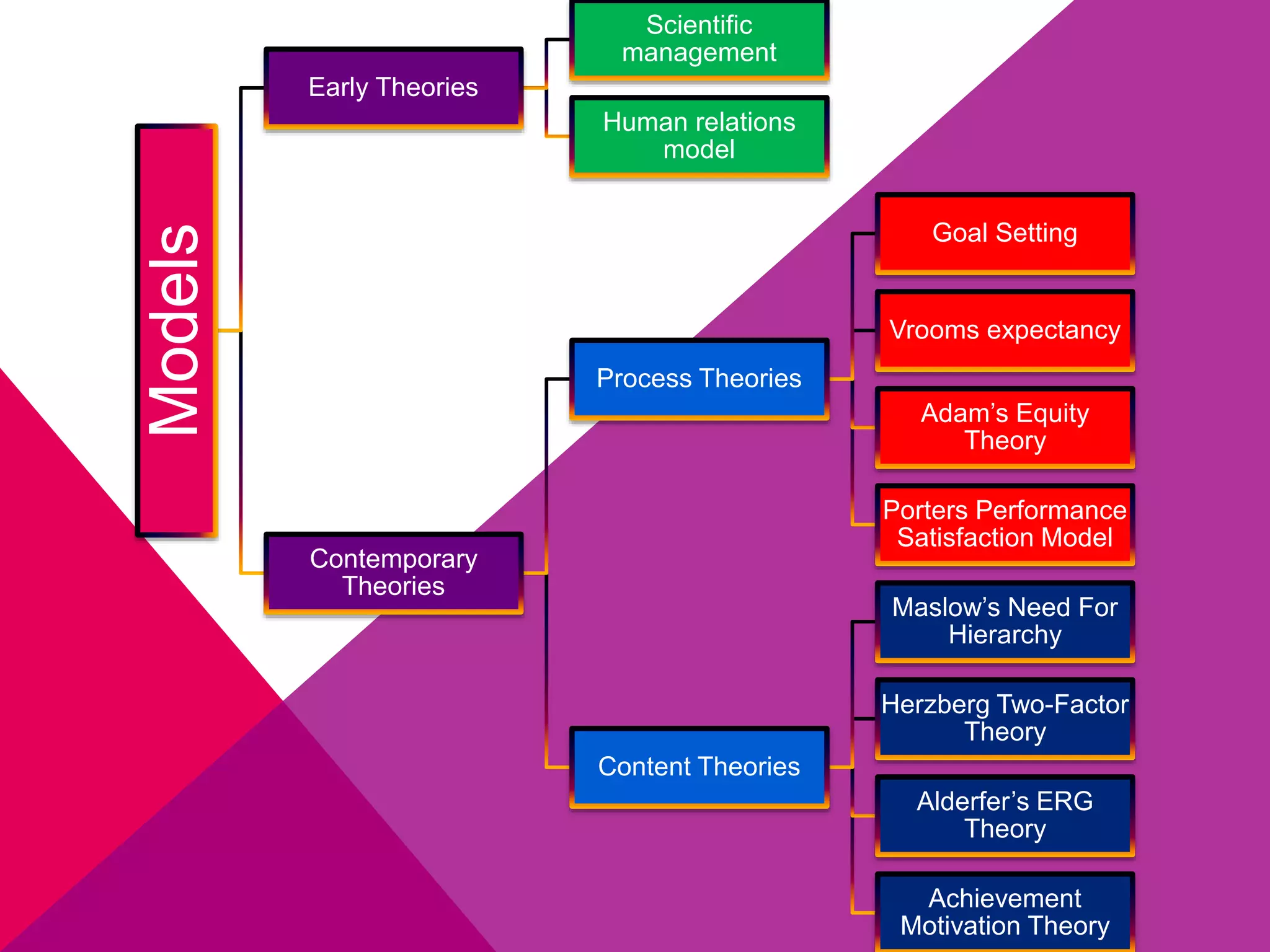
This document discusses various theories of motivation. It begins with definitions of motivation as internal or external forces that energize behavior. It then outlines several models of motivation including early scientific management and human relations models as well as contemporary process, goal-setting, expectancy, equity, and performance-satisfaction models. Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's two-factor theory are discussed as content theories, along with Alderfer's ERG theory and achievement motivation theory. The key differences between Maslow and Herzberg's theories are also summarized.