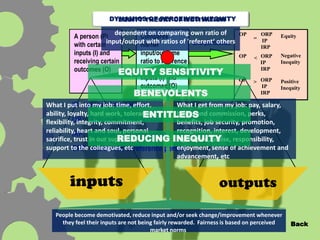
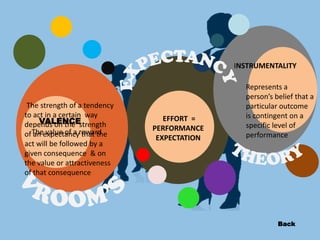
The document discusses equity theory and goal setting theory. Equity theory proposes that employees judge fairness based on comparing their own input-outcome ratio to a reference person. This can lead to inequity which demotivates employees. Goal setting theory suggests that specific, challenging goals improve performance when employees are committed to the goals. Managers can enhance goal commitment by breaking goals into steps, providing feedback, and allowing employee participation in goal setting.