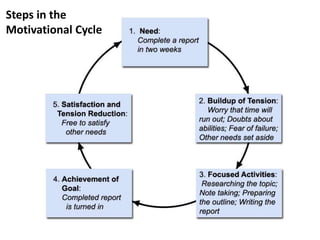
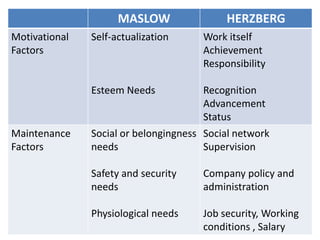
The document discusses different theories of motivation including:
- Internal motivation comes from task completion while external motivation involves anticipated rewards.
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs proposes physiological, safety, belongingness, esteem, and self-actualization needs.
- Herzberg's two-factor theory separates job satisfaction (motivational factors) from dissatisfaction (maintenance factors).
- McGregor's Theory X sees people as inherently lazy while Theory Y sees work as natural and people willing to accept responsibility.
The document also mentions self-fulfilling prophecies and strategies to empower employees through job rotation, enlargement, enrichment, training and removing authority barriers.