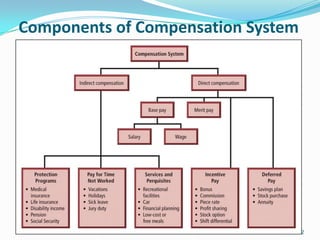
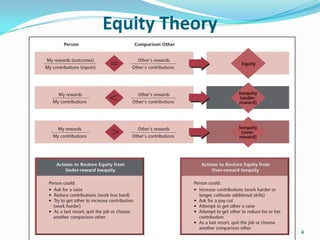
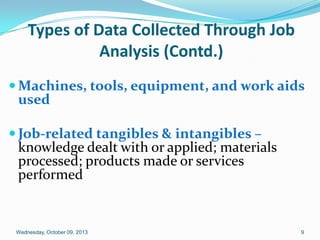
This document discusses building an internally consistent compensation system through job analysis and job evaluation. It explains that job analysis is the systematic study of job duties and responsibilities to obtain relevant information about job skills, factors, environment, and requirements. Through job analysis, various data is collected about work activities, demands, tools, knowledge, performance, context, and personal requirements. The results of job analysis are a job description defining responsibilities and requirements, and a job specification defining the knowledge, skills, and abilities required. Job evaluation then compares jobs to determine appropriate compensation levels.