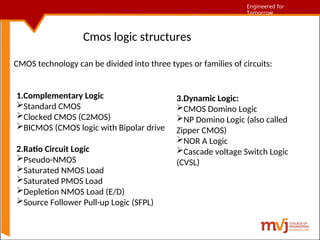
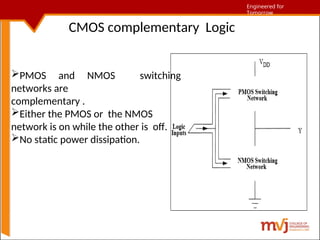
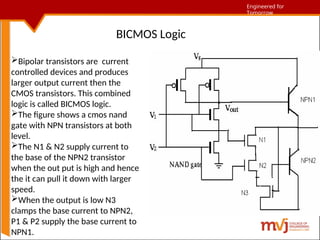
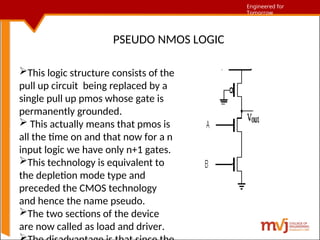
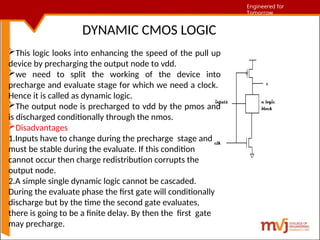
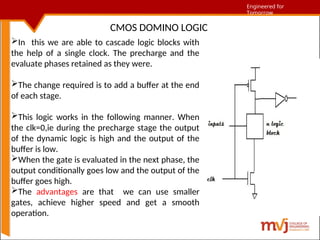
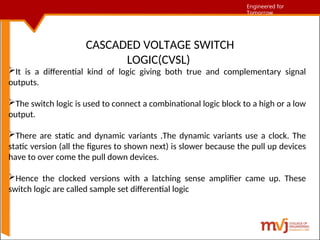
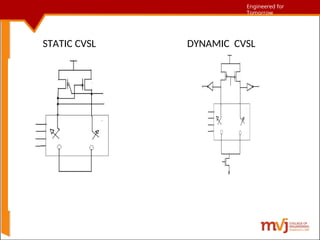
The document outlines fundamentals of CMOS VLSI, covering various CMOS logic structures such as complementary logic, BiCMOS logic, pseudo-NMOS logic, dynamic CMOS logic, and cascaded voltage switch logic. It details the advantages, disadvantages, and operational principles of each logic type, emphasizing dynamic and clocked variations for performance enhancement. The content is geared towards understanding the technical aspects and design considerations in CMOS technology.