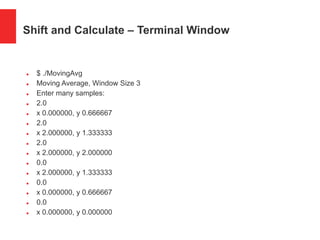
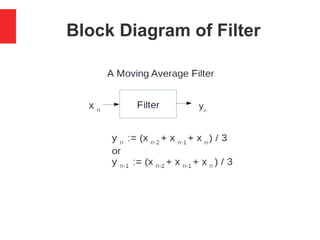
The document presents a simple C program demonstrating a moving average filter for time-series data aimed at aspiring C or C++ developers. It includes details on data types, control flow, and sample input/output for calculating averages from user input. Additionally, it discusses coding considerations, optimization techniques, and applications related to signal processing filters.


![Data Types
0,1 – Boolean constants (False,True)
int – Signed integer
unsigned int – Unsigned integer
double – Floating point (real) number
double x[t], y[t] – Arrays of data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/movingaveragefilterinc-170724014350/85/Moving-Average-Filter-in-C-4-320.jpg)


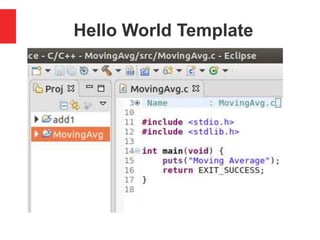
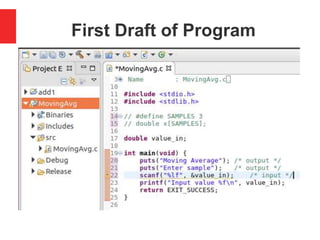

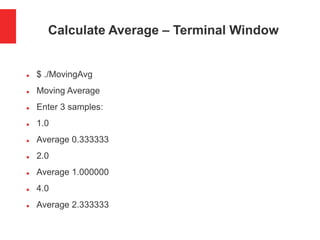
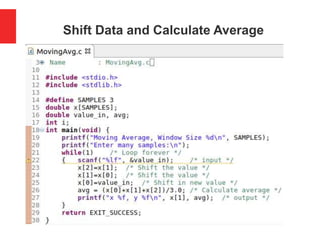
![Calculate Average of Three Numbers
#define SAMPLES 3
double x[SAMPLES];
double value_in, avg;
int i;
int main(void) {
puts("Moving Average"); /* output */
printf("Enter %d samples:n", SAMPLES); /* output */
for(i=0; i<SAMPLES; i++)
{ scanf("%lf", &value_in); /* input */
x[2]=x[1];
x[1]=x[0];
x[0]=value_in;
avg = (x[0]+x[1]+x[2])/3.0;
printf("Average %fn", avg);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/movingaveragefilterinc-170724014350/85/Moving-Average-Filter-in-C-10-320.jpg)