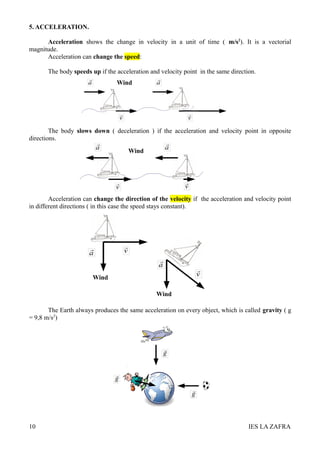
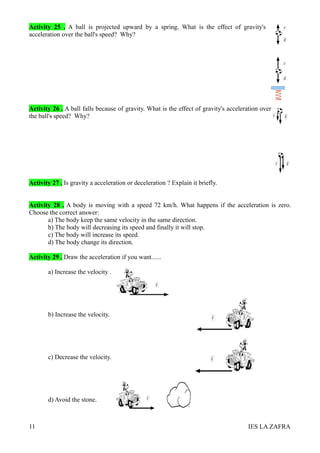
1. The document discusses scalar and vectorial magnitudes, and defines them as magnitudes that either have only a value (scalar) or have both a value and direction (vector). It provides examples of scalar magnitudes like length and temperature, and vector magnitudes like force and velocity.
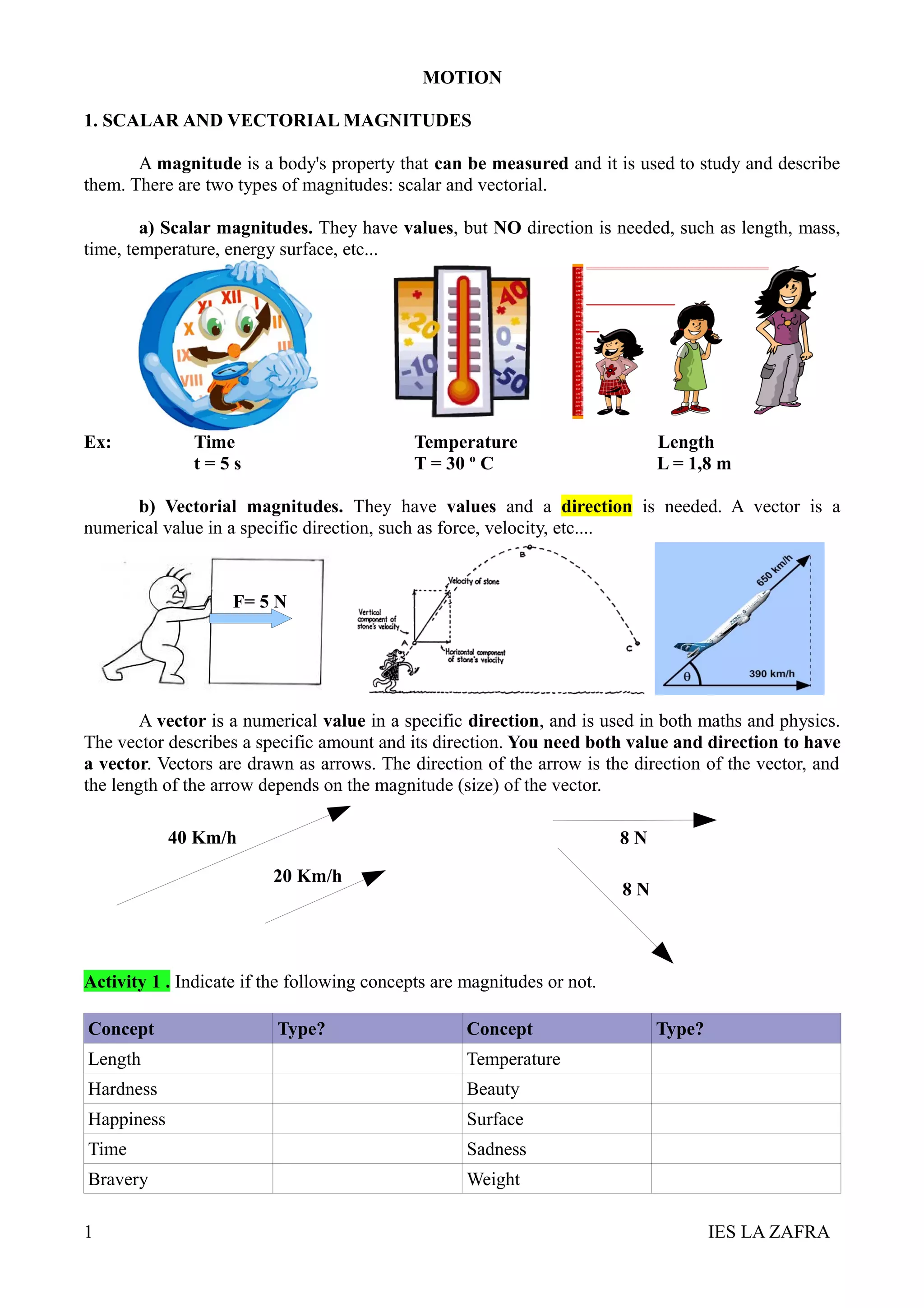
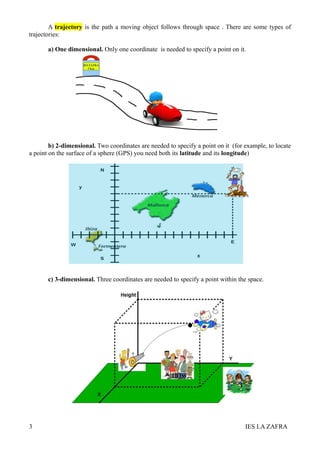
2. A frame of reference is used to describe motion and trajectories. Trajectories can be one-dimensional, two-dimensional, or three-dimensional depending on how many coordinates are needed to specify a point.
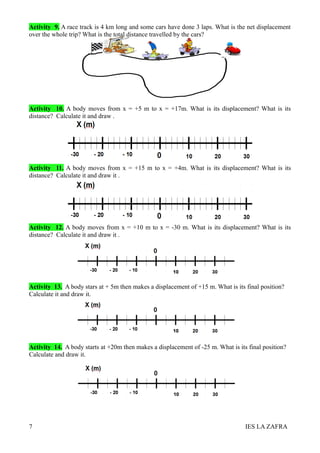
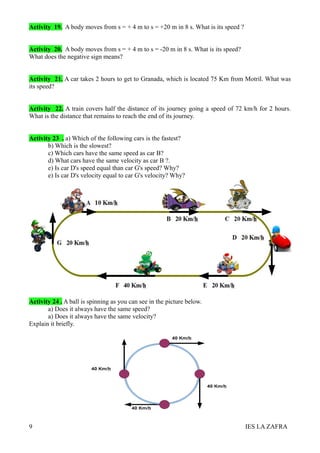
3. Position indicates where an object is located. Distance is the actual length an object travels, while displacement is the shortest distance between initial and final positions. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts.