53.33
During
60
62
65
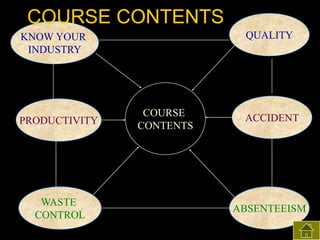
1) The document describes a study conducted to assess the impact of workers' education training provided by the Centre for Budget and Workers Education (CBWE) at Ambica Jute Mill in West Bengal.
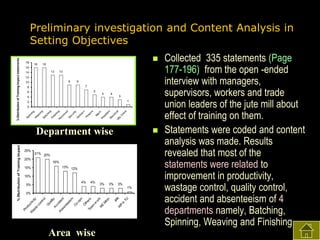
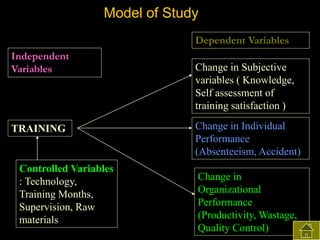
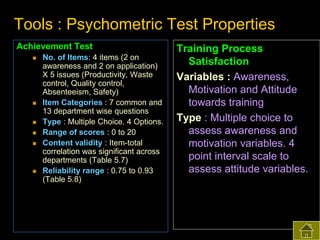
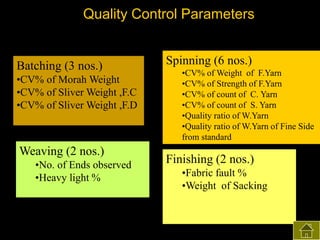
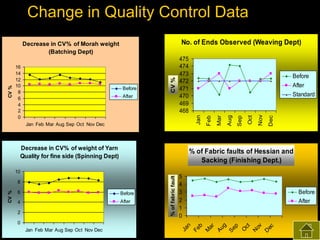
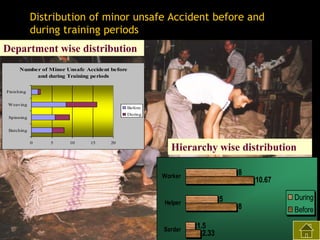
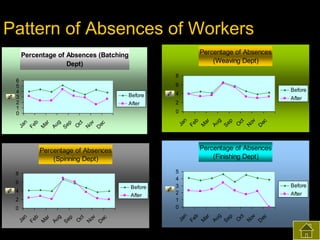
2) Both subjective and objective data were collected before and after training to analyze the impact on knowledge, satisfaction, productivity, waste control, quality control, accidents, and absenteeism.
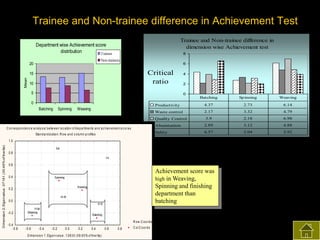
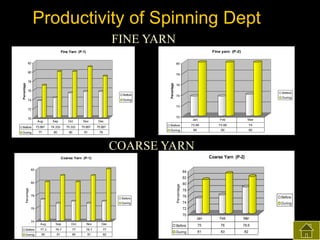
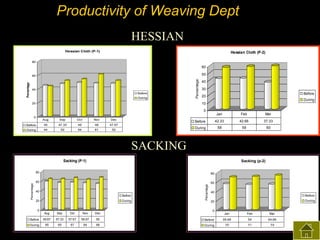
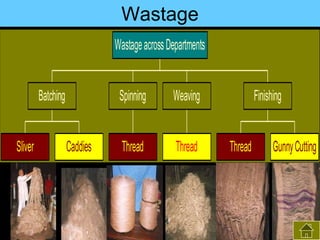
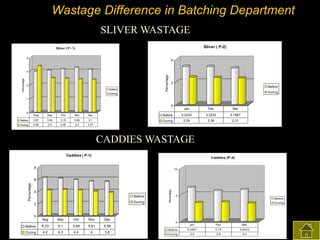
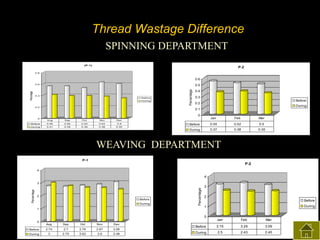
3) The results found significant improvements in trainees' achievement test scores compared to non-trainees. It also found increased productivity, reduced waste and improved quality control in the spinning, weaving and finishing departments after training.