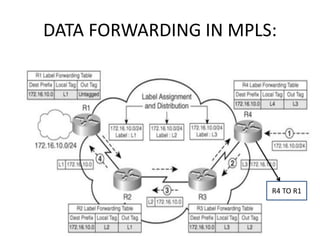
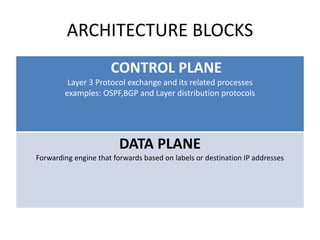
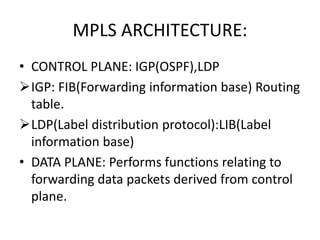
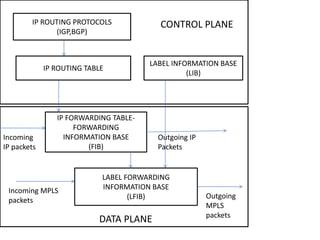
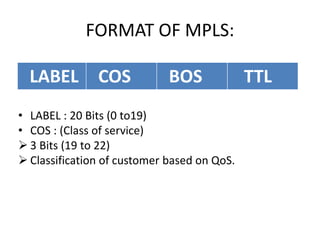
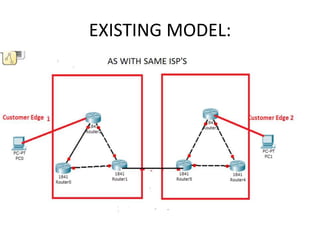
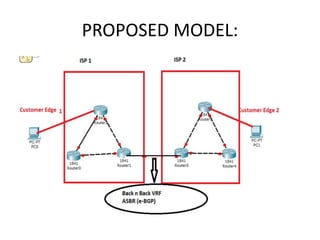
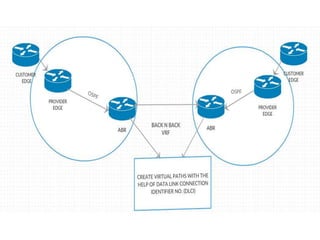
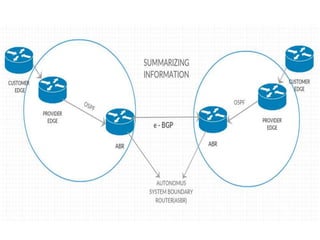
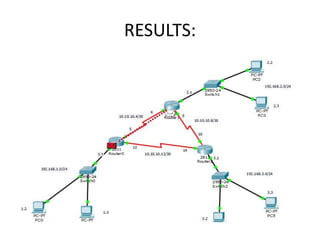
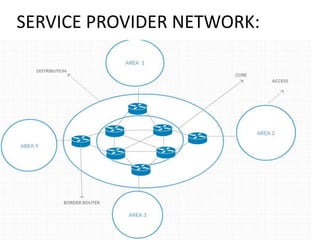
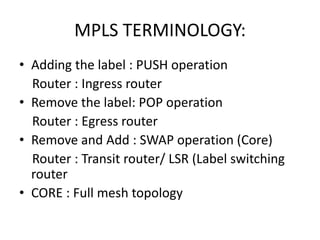
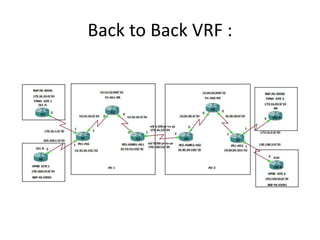
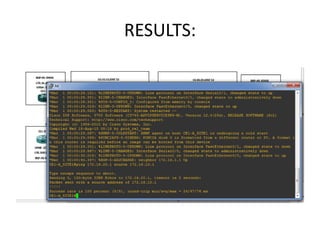
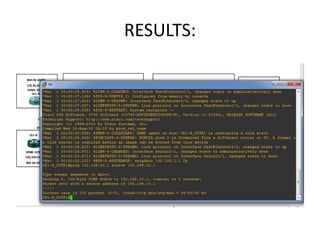
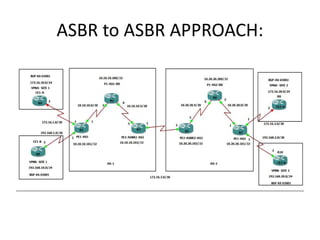
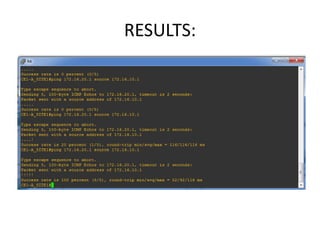
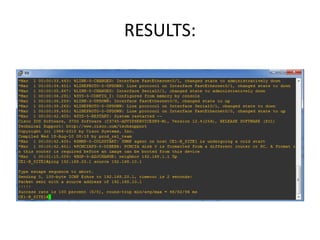
The document discusses MPLS-based VPN connectivity among inter-provider ISPs, focusing on how VPNs utilize shared infrastructures for secure remote access across geographically separated sites. It outlines the architecture and processes involved, including the use of MPLS for efficient data forwarding and the redistribution of VPN information between ISPs. Two methods for achieving cross-ISP VPN connectivity are proposed, namely back-to-back VRF and ASBR-to-ASBR approaches, highlighting their configurations and functionalities.