This document discusses moving beyond teaching excellence through dialogue and collaboration. It begins by noting that true creative dialogue is uncommon, as ideas tend to struggle for dominance rather than have open discussions. Presentations often argue a single position rather than opening up multiple interpretations through dialogue.
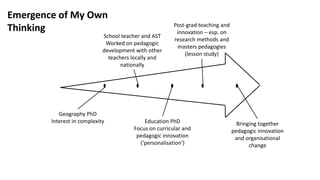
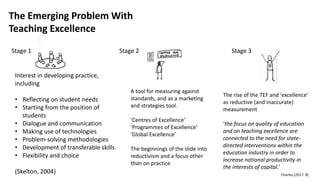
The document then outlines the author's background and interests in pedagogic innovation. It describes how the concept of "teaching excellence" has shifted from a focus on developing practice through dialogue to an overemphasis on measurement and marketing.
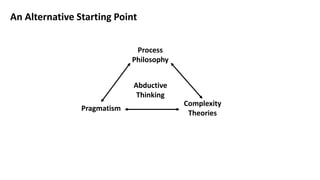
As an alternative, the author proposes a framework called "holiploigy" based on complex interactions between curriculum, teaching, learning and assessment. This emergent process fosters expertise through dialogue within philosophies,