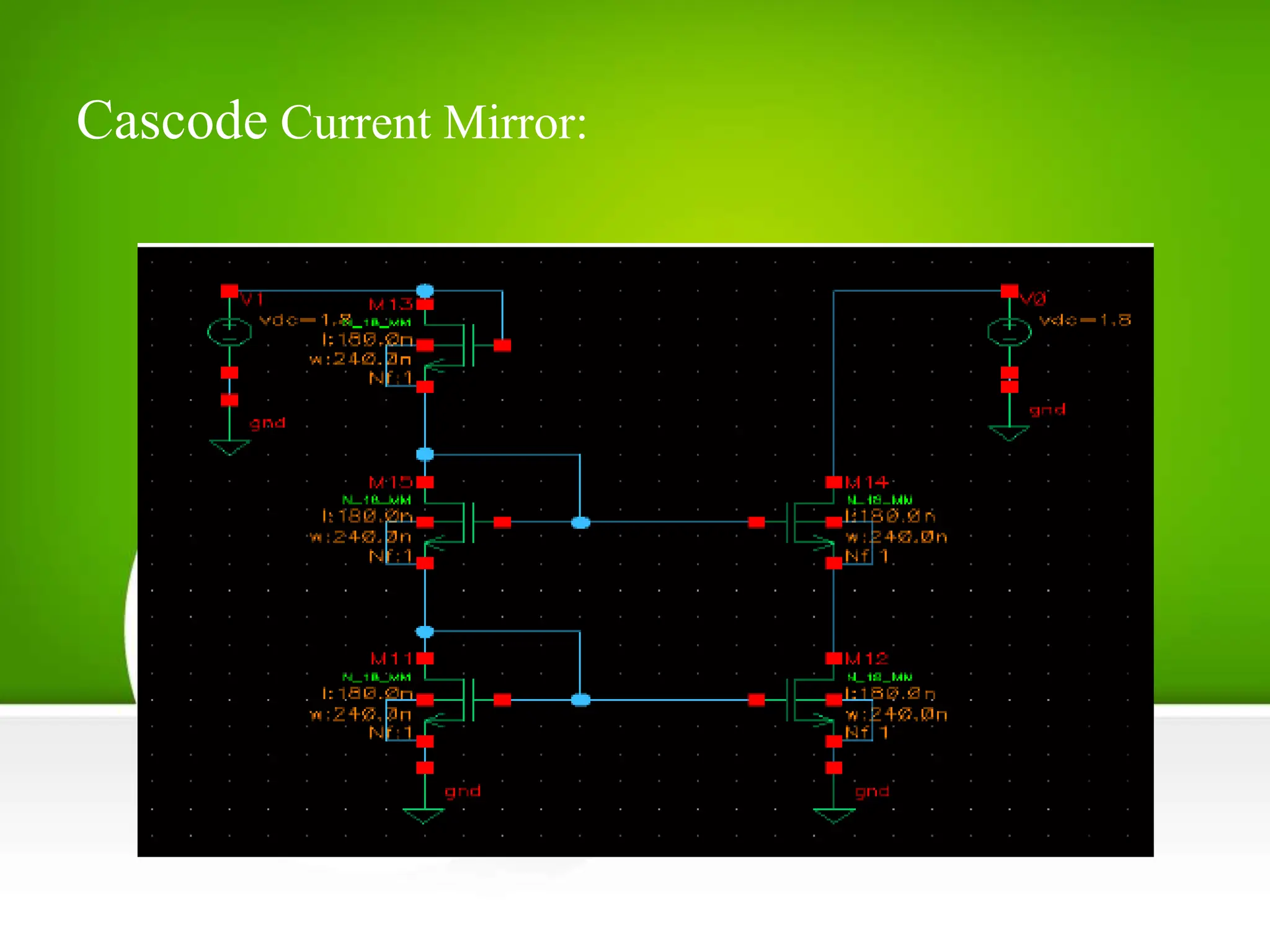
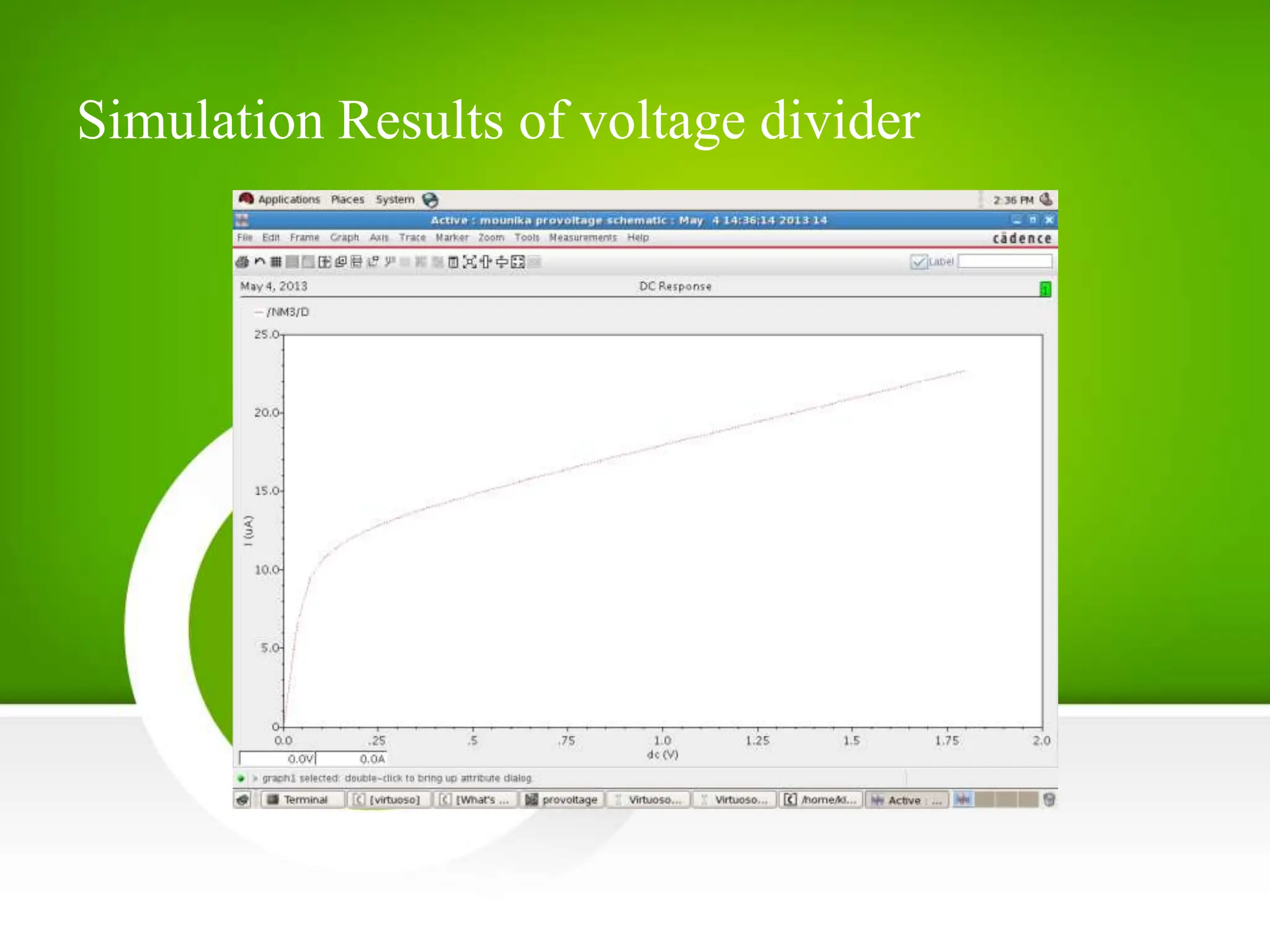
This document describes and compares three types of current mirrors: basic, cascode, and CMOS voltage divider. The basic current mirror uses two identical MOS transistors to mirror the input current but has a finite output resistance. The cascode current mirror increases output resistance but wastes voltage headroom. The CMOS voltage divider current mirror forms a voltage divider with NMOS and PMOS transistors to bias the output transistor, improving on the basic design by consuming less power. Simulation results show the power dissipation for each design. The document concludes the CMOS voltage divider current mirror is well-suited for low current biasing applications due to its low power consumption.